Understanding the Repo Rate is crucial for banking exam aspirants preparing for IBPS, SBI, RBI, SEBI, NABARD, and other competitive exams. The repo rate and related monetary policy tools form an important part of the banking awareness section. This article covers the repo rate meaning, the formula, its link with the bank rate and reverse repo rate, current rates, and its significance for aspirants.
What is Repo Rate?
The Repo Rate (Repurchase Rate) is the rate at which the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) lends short-term funds to commercial banks against approved securities like government bonds. It is a key monetary policy instrument used to regulate liquidity in the banking system and control inflation. When inflation is high, RBI increases the repo rate to reduce money supply; when growth needs to be supported, RBI lowers it to encourage borrowing.
What is the Repo Rate Formula?
While there is no complex mathematical formula, the repo transaction can be understood with the formula below. This formula helps in calculating the effective annualized interest on repo transactions.
Repo Rate = (Repurchase Price – Original Price) / Original Price × (365 / Number of Days) × 100
What is Bank Rate?
The Bank Rate is the rate at which the RBI lends money to commercial banks without demanding collateral or repurchase agreements. It is generally used for long-term lending compared to the repo rate, which deals with short-term needs. The bank rate is usually higher than the Repo Rate and is also used for calculating penalties on defaults in maintaining statutory ratios like CRR and SLR.
Difference Between Bank Rate and Repo Rate
Both Bank Rate and Repo Rate are policy tools, but they differ in nature and usage:
| Feature | Bank Rate | Repo Rate |
| Collateral | No collateral required | Requires securities as collateral |
| Tenure | Long-term lending | Short-term lending (typically overnight) |
| Usage | Controls long-term liquidity | Controls short-term liquidity |
| Rate Level | Higher than Repo Rate | Lower than Bank Rate |
What is Reverse Repo Rate?
The Reverse Repo Rate is the rate at which RBI borrows money from commercial banks. It is always lower than the Repo Rate and is used to absorb excess liquidity from the banking system. By increasing the reverse repo rate, RBI encourages banks to park more funds with it, thereby reducing the money supply in the economy.
Repo Rate vs Reverse Repo Rate
The difference between Repo Rate and Reverse Repo Rate is explained below.
| Feature | Repo Rate | Reverse Repo Rate |
| Definition | Rate at which RBI lends to banks | Rate at which RBI borrows from banks |
| Collateral | Banks provide securities | RBI accepts funds |
| Purpose | Manage short-term liquidity, control inflation | Absorb excess liquidity |
| Current Status | Higher than Reverse Repo Rate | Lower than Repo Rate |
Current Repo Rate in India
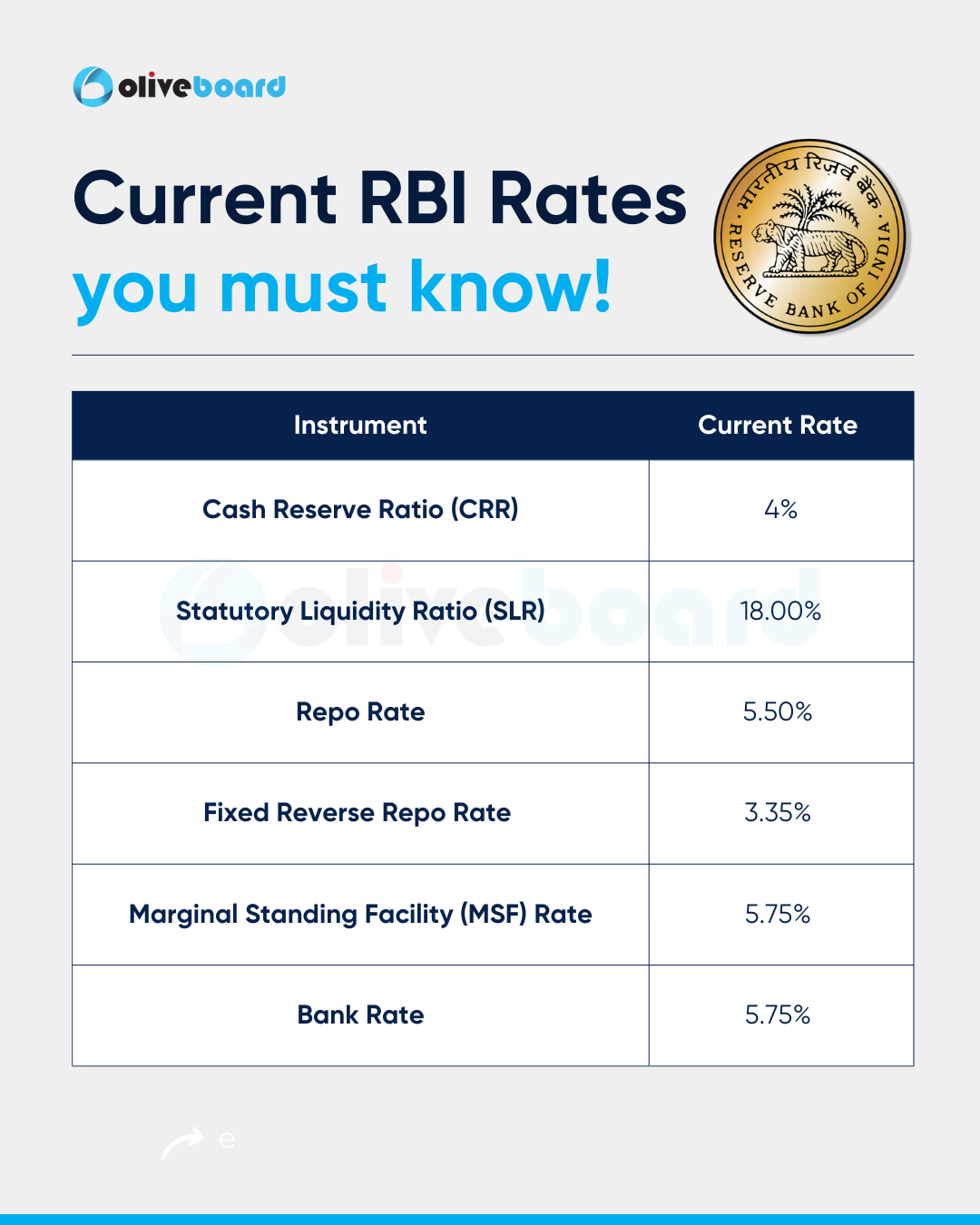
As of August 2025, the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) lowered the Repo Rate by 50 basis points, bringing it down to 5.50% from the previous rate of 6%, as decided in the Monetary Policy Committee (MPC) meeting. It is important to note that the Repo Rate keeps changing as per RBI policies.
How Does the Repo Rate Function?
Banks borrow funds from RBI at the repo rate by pledging government securities. They later repurchase these securities at a higher price, which includes interest. This mechanism directly impacts banks’ lending rates. A hike in the repo rate increases the cost of borrowing for banks, leading to higher loan EMIs for customers, while a cut reduces lending rates and boosts credit growth.
Repo Rate and Home Loans
Repo rate changes directly affect home loan interest rates. When RBI increases the repo rate, banks pass on the higher cost to customers, resulting in higher EMIs. Similarly, a cut in repo rate reduces loan interest rates, making borrowing cheaper for home buyers.
Why Is the Repo Rate Important for Banking Aspirants?
For banking exam aspirants, understanding the repo rate is vital because:
- It is one of the most frequently asked Terms in Banking Awareness.
- Questions can be both conceptual (definitions, differences) and current affairs-based (latest repo rate, RBI announcements).
- The repo rate affects inflation, liquidity, and loan interest rates. All are important from exam and real-life perspectives.
- Aspirants should also understand how the repo rate interacts with other tools like the bank rate, reverse repo rate, CRR, and SLR.
15 Repo Rate Questions for Bank Exam Aspirants
Here is a list of questions related to Repo Rate, bank exam aspirants can practice.
- What is the Repo Rate in banking terminology?
- Who decides the Repo Rate in India?
- What is the difference between Repo Rate and Reverse Repo Rate?
- Is the Repo Rate higher or lower than Bank Rate?
- How does an increase in Repo Rate affect inflation?
- What is the current Repo Rate in India (2024)?
- Which monetary policy committee reviews the Repo Rate?
- How does Repo Rate impact home loans?
- Why is Repo Rate considered a short-term borrowing tool?
- What is the collateral used in Repo Rate transactions?
- How does Repo Rate help RBI manage liquidity?
- Which section of the RBI Act mentions the Bank Rate?
- What is the difference between Overnight Rate and Bank Rate?
- How often does RBI revise the Repo Rate?
- Why should banking aspirants track Repo Rate announcements?
FAQs on Repo Rate
The current Repo Rate is 5.50%, after RBI reduced it by 50 basis points from 6% during the MPC meeting on August 6, 2025.
Raising the Repo Rate makes borrowing costlier, reducing money supply and spending, which helps control inflation.
Repo Rate is the rate at which RBI lends to banks, while Reverse Repo Rate is the rate at which RBI borrows from banks. Repo Rate is always higher than Reverse Repo Rate.
A hike in Repo Rate increases banks’ lending rates, resulting in higher EMIs for borrowers, while a cut decreases EMIs.
Because questions about current rates, MPC decisions, and their impact on the economy frequently appear in Banking Awareness sections of exams like IBPS, SBI, RBI, and NABARD.
- SBI Clerk Mains Answer Key 2026 Response Sheet Date
- Bihar State Cooperative Bank Clerk Final Result 2025 Out
- SBI Clerk Document Verification, List of Documents Required
- SBI Clerk LPT 2025-26, Check Types of Questions Asked
- RBI Office Attendant Exam Analysis 2026, 28th Feb & 1st March 2026
- Nainital Bank SO Final Result 2026 Out for 74 Posts, Download Link
Hi, I’m Tripti, a senior content writer at Oliveboard, where I manage blog content along with community engagement across platforms like Telegram and WhatsApp. With 3+ years of experience in content and SEO optimization related to banking exams, I have led content for popular exams like SSC, banking, railway, and state exams.
