Millions of people, particularly from rural and marginalized communities, had little or no access to the formal banking system before 2014. They relied on informal moneylenders, often at exploitative interest rates, and had no structured way to save, insure, or borrow. Recognizing this gap, the Government of India launched the Pradhan Mantri Jan Dhan Yojana (PMJDY), which has since evolved into the world’s largest financial inclusion initiative. It has not only opened the doors of banks to the underprivileged but also promoted social security, digital payments, and direct benefit transfers at an unprecedented scale.
What is Pradhan Mantri Jan Dhan Yojana (PMJDY)?
The Pradhan Mantri Jan Dhan Yojana is a National Mission for Financial Inclusion that aims to make banking facilities universally accessible to every household in the country. Unlike conventional schemes that cater mainly to the middle class, PMJDY focuses on the poorest sections by offering them basic savings accounts with no minimum balance requirement. Alongside, it provides insurance, pension, and credit facilities at minimal or no cost. This initiative is designed to bring people from the margins of the economy into the mainstream, making them active participants in India’s growth story.
When and why was Pradhan Mantri Jan Dhan Yojana (PMJDY) launched?
The scheme was officially launched on 28 August 2014 by the Government of India, under the slogan “Mera Khata, Bhagya Vidhata” (My Account, Fortune Maker). Its timing was critical: despite rapid economic progress, a significant share of India’s population remained excluded from basic financial services. The scheme aimed to tackle this challenge by ensuring at least one bank account per household, facilitating direct transfer of subsidies, encouraging savings, and reducing dependence on informal credit. The launch itself was historic, with over 77,000 special bank camps held across the country and more than 1.8 crore accounts opened on a single day.
Features of the Pradhan Mantri Jan Dhan Yojana
PMJDY has several unique provisions that differentiate it from traditional banking products. These features ensure inclusivity, accessibility, and long-term security for account holders.
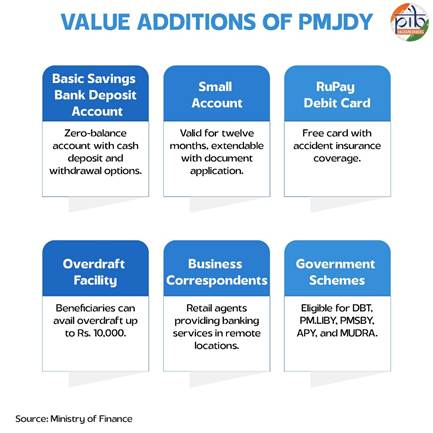
- Zero Balance Savings Account – Households can open an account without maintaining a minimum balance, making it truly universal.
- RuPay Debit Card – Each account holder receives a free debit card, allowing easy access to ATMs and digital payments.
- Insurance Coverage – Accident insurance of ₹2 lakh for RuPay cardholders.
- Life Insurance Cover – One-time life cover of ₹30,000 for eligible beneficiaries (for accounts opened before 26 January 2015).
- Overdraft Facility – Credit support of up to ₹10,000 is available after six months of satisfactory account activity, prioritizing women account holders.
- Direct Benefit Transfer (DBT) – Ensures subsidy and welfare transfers reach beneficiaries directly, reducing leakages.
- Mobile and Digital Banking – Encourages cashless transactions, increasing financial literacy and digital adoption.
- Bank Mitras – Business correspondents act as the last-mile link, offering banking services in remote villages where physical branches are limited.
Objectives of the Pradhan Mantri Jan Dhan Yojana
The scheme was designed with a holistic vision of financial empowerment. Its objectives go beyond just opening bank accounts:
- Universal Banking Access: To ensure that every household has a formal relationship with a bank.
- Promote Savings: To encourage people from low-income groups to develop the habit of saving.
- Affordable Credit: To make small loans and overdrafts accessible at fair terms.
- Insurance and Pension Coverage: To provide social security to vulnerable households.
- Efficient Welfare Distribution: To deliver government subsidies and benefits directly, minimizing corruption and delays.
- Financial Literacy: To educate people about banking, insurance, and digital transactions, thereby empowering them economically.
Significance of the Pradhan Mantri Jan Dhan Yojana
The PMJDY is not just a banking initiative; it is a socio-economic reform tool. By connecting millions to the formal financial system, it has:
- Strengthened the culture of savings among low-income households.
- Reduced the dependence on moneylenders charging high interest rates.
- Empowered women by providing them direct access to financial services.
- Enabled social security and pension coverage for marginalized groups.
- Enhanced transparency in government transfers, reducing corruption.
- Supported the rise of digital transactions, especially through the JAM Trinity (Jan Dhan, Aadhaar, Mobile).
Impact and Achievements of PMJDY So Far
The scale and success of PMJDY have made it a global benchmark for financial inclusion.
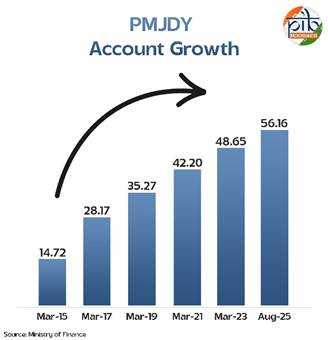
- Accounts Opened: Over 53 crore accounts have been opened since 2014.
- Women’s Participation: Nearly 56% of accounts belong to women, boosting financial independence.
- Rural Penetration: Around 67% of accounts are in rural or semi-urban areas.
- Deposits Mobilized: Total deposits in PMJDY accounts have crossed ₹2 lakh crore, showcasing a shift towards formal savings.
- Direct Benefit Transfers: Over ₹38.5 lakh crore has been disbursed through Jan Dhan accounts as part of the JAM framework.
- Improved Banking Infrastructure: Banks have expanded branches, ATMs, and digital banking facilities to meet growing demand.
- International Recognition: According to the World Bank, India’s bank account ownership rose from 53% in 2014 to 78% in 2021, largely due to PMJDY.
Challenges with the PMJDY
Despite its achievements, PMJDY faces persistent challenges:
- Dormant Accounts: A sizable portion of accounts remain inactive, limiting true financial inclusion.
- Multiple Accounts: Duplication leads to misuse of benefits and data distortions.
- Financial Illiteracy: Many beneficiaries are unaware of overdraft, insurance, and pension facilities.
- Infrastructure Gaps: Lack of ATMs and weak internet connectivity in remote areas reduce accessibility.
- Exclusion of Marginalized Populations: Some tribal and remote groups remain outside the scheme’s reach.
- Gender Norms: Social restrictions in certain regions prevent women from independently using their accounts.
Key Pointers for Bank Exam Aspirants
For competitive exams like IBPS, RBI, NABARD, SEBI, and LIC AAO, candidates should focus on the following aspects of PMJDY:
- Launch Year & Objective → 2014; aimed at “banking the unbanked, securing the unsecured, funding the unfunded, and serving the underserved.”
- Achievements & Records → Over 56 crore accounts opened, Guinness World Record for most accounts in a week (18 million+).
- Gender & Rural Focus → 56% accounts belong to women; 67% of accounts are in rural/semi-urban areas.
- Financial Products & Benefits → Zero-balance BSBD accounts, RuPay debit cards with ₹2 lakh accident insurance, overdraft up to ₹10,000, small accounts (Chhota Khata), micro-insurance & pension.
- Government Scheme Linkages → Eligibility for DBT, PMJJBY, PMSBY, APY, and MUDRA loans.
- Economic Impact → Boost to digital transactions, ₹2.67 lakh crore deposits (2025), foundation for DBT in 327+ government schemes.
- Recent Developments → 2025 outreach campaign with 99,000+ enrolment camps, nearly 6.6 lakh new accounts opened in July 2025 alone.
Practice Questions on Pradhan Mantri Jan Dhan Yojana (PMJDY)
- In which year was PMJDY launched?
- What is the official slogan of PMJDY?
- Under which ministry does the scheme operate?
- What is the overdraft facility available under PMJDY?
- How much accident insurance cover is provided under the scheme?
- What is the life insurance cover under PMJDY and who is eligible?
- What is the full form of PMJDY?
- How many Jan Dhan accounts have been opened till 2023?
- What percentage of account holders are women?
- What percentage of accounts are in rural/semi-urban areas?
- What are the three pillars of JAM Trinity?
- Which state has opened the highest number of Jan Dhan accounts?
- What is the total value of deposits in Jan Dhan accounts as of 2023?
- Who are Bank Mitras and what is their role?
- Why is PMJDY considered significant for financial inclusion in India?
FAQs
PMJDY is a financial inclusion scheme launched in 2014 to provide bank accounts, credit, insurance, and pension access to the unbanked population.
As of August 2025, over 56.16 crore Jan Dhan accounts have been opened with deposits of more than ₹2.67 lakh crore.
PMJDY provides zero-balance savings accounts, RuPay debit cards with accident insurance of ₹2 lakhs, overdraft up to ₹10,000, and access to pension and insurance schemes.
For banking exams, aspirants must remember PMJDY’s launch year (2014), objectives, Guinness World Record achievement, account statistics, deposit growth, and linkages with DBT and other schemes.
Around 56% of PMJDY accounts belong to women, making it a key driver of gender equality in financial access and social security coverage.
- RRB NTPC Train Clerk Job Profile and Salary, Check Details

- SBI Clerk Mains Answer Key 2026 Response Sheet Date

- SEBI and Its Functions, Short Notes for JAIIB 2026

- SEBI IT Officer Syllabus 2026, Exam Pattern, Download PDF

- SEBI Law Officer Recruitment 2026, Download Notification PDF

- SEBI IT Officer Recruitment 2026 Notification, Download PDF

Hi, I’m Tripti, a senior content writer at Oliveboard, where I manage blog content along with community engagement across platforms like Telegram and WhatsApp. With 3+ years of experience in content and SEO optimization related to banking exams, I have led content for popular exams like SSC, banking, railway, and state exams.
