In SSC CGL Tier 2 SSC JSO (Junior Statistical Officer Paper II), questions on Random Variables and Probability Distributions are very important. These concepts help in modelling uncertainty, understanding data patterns, and predicting outcomes.This blog covers random variables, types of distributions, and joint distributions with easy examples and formulas.
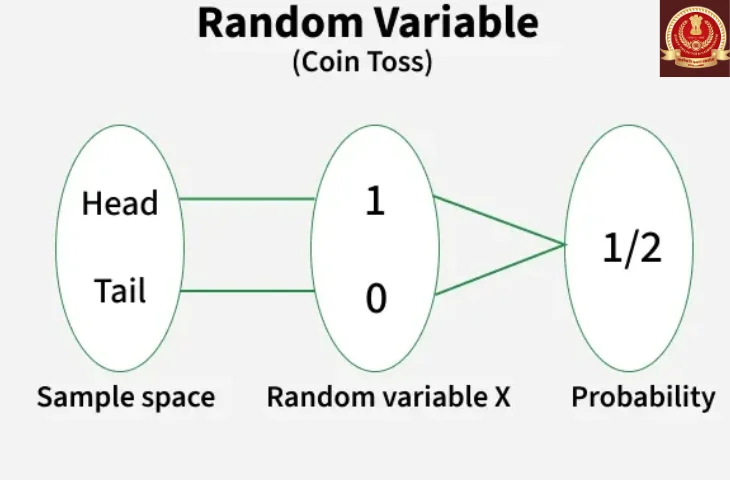
1. Random Variable (RV)
Definition
A random variable is a numerical outcome of a random experiment.
- Types of Random Variables:
- Discrete Random Variable – takes countable values (e.g., number of heads in 3 coin tosses).
- Continuous Random Variable – takes uncountable values in an interval (e.g., height, weight).
Example:
- Toss a die → X = number on top face → Discrete
- Time to complete a task → Y = time in minutes → Continuous
Also check out Most Repeated Quantitative Aptitude Questions for SSC CGL Tier 2
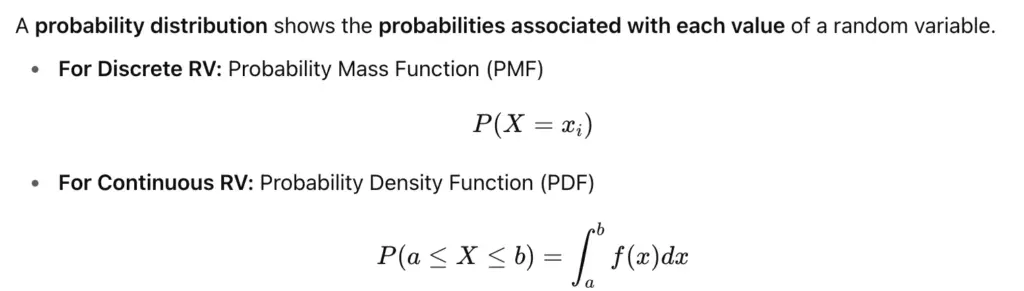
2. Probability Distributions
Also check out Most Repeated Quantitative Aptitude Questions for SSC CGL Tier 2
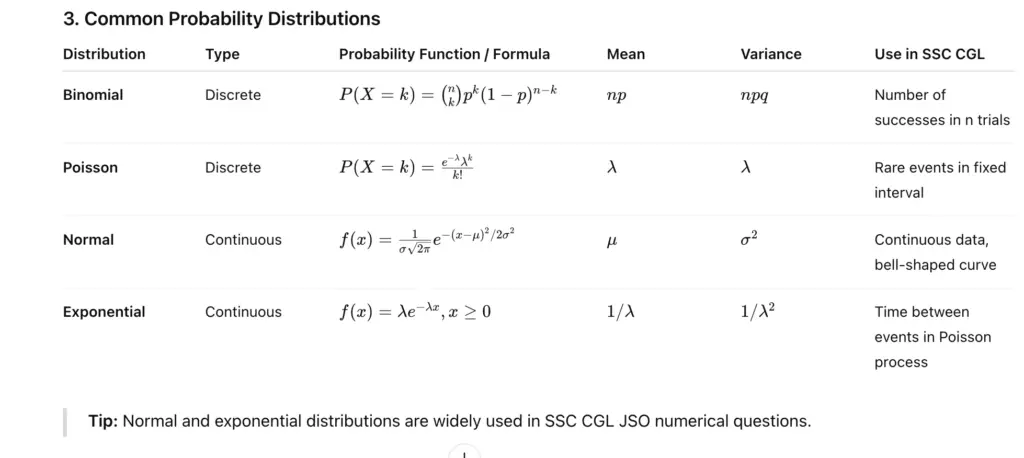
3. Common Probability Distributions
Check out Most Repeated Computer Awareness Questions for SSC CGL Tier 2
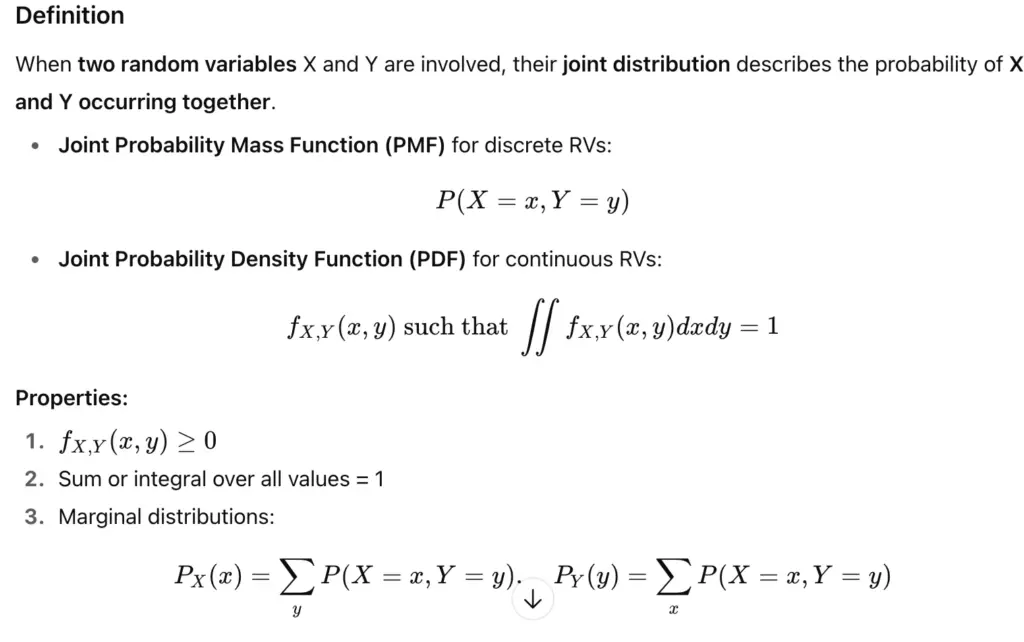
4. Joint Probability Distributions
Definition
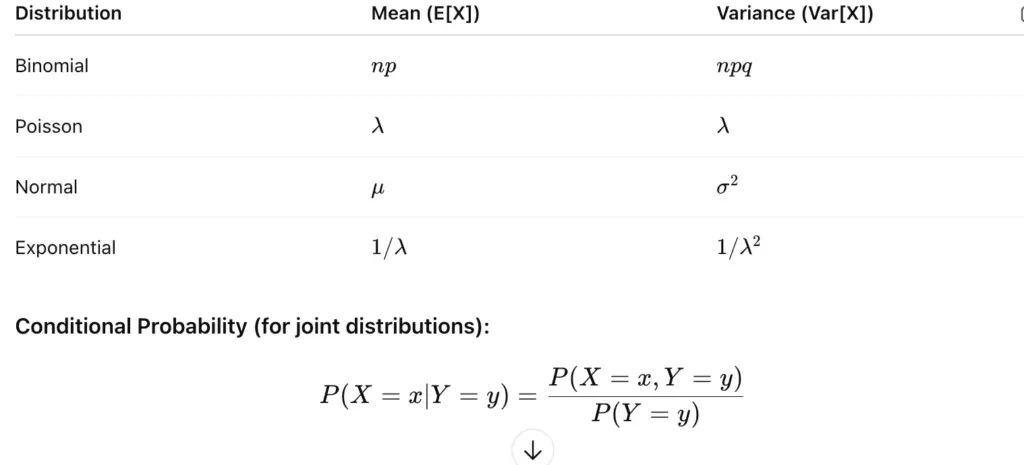
5. Key Formulas:
Below are the key formulas:
Check other SSC JSO related blogs:
Key Takeaways for SSC CGL Tier 2
- Random Variable → numeric outcome of experiment.
- Discrete vs Continuous → countable vs uncountable values.
- Binomial & Poisson → discrete distributions.
- Normal & Exponential → continuous distributions.
- Joint distribution → probability of two RVs together.
- Practice marginal and conditional distributions for exam speed.
FAQs
A numerical outcome of a random experiment, discrete or continuous.
Binomial and Poisson distributions.
Normal and Exponential distributions.
Probability distribution of two random variables together.
Predict probabilities, calculate means and variances, and solve joint/marginal distribution problems.
- Nitin’s SSC CGL Success Story and His Preparation Strategy
- SSC CGL Tier 2 Weightage of English and Quants, Check Here
- Most Repeated English Questions for SSC CGL Tier 2
- SSC CGL English Questions with Answers, Download Free PDF
- How to Prepare for SSC CGL English? Know the best tips
- Average Problems for SSC Exams, Practice Questions with Solutions

I’m Mahima Khurana, a writer with a strong passion for creating meaningful, learner-focused content especially in the field of competitive exam preparation. From authoring books and developing thousands of practice questions to crafting articles and study material, I specialize in transforming complex exam-related topics into clear, engaging, and accessible content. I have first hand experience of 5+ months in SSC Exams. Writing, for me, is not just a skill but a way to support and guide aspirants through their preparation journey one well-written explanation at a time.