Atmanirbhar Bharat Abhiyan, or “Self-Reliant India Mission,” is an economic stimulus package launched by the Indian Government in May 2020 to tackle the COVID-19 crisis. The campaign aims to strengthen India’s economy, reduce import dependence, and promote domestic manufacturing, services, and innovation.
The initiative was announced in four tranches by Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharaman, totaling ₹20 lakh crore, equivalent to nearly 10% of India’s GDP. The Abhiyan also integrates the Pradhan Mantri Garib Kalyan Yojana (PMGKY), aimed at providing relief to the economically vulnerable sections of society.
Why was Atmanirbhar Bharat Abhiyan launched?
The COVID-19 pandemic disrupted the Indian economy, affecting millions of jobs, businesses, and livelihoods. To mitigate the impact, the government introduced Atmanirbhar Bharat Abhiyan with multiple objectives:
- Strengthen local and regional manufacturers and service providers.
- Improve the standard of living by addressing trade deficits and the balance of payments.
- Achieve self-reliance for the country and its citizens in all aspects.
- Transform India into a global supply chain hub.
- Revive all sectors of the economy through fiscal stimulus.
It emphasized reforms in land, labor, liquidity, and laws while providing economic support to farmers, migrants, MSMEs, and industries.
What are the Five Pillars of Atmanirbhar Bharat Abhiyan?
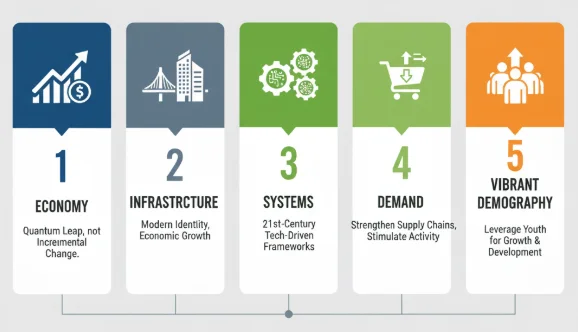
Prime Minister Narendra Modi outlined five foundational pillars for a self-reliant India:
- Economy: Focus on making a quantum leap rather than incremental adjustments to turn challenges into opportunities.
- Infrastructure: Modern infrastructure represents India’s identity and contributes to economic growth.
- Systems: Implementation of 21st-century technology-driven systems rather than outdated frameworks.
- Demand: Strengthening the demand and supply chains to stimulate economic activity.
- Vibrant Demography: Leveraging the potential of India’s young population for growth and development.
These pillars provide a structured approach to ensuring that self-reliance is sustainable and inclusive.
What are the Main Objectives of Atmanirbhar Bharat Abhiyan?
The primary objectives of the mission include:
- Job Creation: Increased employment opportunities in manufacturing, agriculture, and public schemes like MGNREGA.
- Boost Domestic Manufacturing: Enhancing the share of domestic products in the Gross Value Added (GVA).
- Reduce Import Dependency: Focus on import substitution and improving exports.
- Promote Indigenous Products: Encourage citizens to buy locally manufactured goods.
- Reform Outdated Policies: Simplifying laws, rational taxation, robust financial systems, and supply chain reforms.
- Support to Vulnerable Sections: Economic support for MSMEs, farmers, migrants, and daily wage laborers.
Get ready to crack government job exams with leading educators
How is Atmanirbhar Bharat Abhiyan Structured?
The economic package is implemented in four tranches, each addressing specific sectors:
Tranche 1: Support to Businesses and Financial Sector
| Sector | Measures |
| Employees / Taxpayers | – Extended income tax return deadlines (FY 2019-20) – TDS & TCS reduced by 25% – EPF support extended for low-income workers |
| MSMEs | – ₹3 lakh crore emergency credit line – ₹20,000 crore subordinate debt – ₹50,000 crore equity infusion – Expansion of MSME definition |
| NBFCs & HFCs | – ₹30,000 crore special liquidity scheme – Partial credit guarantee scheme extension |
| Discoms | – ₹90,000 crore liquidity infusion |
| Real Estate | – Extension of registration and project completion deadlines by 6 months |
Tranche 2: Support for Migrants, Poor, and Farmers
| Sector | Measures |
| Migrants & Poor | – ₹3,500 crore free food grains for migrant workers without ration cards |
| Farmers & Street Vendors | – ₹5,000 crore credit for street vendors – ₹2 lakh crore concessional credit for farmers – NABARD refinance support of ₹30,000 crore |
| Housing | – Affordable rental housing complexes under PMAY-ARHC – Extension of credit-linked subsidy scheme for middle-income groups |
| One Nation One Ration Card | – Portability of ration cards across states |
| MGNREGA | – Enrolment of returning migrant workers |
Tranche 3: Agriculture Reforms
| Sector | Measures |
| Inter-state Trade | – Facilitation of barrier-free trading of agricultural commodities |
| Contract Farming | – Legal framework to ensure assured pricing and private sector participation |
| Deregulation of Produce | – Six agricultural products deregulated: cereals, pulses, oilseeds, onions, potatoes, edible oils |
| Agriculture Infrastructure | – ₹1.5 lakh crore for farm-gate infrastructure (cold storage, logistics, post-harvest facilities) |
Tranche 4: Strategic Sectors and Privatization
| Sector | Measures |
| Defence | – Import bans on select items – FDI limit increased to 74% – Corporatization of Ordnance Factory Boards |
| Minerals | – Commercial mining – Private participation in coal blocks – Removal of government monopoly |
| Space | – Encouraging private sector participation via IN-SPACe |
| Aviation | – Auction of airports – Easing airspace restrictions – Rationalizing MRO tax structure |
| Power & Atomic | – Privatization of power distribution in UTs – Research reactors in PPP mode for medical isotopes production |
What are the Potential Benefits of Atmanirbhar Bharat Abhiyan?
The benefits of the Atmanirbhar Bharat Abhiyan are as follows:
- Job Creation: Employment through MGNREGA, MSMEs, and manufacturing initiatives.
- Credit Facilities: Easy access to loans for MSMEs, farmers, and small businesses.
- Liquidity Infusion: Ensures financial stability for businesses and banks.
- Private Sector Participation: Encourages domestic and foreign investment in strategic sectors.
- Health Infrastructure: Funding for COVID-19 vaccine development and public health initiatives.
- Agricultural Boost: Infrastructure and financial support for farmers, fishers, and livestock farmers.
- Education and Skill Development: Technology-driven learning platforms and skill enhancement programs.
What are the Challenges and Concerns of Atmanirbhar Bharat Abhiyan?
The challenges faced while implementing Atmanirbhar Bharat Abhiyan are as follows:
- Impact on International Trade: Import substitution, increased tariffs, and non-tariff barriers may reduce trade and foreign investment.
- Data Localisation Issues: Storing data within the country may limit global supply chain integration.
- Defence Sector Constraints: Import embargo on 101 items could affect foreign collaboration.
- Space Sector Clarity: Regulatory and procedural clarity needed for private sector participation.
- Policy Enforcement: Intellectual property, pharmaceutical regulations, and governance challenges.
Why is Atmanirbhar Bharat Abhiyan Relevant Today?
Recent global developments emphasize the importance of self-reliance:
- China Border Tensions: Galwan Valley clash highlights the need for indigenous defense capabilities.
- Afghanistan Crisis (2021): Global political instability affecting India’s strategic interests.
- Russia-Ukraine Conflict: Emphasizes the need for independent economic and defense strategies.
These developments show that Atmanirbhar Bharat Abhiyan is crucial not only for economic growth but also for strategic autonomy and security preparedness.
Key Takeaways
| Aspect | Key Points |
| Launch | May 2020, ₹20 lakh crore package |
| Objectives | Self-reliance, job creation, boost domestic manufacturing, reduce imports, strengthen economy |
| Five Pillars | Economy, Infrastructure, Systems, Demand, Vibrant Demography |
| Tranches | 1. MSMEs & financial support 2. Migrants, farmers, housing 3. Agriculture & trade reforms 4. Strategic sectors & privatization |
| Benefits | Job creation, credit facilities, liquidity infusion, private sector participation, health and agricultural infrastructure |
| Challenges | Trade restrictions, data localization, defense imports, regulatory clarity, policy enforcement |
| Steps Forward | Strategic planning, innovation, free trade, digital integration, sustainable policies, holistic reforms |
Questions Based on Atmanirbhar Bharat Abhiyan
Q1. What is the total financial outlay of Atmanirbhar Bharat Abhiyan?
(a) ₹10 lakh crore
(b) ₹15 lakh crore
(c) ₹20 lakh crore
(d) ₹25 lakh crore
(e) ₹30 lakh crore
Q2. Which of the following is NOT one of the five pillars of Atmanirbhar Bharat?
(a) Economy
(b) Infrastructure
(c) Systems
(d) Democracy
(e) Demand
Q3. Which tranche primarily focused on migrant workers and farmers?
(a) Tranche 1
(b) Tranche 2
(c) Tranche 3
(d) Tranche 4
(e) None of the above
Q4. What is the primary aim of Atmanirbhar Bharat?
(a) Isolationist economy
(b) Self-reliance and economic revival
(c) Promote only foreign trade
(d) Privatization only
(e) Reduce employment
Q5. Which sector received ₹1.5 lakh crore for infrastructure under Tranche 3?
(a) Defense
(b) Agriculture
(c) Aviation
(d) Space
(e) Power
Q6. What does PMGKY stand for?
(a) Pradhan Mantri Garib Kalyan Yojana
(b) Pradhan Mantri Gram Kalyan Yojana
(c) Pradhan Mantri Ghar Kalyan Yojana
(d) Pradhan Mantri Gramin Kalyan Yojana
(e) None of the above
Q7. Which agency provides a level playing field for private companies in India’s space sector?
(a) ISRO
(b) IN-SPACe
(c) DRDO
(d) NABARD
(e) BHEL
Q8. What is the main focus of Atmanirbhar Bharat in agriculture?
(a) Import agricultural products
(b) Supply chain reforms and farm-gate infrastructure
(c) Reduce farmer credit
(d) Privatize irrigation
(e) Export subsidies
Q9. Which of these is a concern raised regarding Atmanirbhar Bharat?
(a) Promoting local products
(b) Curtailment of international trade and investment
(c) Strengthening MSMEs
(d) Boosting health infrastructure
(e) Providing jobs
Q10. Which recent international event highlighted the relevance of Atmanirbhar Bharat?
(a) Galwan Valley clash
(b) US elections
(c) Tokyo Olympics
(d) Climate Summit
(e) G20 Summit
Also Read:
Answer Key:
| Question Number | Answer | Question Number | Answer |
| Q1 | C | Q6 | A |
| Q2 | D | Q7 | B |
| Q3 | B | Q8 | B |
| Q4 | B | Q9 | B |
| Q5 | B | Q10 | A |
- How Some Aspirants Clear Multiple Government Exams: Strategy, Discipline & Exam Psychology
- Crop Diversification Program, Transforming Indian Agriculture
- Government Schemes for NABARD Grade A 2026
- National Dairy Plan Phase 1 and Phase 2, Boosting India’s Dairy Sector
- Mera Gaon Mera Gaurav Scheme, Bridging Lab to Land
- Farmers First Initiative, Empowering Farmers Through Innovation
Hi, I’m Tripti, a senior content writer at Oliveboard, where I manage blog content along with community engagement across platforms like Telegram and WhatsApp. With 3+ years of experience in content and SEO optimization related to banking exams, I have led content for popular exams like SSC, banking, railway, and state exams.