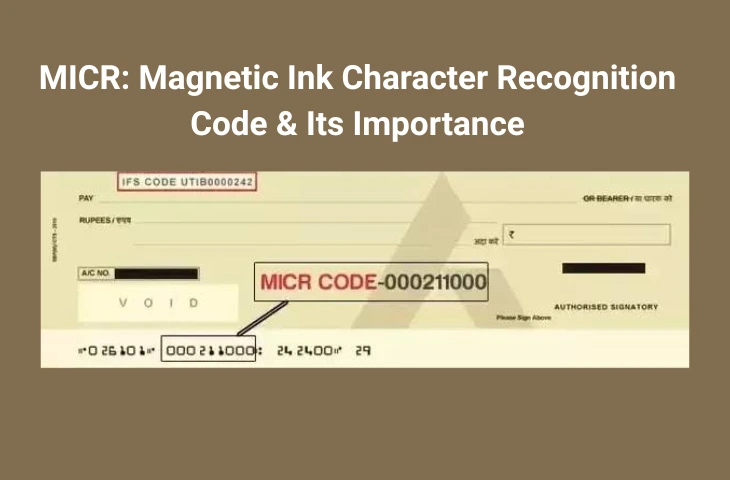
MICR (Magnetic Ink Character Recognition) is a technology used in the banking system to verify and process cheques quickly and securely. It uses special magnetic ink and unique fonts to print information such as the cheque number, bank code, and branch code. This helps in fast and accurate processing of cheques through machines.
The use of MICR technology ensures that cheques are cleared efficiently without manual errors. Introduced by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI), MICR has become an essential part of India’s cheque-clearing system, promoting speed, reliability, and automation in banking operations.
What is MICR?
MICR, or Magnetic Ink Character Recognition, is a system that allows banks to identify, read, and process cheques and other documents using magnetic ink and special characters. The key information printed in MICR format appears at the bottom of a cheque and includes details like the bank code, branch code, account number, and cheque number.
The magnetic ink used in MICR printing contains iron oxide, which enables machines to read the characters accurately, even if the document is stamped or slightly soiled. This technology enhances both security and efficiency in the cheque-clearing process.
Structure of MICR Code
Every bank branch in India has a unique MICR code assigned by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI). This code is printed at the bottom of every cheque and consists of 9 digits.
| Component | Description |
| Total Digits | 9 |
| First 3 Digits | Represent the city (aligned with the PIN code of the area) |
| Next 3 Digits | Represent the specific bank |
| Last 3 Digits | Represent the particular branch |
Example: If a cheque has MICR code 400002021:
- 400 = Mumbai (city code)
- 002 = State Bank of India (bank code)
- 021 = Fort Branch (branch code)
This structure ensures that every bank branch across the country can be uniquely identified during the clearing process.
Importance of MICR in Banking
The introduction of MICR technology has transformed the cheque-clearing process in India. It allows for faster, error-free, and more secure processing of cheques compared to manual methods.
| Importance | Explanation |
| Speedy Processing | Cheques are scanned and cleared quickly through MICR readers. |
| Accuracy | Reduces the chances of human error in reading or verifying cheque details. |
| Security | Magnetic ink prevents duplication or forgery of cheque information. |
| Automation | Enables banks to handle large volumes of cheques efficiently. |
| Nationwide Standardization | Ensures uniformity in cheque processing across all banks in India. |
By combining magnetic and optical technology, MICR provides reliability and consistency in cheque-based transactions.
How MICR Technology Works?
MICR technology functions through a process that reads the magnetic ink characters at the bottom of cheques using specialized MICR scanners. These machines detect the magnetic properties of the ink and translate them into readable data for automated processing.
Steps in MICR Processing:
- The cheque is fed into a MICR reader.
- The magnetic ink characters are scanned and decoded.
- The system verifies the bank, branch, and account details.
- The cheque is cleared through the electronic clearing system.
MICR vs IFSC
While both MICR and IFSC are identification systems used in banking, they serve different purposes. The IFSC code is used for electronic fund transfers, whereas the MICR code is used for physical cheque clearance.
| Basis | MICR | IFSC |
| Full Form | Magnetic Ink Character Recognition | Indian Financial System Code |
| Purpose | Used for cheque clearance | Used for electronic fund transfers (NEFT, RTGS, IMPS) |
| Format | 9-digit numeric code | 11-character alphanumeric code |
| Technology Used | Magnetic ink and character recognition | Digital code for online transactions |
| Assigned By | Reserve Bank of India | Reserve Bank of India |
Both codes together contribute to a seamless, secure, and integrated banking system in India.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1: What is the full form of MICR?
A1: The full form of MICR is Magnetic Ink Character Recognition. It is a technology used by banks to verify and process cheques using magnetic ink and special fonts.
Q2: What is the structure of a MICR code?
A2: A MICR code is a 9-digit number where the first three digits represent the city, the next three represent the bank, and the last three represent the branch.
Q3: Where can I find the MICR code on a cheque?
A3: The MICR code is printed at the bottom of every cheque, usually next to the cheque number, using magnetic ink.
Q4: How does MICR differ from IFSC?
A4: MICR is used for cheque clearance in physical banking, while IFSC is used for electronic fund transfers like NEFT, RTGS, and IMPS.
Q5: Why is MICR important in banking?
A5: MICR ensures fast, accurate, and secure cheque processing, reduces human error, and prevents fraud or duplication in cheque-based transactions.
- UPSC EPFO Exam Analysis 2025, 30th November, Difficulty Level & Good Attempts
- UPSC EPFO Admit Card 2025 Out, APFC & EO/AO Hall Ticket Link
- Industrial Relations & Labour Laws Notes for UPSC EPFO 2025, Free PDF
- UPSC EPFO Topper’s Strategy, AIR 1’s Journery and Success Story
- UPSC EPFO Posting for EO/AO & APFC: Transfers & Growth
- UPSC EPFO Exam Date 2025, Admit Card Link for 230 Posts
Hi, I’m Tripti, a senior content writer at Oliveboard, where I manage blog content along with community engagement across platforms like Telegram and WhatsApp. With 3+ years of experience in content and SEO optimization related to banking exams, I have led content for popular exams like SSC, banking, railway, and state exams.