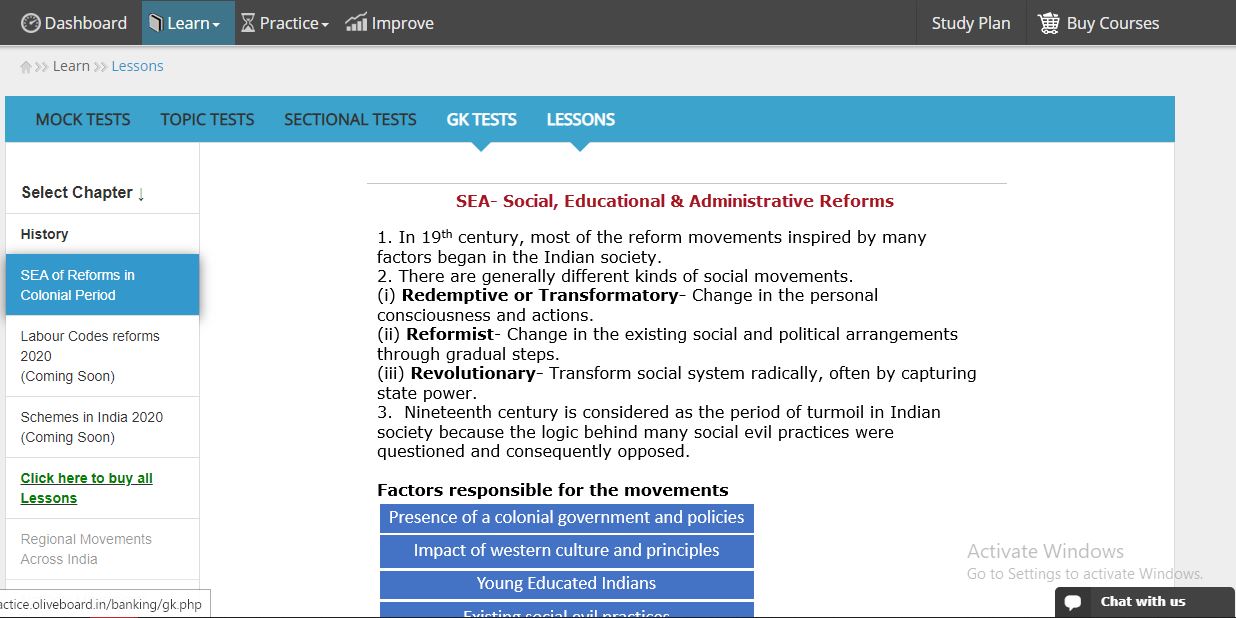
The UPSC EPFO Enforcement Officer Exam contains a good amount of questions from the Industrial Relations and Labour Laws topic. Since the course is vast and it is very important for you to cover each and every topic in a given period of time. In this article, we will be providing you with the study notes on Industrial Relations and Labour Laws which will help you in your UPSC EPFO EO exam preparation.
We have also provided UPSC EPFO EO Accounting Principles Study Notes. Click here to get the General Accounting Principles Study Notes. Have a look at the types of questions asked in the UPSC EPFO EO examination for free. Register here to take up practice questions.
Let’s start with the blog on Industrial Relations and Labour Laws PDF Notes UPSC EPFO EO 2021. Before moving on Industrial Relations and Labour Laws Notes let’s have a look at daily Lockdown Live Tests provided for free.
1. Industrial Relations and Labour Laws PDF Notes
1.1 Introduction
Productivity in any organisation is the outcome of the joint efforts of two distinct elements namely technological and human resources. The factor of production other than labour can be manipulated easily. However, the human aspect in the organisation is the most difficult to manipulate or manage in a proper perspective.
The human elements are the causes and the result of the interaction, social issues, duties, responsibilities, and other activities. The high rate of industrial growth, increased pace of technological development and complex nature of the jobs made the workforce of an organization the source of completive success.
Hence, managing men has become a vital part of the present-day of management. Any negligence of the human element leads to misunderstanding between the management and workers. The results of which can be seen in the form of increased labour turnover, absenteeism, indiscipline, the decline in the quality of work done, increased cost production, and various problems in the market.
Therefore, in this context, the concept of industrial relations receives widespread attention all over the world.
1.2 Definitions of Industrial Relations
The term Industrial Relations comprises Industry and Relations. Industry means any productive activity in which an individual is engaged. It includes –
(a) primary activities like agriculture, fisheries, plantation, forestry, horticulture, mining, etc and
(b) secondary activities like manufacturing, construction, trade, transport, commerce, banking, communication, etc.
Economically speaking, industry means the secondary sector where factors of production (land, labour, capital and enterprise or four M’s – men, materials, money, machines) are gainfully employed for the purpose of production, and where a business organisation exists.
Relations means the relations that exist in the industry between the employer and his workforce. Different authors have defined the terms of industrial relations in a somewhat different way.
Also Check: SSC MTS Answer Key 2024
1.3 Objectives of Industrial Relations
Two-fold objectives of good industrial relations are to preserve industrial peace and to secure industrial co-operation.
If we have to establish industrial peace, the workers must be assured of fair wages, good conditions of work, reasonable working hours, holidays and minimum amenities of life.
Get Complete Study Notes PDF By Registering Here
1.4 Types of Industrial Relations
Industrial Relations is chiefly concerned with the management and the worker’s relations or employer-employee relations. But its scope is not limited only to this aspect. It also includes labour relations and public or community relations.
The industrial relations includes four types of relations:
(i) Labour relations
(ii) Group relations
(iii) Employer-Employee Relations
(iv) Community or Public Relations.
Want to know in detail regarding Types of Industrial Relations? Register Here To Get Study Notes
1.5 Model’s of Industrial Relations
1. Dunlop’s Industrial Relations System Model-Four Interrelated Elements.
(i) Actors
(ii) Shared Ideology
(iii) Contexts
(iv) Rules
2. Craig’s Industrial Relation System Model
(i) Adds an actor – end-user
(ii) Elements from the external environment converted into outputs.
(iii) Series of conversion mechanisms.
(iv) Outputs flow back into the environment through a feedback loop.
1.6 Layers of Industrial Relations
The following are the layers of Industrial Relations:
- The Employer
- The Employee
- The Government
- Trade Unions
Get Complete Study Notes On Model’s & Layer Of Industrial Relations Here
1.7 Approaches To Industrial Relations
The various approaches to Industrial Relations are as follows:
- Psychological Approach
- Sociological Approach
- Human Relations Approach
- Socio Ethical Aspects
- Gandhian Approach
- Unitary Approach
- Pluralistic Approach
- Marxist Approach
1.8 Five Year Plan and Industrial Relations
A country like India which is in the progress of transforming its economy from a backward agricultural economy to a developed industrial one, peaceful relations between management and labour is the need of the hour. Emphasis on increased production for the smooth and steady 19 economy growth, India cannot afford work stoppages due to protracted friction between employers and employees which will jeopardise the main objectives of our five-year plan.
For economic progress, India in her First Five Year Plan (1951-56) concentrated on five aspects of labour policy:
(i) industrial relations
(ii) wages
(iii) working conditions
(iv) productivity
Get Complete Study Notes By Registering Here
2. Labour Laws Background
The Ministry of Labour and Employment seeks to protect and safeguard the interests of workers in general and those who constitute the poor, deprived and disadvantaged sections of the society, in particular, with due regard to creating a healthy work environment for higher production and productivity, and developing and coordinating vocational skill training and employment services.
Government’s attention is also focused on the promotion of welfare activities and providing social security to the labour force both in the organised and unorganised sectors, in tandem with the process of liberalisation. These objectives are sought to be achieved through enactment and implementation of various labour laws, which regulate the terms and conditions of service and employment of workers.
The following are the thrust areas of the Government concerning labour laws:
- Labour policy and legislation;
- Safety, health and welfare of labour;
- Social security of labour;
- Policy relating to special target groups such as women and child labour;
- Industrial relations and enforcement of labour laws in the central sphere;
- Adjudication of industrial disputes through Central Government Industrial Tribunals-cum-Labour Courts and National Industrial Tribunals;
- Workers’ education;
- Labour and employment statistics;
- Emigration of labour for employment abroad;
- Employment services and vocational training;
- Administration of central labour and employment services; and
- International cooperation in labour and employment matters.
The various labour legislation enacted by the Central Government can be classified into the following different broad categories:
- Laws relating to Industrial Relations-
- Industrial Disputes Act, 1947
- Trade Unions Act, 1926
- Laws relating to Wages
- Minimum Wages Act, 1948
- Payment of Wages Act, 1936
- Payment of Bonus Act, 1965
- Laws relating to Social Security
- Employees’ Provident Funds and Miscellaneous Provisions Act, 1952
- Employees’ State Insurance Act, 1948
- Labour Welfare Fund Act (of respective States)
- Payment of Gratuity Act, 1972
- Employee’s Compensation Act, 1923
- Laws relating to Working Hours, Conditions of Services and Employment
- Factories Act, 1948
- Industrial Employment (Standing Orders) Act, 1946
- Shops and Commercial Establishments Act (of respective States)
- Contract Labour (Regulation and Abolition) Act, 1970
- Inter-State Migrant Workmen (Regulation of Employment and Conditions of Service) Act, 1979
- Weekly Holiday Act, 1942
- National and Festival Holidays Act (of respective States) 1963
- The Plantation Labour Act, 1951
- The Mines Act, 1952
- The Dock Workers (Safety, Health & Welfare) Act, 1986
- Laws relating to Equality and Empowerment of Women
- Equal Remuneration Act, 1976
- Maternity Benefits Act, 1961
- Prohibitive Labour Laws
- Bonded Labour System (Abolition), Act, 1976
- Child Labour (Prohibition & Regulation) Act, 1986
- The Beedi and Cigar Workers (Conditions of Employment) Act, 1966
- The Sexual Harassment at the Workplace (Prevention, Prohibition and Redressal) Act, 2013
- Laws relating to Employment and Training
- Apprentices Act, 1961
- Employment Exchanges (Compulsory Notification of Vacancies) Act, 1959
3. UPSC EPFO EO Study Notes
1. 10 Mock Tests for EPFO EO in the latest pattern with detailed solutions
2. Summary PDF Notes for all sections (except Quant, Eng)

- Indian Freedom Struggle (Click Here For PDF Notes)
- Indian Polity and Economy (Click Here For Notes)
- General Accounting Principles (Click Here For Notes)
- Industrial Relations and Labor Laws (Click Here For Notes)
- General Science and Knowledge of Computer Applications (Click Here For Notes)
- Social Security in India (Click Here For Notes)
4. UPSC EPFO EO Study Material | Preparation Strategy
For topic-wise EPFO EO preparation strategy and preparation tips click on the blog link given below.
UPSC EPFO EO preparation strategy and preparation tips
This was all from us in this blog Industrial Relations and Labour laws Notes UPSC EPFO EO Exam. Hope the information provided above will help you in your exam preparation. Stay tuned for more exam related information.
All The Best For Your Exam Preparation!
Also, Check:
Recommended Free Downloads
- Weekly Current Affairs 2025 PDF For Bank, SSC, UPSC Exams
- Monthly Current Affairs 2025 PDF For SSC, Banking, Railways
- Practice Wrong Number Series for Banking Exams 2025 Solved Questions
- Quick Maths Tricks for Fast Calculations
- Blood Relation Questions for IBPS RRB PO & Clerk Exams, Download Free PDF
- Computer Awareness For Bank Exams, Important Terms






