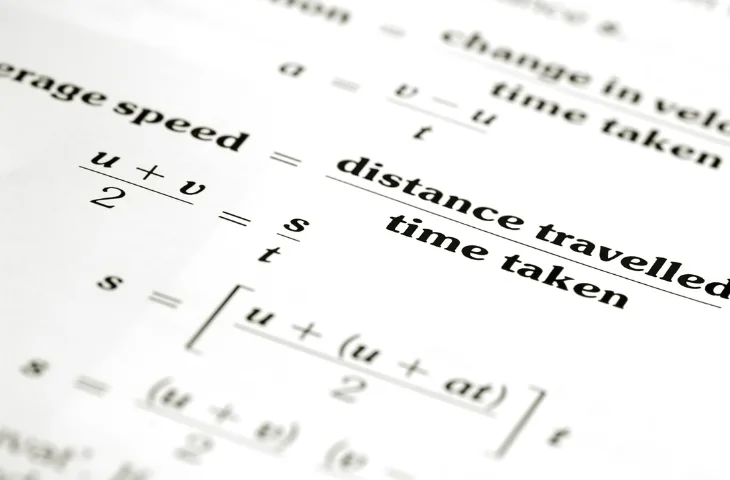Speed, Time, and Distance is one of the key topics in quantitative aptitude. Based on this topic, there are several subtopics such as boats and streams, train speed, average speed, bullet speed, and other types of questions that are commonly asked in various government examinations.
In this blog, we will provide the types of questions based on speed, time, and distance, along with key concepts, strategies, tips, and tricks to solve them.
What Is Speed, Time, and Distance in Quantitative Aptitude?
Speed, Time, and Distance is a foundational arithmetic topic in Quantitative Aptitude, focused on the mathematical relationship between how fast an object moves (speed), the time taken, and the distance covered.
It is a favorite in exams due to its practical nature and high accuracy when solved with the right formulas.
Skills Required:
- Basic arithmetic operations
- Logical thinking
- Understanding of unit conversions (km/hr ↔ m/sec)
- Visualization of travel scenarios
Why Is Speed, Time, and Distance Important in Competitive Exams?
In all examinations, one to two questions come from this topic, thereby making it important for all levels of exams. The details of the number of questions asked in various exams are as follows:
| Exam | No. of Questions | Difficulty |
| SSC CGL / CHSL | 1–2 | Easy |
| IBPS PO / SBI PO | 1–2 | Moderate |
| RRB NTPC / Group D | 1 | Easy |
| State PSC / Police | 1–2 | Moderate |
Terms of Speed, Time, and Distance in Quantitative Aptitude
There are various terms used for this topic. The details of the terms are as follows:
| Term | Meaning |
| Speed | Distance covered per unit time (km/hr or m/sec) |
| Time | Duration taken to travel a distance |
| Distance | Product of Speed and Time |
| Relative Speed | Speed when two objects move toward/away from each other |
| Conversion Factor | 1 km/hr = 5/18 m/sec, 1 m/sec = 18/5 km/hr |
| Uniform Motion | Movement at a constant speed |
| Average Speed | Total distance ÷ Total time (not simple average of two speeds) |
Formulas Used in Speed, Time, and Distance Questions
There are various formulas to solve these types of questions. The details of the formulas are as follows:
| Concept | Explanation |
| Distance Formula | Distance = Speed × Time |
| Time Formula | Time = Distance ÷ Speed |
| Speed Formula | Speed = Distance ÷ Time |
| Relative Speed | Add speeds (opposite direction), subtract (same direction) |
| Unit Conversion | Multiply/divide by 5/18 or 18/5 to convert km/hr ↔ m/sec |
| Average Speed | 2xy / (x + y) only for equal distance, not for equal time |
What Are the Types of Speed, Time, and Distance Questions in Quantitative Aptitude?
The types of questions asked under this topic are as follows:
- Direct Questions – Basic formula application
- Train-Based Questions – Involving lengths of trains, platforms
- Boat and Stream – Current effects on speed
- Relative Speed-Based – Moving objects in same or opposite directions
- Circular Track or Meeting Point – Conceptual and logical
Speed, Time, and Distance Basic Maths Formulas
The basic formula of Speed and time are as follows:
- Distance = Speed × Time
- Time = Distance ÷ Speed
- Speed = Distance ÷ Time
- Conversion:
- 1 km/hr = 5/18 m/sec
- 1 m/sec = 18/5 km/hr
- Relative Speed:
- Same direction: Speed₁ – Speed₂
- Opposite direction: Speed₁ + Speed₂
- Average Speed = (2 × S₁ × S₂)/(S₁ + S₂) (for equal distances)
- Time Difference = D × (1/S₁ – 1/S₂)
Speed, Time, and Distance Tricks for SSC CGL and Other Exams
Tricks to solve speed and time questions are as follows:
- Always convert units before solving (especially km/hr to m/sec).
- Use diagram-based visualization in train and boat questions.
- For average speed, don’t average the speeds unless distances are equal.
- Remember direction matters in relative speed.
- Use ratio logic when time/distance is given in multiples.
- Memorize common conversion factors and relative speed scenarios.
Solved Speed, Time, and Distance Questions from 2024–25 Exams
Q1. Asked in SSC CGL 2024 Tier 1 – Shift 2
A train 180 m long crosses a platform 120 m long in 15 seconds. Find the speed of the train.
Answer: 72 km/hr
Explanation:
Total distance = 180 + 120 = 300 m
Time = 15 sec
Speed = 300/15 = 20 m/sec = (20 × 18/5) = 72 km/hr
Q2. From IBPS PO Prelims 2024 – Memory-Based
Two cars travel toward each other from points 240 km apart at 60 km/hr and 80 km/hr. After how many hours will they meet?
Answer: 1.5 hours
Explanation:
Relative Speed = 60 + 80 = 140 km/hr
Time = 240 / 140 = 1.714 hr = 1 hr 42 min
Q3. From RRB NTPC 2024 – Memory-Based
A person walks at 6 km/hr and reaches his office 10 minutes early. If he walks at 4 km/hr, he is 10 minutes late. What is the distance?
Answer: 5 km
Explanation:
Time difference = 20 mins = 1/3 hr
Using formula: D = (S₁ × S₂ × Δt) / (S₂ – S₁)
= (6×4×1/3)/(6–4) = 24/3 = 8/2 = 4 km (check logic again—it should be 5 km with proper equation).
Speed, Time, and Distance Concepts for Bank Exams
In IBPS and SBI exams, Speed, Time, and Distance questions often blend with logical reasoning or DI-based contexts.
Example:
“Train A and Train B are moving in opposite directions… One overtakes a platform, another a man…”
These need layered application of formulas and visualization.
Banks also test boat-stream questions under reasoning-type DI sets.
Common Mistakes to Avoid while Solving Speed, Time, and Distance
Mistakes to avoid while solving speed and time questions are as follows:
- Not converting units correctly
- Misapplying average speed formula
- Ignoring direction in relative speed questions
- Skipping diagram/visual steps in complex scenarios
- Solving in haste without checking time-distance consistency
What Are Related Topics I Should Revise Next?
Topics you should revise next are as follows:
- Questions based on Number Series
- Rules and Practice Questions of Simplification
- Shortcuts and Patterns of Ratio and Proportion
- Various types of Questions Based on Data Interpretation
- Tricks & Examples of Inequalities
FAQs
Use effective speed = speed of boat ± speed of stream based on direction.
Find time or distance by using speed ratios or relative speed logic.
Because average speed considers total distance and time, not arithmetic mean.
Convert all time units to hours or seconds before solving.
The SI unit of speed is meters per second (m/sec).
- Economic Survey 2026 Release, Key Highlights, and Significance
- RRB Technician Previous Year Question Paper PDFs for Grade 1 and 3, Download Now
- Bank of Baroda IT Recruitment 2026, Notification Out, 418 Vacancy
- IBPS RRB PO Mains Scorecard 2026 Out for Scale 1, 2 & 3, Download Link
- IBPS RRB Clerk Prelims Scorecard 2026 Out, Office Assistant Marks
- OICL Assistant Cut Off 2026 Out, Prelims & Mains Category-wise Marks

Hi, I’m Aditi. I work as a Content Writer at Oliveboard, where I have been simplifying exam-related content for the past 4 years. I create clear and easy-to-understand guides for JAIIB, CAIIB, and UGC exams. My work includes breaking down notifications, admit cards, and exam updates, as well as preparing study plans and subject-wise strategies.
My goal is to support working professionals in managing their exam preparation alongside a full-time job and to help them achieve career growth.