The Industrial Revolution was a period of major transformation in human history when societies shifted from agrarian economies to industrialized and urbanized systems. Beginning in Britain in the late 18th century, it spread across Europe, America, and eventually the world. It brought in machinery, factories, new inventions, and mass production, replacing manual labour and traditional cottage industries.
Some major highlights of the First Industrial Revolution include:
- Invention of the Spinning Jenny (1764) by James Hargreaves.
- Introduction of the Steam Engine, which powered industries and transport.
- Power loom mechanizing textile production.
- Development of iron and steel industries, fueling construction and shipbuilding.
This revolution marked a turning point in history, influencing economic growth, social changes, and global trade.
How Did the Industrial Revolutions Evolve?
The journey of industrial revolutions can be divided into four phases:
| Industrial Revolution | Key Features | Major Innovations |
| First (18th–19th century) | Powered by water and steam engines; start of factories and mechanization | Steam Engine, Spinning Jenny, Cotton Gin, Cement, Telegraph, Bessemer Process |
| Second (Late 19th–Early 20th century) | Based on electric power; mass production with assembly lines | Automobiles, Electricity, Steel Industries, Assembly Line Production |
| Third (Mid-20th century) | Digital Revolution; machines electronically driven and automated | Electronics, Computers, Information Technology, Digital Automation |
| Fourth (21st century) | Fusion of physical, digital, and biological technologies; smart automation | Artificial Intelligence, Robotics, Big Data, Cloud Computing, IoT |
What is the Fourth Industrial Revolution?
Coined by Klaus Schwab, Founder of the World Economic Forum (WEF), in 2016, the Fourth Industrial Revolution (4IR) describes the digital transformation of industries. It involves smart factories, cyber-physical systems, and interconnected technologies. Key features of 4IR:
- Fusion of technologies across physical, digital, and biological domains.
- Creation of smart factories with real-time data integration.
- Heavy reliance on automation, robotics, and AI.
- Transformation of supply chains, healthcare, education, and governance.
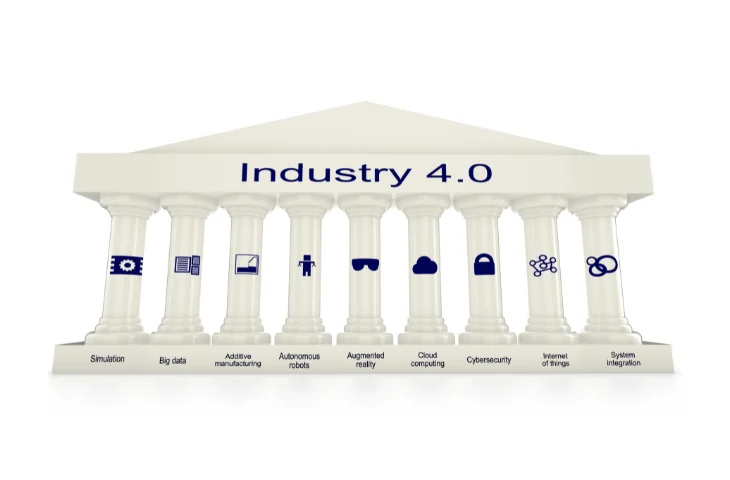
What are the Key Technologies of Industry 4.0?
Several advanced technologies drive Industry 4.0:
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning: Enable predictive analytics, intelligent automation, and decision-making.
- Internet of Things (IoT) and IIoT: Devices and sensors connected to networks for real-time data exchange.
- Big Data and Analytics: Processing large datasets for better insights.
- Cloud Computing: Scalable storage and computing power.
- Cyber-Physical Systems: Integration of digital controls with physical processes.
- Robotics and Automation: Machines performing repetitive and precision tasks.
- 3D Printing (Additive Manufacturing): On-demand customized production.
- Augmented/Virtual Reality (AR/VR): Training, design, and immersive experiences.
- Autonomous Vehicles and Drones: Redefining logistics and mobility.
Get ready to crack government job exams with leading educators
How Does Industry 4.0 Differ from Previous Generations?
Unlike earlier revolutions, Industry 4.0 is not limited to one domain but brings convergence of multiple technologies and affects all sectors of life.
- 1st Revolution: Mechanization through water and steam.
- 2nd Revolution: Mass production through electricity.
- 3rd Revolution: Automation through electronics and IT.
- 4th Revolution: Smart automation through AI, IoT, robotics, and integration of biological and digital systems.
What are the Impacts of Industry 4.0?
Some of the positive and negative impacts of the Industrial Revolution 4.0 are as follows:
| Aspect | Positive Impacts | Negative Impacts |
| Productivity | Increased Productivity: Automation and AI-driven systems enhance efficiency. | Job Displacement: Automation may reduce labour-intensive opportunities. |
| Supply Chain | Supply Chain Optimization: Real-time visibility across production and logistics. | Economic Inequality: Divide between high-skilled and low-skilled workers. |
| Maintenance & Operations | Predictive Maintenance: Reduces downtime and improves machine life. | Cybersecurity Risks: Loss of privacy, data breaches, and misuse of information. |
| Healthcare | Improved Healthcare: AI-based diagnostics, telemedicine, personalized treatment. | Ethical Concerns: Over-dependence on technology may create social tensions. |
| Agriculture | Smart Agriculture: Real-time monitoring of crops, pest detection, yield prediction. | — |
| Governance | Better Governance: Digital platforms improving transparency and service delivery. | Environmental Impact: Increased digital energy consumption. |
What Steps has India Taken Towards Industry 4.0?
India has recognized the importance of Industry 4.0 and has launched multiple initiatives:
- Centre for Fourth Industrial Revolution (C4IR): Established in India in collaboration with WEF. Telangana also signed an agreement to set up a C4IR in Hyderabad.
- SAMARTH Udyog Bharat 4.0: Initiative by the Ministry of Heavy Industries for awareness and adoption of Industry 4.0 in the capital goods sector.
- AI for Agriculture Innovation (AI4AI): Supporting farmers with AI-driven solutions.
- Urban Transformation Hub: For sustainable smart city planning with emerging technologies.
- Education 4.0 in partnership with UNICEF: Roadmap for school-to-work transition and foundational literacy.
- FIRST Healthcare in Meghalaya: Digital solutions for better healthcare access.
- Drone Policy: Expanding use of drones for mapping, traffic management, and security.
How Can Industry 4.0 Benefit India?
In India, this revolution holds immense potential to improve healthcare access through AI-driven diagnostics, boost agricultural output with real-time data, enhance skill development, strengthen supply chains, and position the country as a global manufacturing hub.
- Poverty Alleviation: Better healthcare and agricultural output.
- Healthcare Access: AI-driven diagnostics and telemedicine.
- Agriculture Growth: Real-time data to increase farmer incomes.
- Skill Development: Skilling, re-skilling, and up-skilling of workforce.
- Global Manufacturing Hub: Using demography, demand, and governance to strengthen India’s role in manufacturing.
- Supply Chain Efficiency: Reduced waste and improved logistics.
- Digital Empowerment: Benefits reaching villages and marginalized communities.
What are the Challenges for India in Adopting 4IR?
Challenges faced by India while adopting 4IR are as follows:
- Job Displacement: Fear of unemployment due to automation.
- Skilled Workforce Gap: Need for training in AI, IoT, 3D printing.
- Economic Inequality: Rich-poor gap widening.
- Cybersecurity Threats: Data misuse and fake news.
- Environmental Impact: Growing digital carbon footprint.
- Ethical and Social Concerns: Fear of corporate monopolies, misuse of personal data.
Also Check: Bharat Skill Connect Portal
What is the Way Forward?
India must adopt a balanced approach:
- Focus on skill development and vocational training.
- Create cybersecurity frameworks to safeguard privacy.
- Promote sustainable digital practices.
- Encourage inclusive growth where benefits of 4IR reach all.
- Develop policy frameworks for ethical use of AI and emerging technologies.
Key Takeaway
| Aspect | Key Points |
| Definition | Fusion of physical, digital, and biological technologies |
| Origin | Coined by Klaus Schwab, WEF, 2016 |
| Core Technologies | AI, IoT, Robotics, Big Data, Cloud Computing, AR/VR, 3D Printing |
| Benefits | Productivity, predictive maintenance, better healthcare, agriculture growth |
| Challenges | Inequality, job loss, cybersecurity, environmental footprint |
| India’s Initiatives | C4IR, SAMARTH, AI4AI, Education 4.0, FIRST Healthcare |
| Way Forward | Skilling, cybersecurity, sustainability, inclusive policies |
Also Read:
Questions Based on Industrial Revolution 4.0
- Who coined the term “Fourth Industrial Revolution”?
- (a) James Watt
- (b) Klaus Schwab
- (c) Samuel Compton
- (d) Edmund Cartwright
- (e) Andrew Ure
Answer: (b)
- Which invention is associated with the First Industrial Revolution?
- (a) Internet
- (b) Spinning Jenny
- (c) Electric Bulb
- (d) Computer
- (e) Automobile
Answer: (b)
- Which industrial revolution is also known as the Digital Revolution?
- (a) First
- (b) Second
- (c) Third
- (d) Fourth
- (e) None
Answer: (c)
- The Fourth Industrial Revolution mainly focuses on:
- (a) Steam power
- (b) Electric power
- (c) Electronics and IT
- (d) Fusion of digital, physical, and biological tech
- (e) None
Answer: (d)
- Which Indian state signed an agreement with WEF to set up a Centre for Industrial Revolution in Hyderabad?
- (a) Maharashtra
- (b) Karnataka
- (c) Telangana
- (d) Gujarat
- (e) Tamil Nadu
Answer: (c)
- SAMARTH Udyog Bharat 4.0 relates to:
- (a) Agriculture
- (b) Heavy Industries
- (c) Education
- (d) Health Sector
- (e) Space Technology
Answer: (b)
- Which of the following is NOT a key technology of Industry 4.0?
- (a) Artificial Intelligence
- (b) Internet of Things
- (c) Steam Engines
- (d) Big Data
- (e) Cloud Computing
Answer: (c)
- The FIRST Healthcare initiative was launched in which Indian state?
- (a) Meghalaya
- (b) Telangana
- (c) Maharashtra
- (d) Karnataka
- (e) Odisha
Answer: (a)
- Which sector can benefit from predictive maintenance in Industry 4.0?
- (a) Textile
- (b) Manufacturing
- (c) Healthcare
- (d) Agriculture
- (e) All of the above
Answer: (e)
- Which international organization is closely linked with the concept of Industry 4.0?
- (a) United Nations
- (b) World Bank
- (c) World Economic Forum
- (d) IMF
- (e) WTO
Answer: (c)
- How Some Aspirants Clear Multiple Government Exams: Strategy, Discipline & Exam Psychology
- Crop Diversification Program, Transforming Indian Agriculture
- Government Schemes for NABARD Grade A 2026
- National Dairy Plan Phase 1 and Phase 2, Boosting India’s Dairy Sector
- Mera Gaon Mera Gaurav Scheme, Bridging Lab to Land
- Farmers First Initiative, Empowering Farmers Through Innovation

Hi, I’m Aditi. I work as a Content Writer at Oliveboard, where I have been simplifying exam-related content for the past 4 years. I create clear and easy-to-understand guides for JAIIB, CAIIB, and UGC exams. My work includes breaking down notifications, admit cards, and exam updates, as well as preparing study plans and subject-wise strategies.
My goal is to support working professionals in managing their exam preparation alongside a full-time job and to help them achieve career growth.