Direct And Indirect Speech : Direct and indirect Speeches are used during our day to day life conversations. Generally while speaking in general conversation, we use indirect speech. There are many instances where we need to describe an event or action that happened (while telling about a particular event), and very often that includes repeating what someone said. For example, Payal came in and said, “I’m really hungry.” In this someone is describing the event that happened. Such occasions occur frequently in our daily life. In order to describe what someone said, we use direct and indirect speech frequently. Direct and Indirect speeches are not just important to our daily conversations, but they are also important for our exams. A number of questions are asked from direct and indirect speeches in the exams like, IBPS PO, SBI PO, IBPS Clerk, etc. So, in this blog, we will know everything about direct and indirect speeches like rules, examples, how to convert direct to indirect speech, and practice questions. So, without further ado, let’s get started.
Direct Speech
When we want to describe what someone said to us, we commonly use direct speech. We simply repeat what someone said, putting the phrase between speech marks. For example; Payal came in and said, “I’m really hungry.”
Here in this example, someone is describing what Payal said.
We commonly use this type of language in TV news and newspapers. For example : The Police officer said “We are looking into the situation”
Examples of Direct Speech :
Some other examples of the direct speech are :
- He said, “I will go to the market.”
- The officer said to the clerk, “File these papers immediately”
- He said to Sheela, “you have committed a mistake here”
- Vamsi said, “We are playing a match today.”
- He said to the boy, “Where did you learn classical music?”
Indirect Speech (Reported Speech)
When we want to tell about what someone said without speech marks and without necessarily using exactly the same words, we can use indirect speech, also known as reported Speech. For example-
Direct Speech : The librarian said to me, “You can keep this book with you”
Indirect Speech : The librarian told me that I can keep this book with me.
Direct Speech : I said to you, “She should not be in the garden”
Indirect Speech : I told you that she should not be in the garden.
Direct Speech : Tony said, “We cannot enter the park”
Indirect Speech : Tony said that they could not enter the park.
Direct Speech : She said, “I am doing my homework”
Indirect Speech : She said that she was doing her homework.
Direct Speech : He said, “I have eaten a mango.”
Indirect Speech : He said that he had eaten a mango.
Direct Speech : She said, “It has been snowing for 5 days”
Indirect Speech : She said that it had been snowing for 5 days.
Direct Speech : Geeta said, “They went to the park”
Indirect Speech : Geeta said that they had gone to the park.
Direct Speech : Raj said to me, “I was waiting to see you”
Indirect Speech : Raj said to me that he had been waiting to see me.
Direct Speech : She said, “I had eaten a pizza”
Indirect Speech : She said that she had eaten a pizza.
Direct Speech : Chris said, “I will buy a chocolate”
Indirect Speech : Chris said that he would buy chocolate.
Direct Speech : Ben said, “I will be catching a taxi”
Indirect Speech : Ben said that he would be catching a taxi.
Direct Speech : John said, “I will have eaten the pizza”
Indirect Speech : John said that he would have eaten the pizza.
How to Convert Direct Speech Into Indirect speech?
Most of the questions asked in the competitive exams revolve around changing the speech of a given sentence. Sometimes from direct to indirect or vice versa. So here, we will see how you can easily convert direct speech into indirect speech without much effort.
Rule 1:
| Present Simple Tense do /does | Past Simple Tense did |
| Present Continuous Tense is/am/are | Past Continuous Tense was /were |
| Present Perfect Tense has /have | Past Perfect Tense had |
| Present Perfect Continuous has been /have been | Past Perfect Continuous had been |
| Past Simple Tense did | Past Perfect Tense had |
| Past Perfect Tense had | Past Perfect Tense had |
| Past Perfect Continuous had been | Past Perfect Tense had + V3 Past Perfect Continuous had been + V4 |
| Future Simple Tense will | would |
| Future Continuous Tense will be | would be |
| Future Perfect Tense will have | would have |
| Future Perfect Continuous will have been | would have been |
Rule 2:
| Reported Verb | Reported Speech |
| Subject | First person (I, we) Changes according to the subject of the reported verb |
| Object | Second person (you) Changes according to the object of the reported verb |
| No Change | Third person (he, she, it, they) No change |
Also Remember : The tense of the reported speech remains the same if the reported speech expresses a universal truth/a habitual fact. Example:
Direct : The professor said, “The planets revolve around the sun”
Indirect : The professor said that the planets revolve around the run.
Changing certain words in Direct-Indirect Speech
| Direct Speech Word | Indirect Speech Word |
| Here | There |
| Today | that day |
| this morning | that morning |
| Yesterday | the day before |
| Tomorrow | the next day |
| next week | the following week |
| next month | the following month |
| Now | Then |
| Ago | Before |
| Thus | So |
| Last Night | the night before |
| This | That |
| These | Those |
| Hither | Thither |
| Hence | Thence |
| Come | Go |
Types of sentences
Declarative: Makes a statement/Expresses an opinion (declaration). These sentences end with a full stop or period. Example: “He is a good person.”
Interrogative: Asks a question. These often begin with a what, who, which, how, etc., and end with a question mark. Example: “How is the weather?”
- When changing an interrogative sentence into indirect speech, change the reporting verb into words like, asked, inquired, wondered, wanted to know, interrogated, etc.
- The interrogative should be removed and the interrogative form is changed to assertive form, i.e., the question mark is removed and replaced with a full stop.
- If the question begins with words like whose, what, who, which, when etc. no conjunction is used.
Example:
Direct : He said to me, “Is there something I can help you with?”
Indirect : He asked me if there was something he could help me with.
Imperative: These sentences make a request/give a command and end either with a full stop or an exclamation mark. Example: “Please enter the room.”
- Reporting verb is changed into a verb indicating a request, an order, forbidding, suggestion, proposal, etc.
- The command in the indirect speech can be expressed through words like charge, tell, order, etc. whereas the requests can be expressed using beg, ask, beseech, implore, etc.
- The conjunction ‘to’ is used, followed by the verb.
- Words like persuade, incite, forbid, can be used according to the context of the speech.
- The verb in reported speech is changed into an infinitive. The word “not” is placed before the infinitive if the reported speech is negative.
Examples:
She said to me, “Help me pick this up”
She requested me to help her pick that up.
The doctor said to the patient, “Stay hydrated”
The doctor advised the patient to stay hydrated.
The teacher said to her students, “All of you should participate in cultural events”
The teacher urged all her students to participate in cultural events.
Note: Some imperative sentences have the word “let” in it. For such sentences use suggested/proposed. Example:
He said to us, “Let’s go to Goa”
He suggested us that we should to go Goa.
“Let us host a party”, said my friend.
My friend proposed that we should host a party.
Exclamatory: Expresses an emotion; joy, sorrow, excitement, etc. and ends with an exclamatory mark. Example: “What a beautiful cake!”
- Reporting verb is changed to exclaim with happiness/sorrow/fear/anger/etc.
- The “that” conjunction is used to introduce the reported speech.
- Sentence is changed into an assertive one.
- Exclamations & interjections are removed, as they’re conveyed by adverbs or adverbial phrases.
Example:
“What a rude person!”, exclaimed my friend.
My friend exclaimed that that person was rude.
“How charming is this!”, said he.
He joyfully exclaimed that it was charming.
How do Modals change while converting from direct to indirect Speech?
- Modals in present tense are changed into past tense.
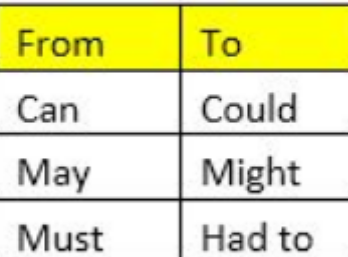
Example:
She said, “I can climb that tree”
She said that she could climb that tree.
He said, “I may take up the summer internship”
He said that he might take up the summer internship.
Manu said, “I must take her autograph”
Manu said that he had to take her autograph.
Indirect speech for sentence having MODALS should, ought to, might, would and could
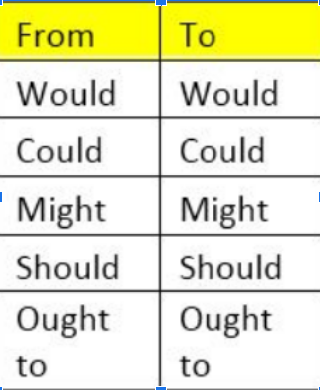
Example:
Ramesh said, “We would take the other road”
Ramesh said that they would take the other road.
Ajay said, “He could dance”
Ajay said that he could dance.
Mr Miller said, “His family might come”
Mr Miller said that his family might come.
Raj said, “I should buy a car”
Raj said that he should buy a car.
She said to me, “You ought to dance for us”
She said to me that I ought to dance for them.
Direct and Indirect Speech Practice Questions:
Q1. The officer said to the clerk, “File these papers immediately”
- The officer said to the clerk to file these papers immediately.
- The officer ordered to the clerk to file those papers immediately.
- The officer ordered the clerk to file those papers immediately.
- None.
Q2. He said to Sheela, “you have committed a mistake here.??
- He told Sheela that she committed a mistake here.
- He told Sheela that she had committed a mistake there.
- He told Sheela that she would commit a mistake there.
- None.
Q3. The designer said to her, ‘will you have the dress ready by tomorrow evening?’
- The designer asked her if she would have the dress ready by next evening.
- The designer asked her that she would have the dress ready by next evening.
- The designer asked her that if she will like to have the dress by next evening.
- The designer asked her that she will have the suit ready by next evening.
Q4. Vamsi said, “We are playing a match today.??
- Vamsi said that they were playing a match today.
- Vamsi said that they are playing a match today.
- Vamsi said that they have been playing a match that day.
- Vamsi said that they were playing a match that day.
Q5. The driver said to the passerby, “Do you know the way to the market
- The driver asked the passerby did he know the way to the market.
- The driver asked the passerby if he knows the way to the market.
- The driver asked the passerby whether you know the way to the market.
- The driver asked the passerby if he knew the way to the market.
Q6. Amit said to me, “Your parents are waiting for you.”
- Amit told me that your parents are waiting for you.
- Amit told me that his parents were waiting for me.
- Amit asked me if my parents were waiting for me.
- Amit told me that my parents were waiting for me.
Q7. He said, “Children go to school every day’
- He said children go to school every day.
- He said that children go to school every day.
- He said that children go to school that day.
- None.
Q8. The teacher said, “Are you preparing well for the exams?”
- The teacher said that they are preparing well for the exams.
- The teacher asked if I am preparing well for the exams.
- The teacher asked if I was preparing well for the exams.
- The teachers asked whether I have been preparing well for the exams.
Q9. She asked the child, “Have you taken your meal?”
- She asked the child if he/she had taken his/her meal.
- She asked the child if he/she has taken his/her meal.
- She asked the child if he/she will take his/her meal.
- She asked the child if he/she would take his/her meal.
Q10. She said to the boy, “Where did you learn classical music?”
- She asked the boy where he learnt classical music.
- She asked the boy where he learns classical music.
- She asked the boy where he would learn classical music.
- She asked the boy where he had learnt classical music.
Q.11 I said to Pramod, “How did you break your leg?”
(a) I asked Pramod how he had broken your leg.
(b) I asked Pramod how did you break your leg.
(c) I asked Pramod how he had broken his leg.
(d) I asked Pramod how you broke your leg.
Q.12 The driver said to the passerby, “Do you know the way to the market
(a) The driver asked the passerby did he know the way to the market.
(b) The driver asked the passerby if he knows the way to the market.
(c) The driver asked the passerby whether you know the way to the market.
(d) The driver asked the passerby if he knew the way to the market.
Q.13 Anshul told me that his mother was not at home and that she would be back the following day.
(a) Anshul said to me, “My mother is not at home. She will be back tomorrow.”
(b) Anshul said to me, “My mother was not at home. She will be back the following day.”
(c) Anshul said to me, “My mother is not at home. She would be back the following day.”
(d) Anshul said to me, “His mother was not at home. She would be back tomorrow.”
Q.14 Rani said to me, “A monkey bit me in the park.”
(a) Rani told me that a monkey has bitten her in the park.
(b) Rani told me that a monkey had bitten her in the park.
(c) Rani told me that a monkey bit me in the park.
(d) Rani asked me if a monkey bit me in the park.
Q.15 Amit said to me, “Your parents are waiting for you.”
(a) Amit told me that your parents are waiting for you.
(b) Amit told me that his parents were waiting for me.
(c) Amit asked me if my parents were waiting for me.
(d) Amit told me that my parents were waiting for me.
Read More:
45 Most important Direct Indirect Speech Questions Notes: Free PDF Download for IBPS Exams
Direct and Indirect Speech FAQs
You can practice the Direct and Indirect speech questions in this blog.
Direct Speech : When we want to describe what someone said to us, we commonly use direct speech. We simply repeat what someone said, putting the phrase between speech marks.
Indirect Speech : When we want to tell about what someone said without speech marks and without necessarily using exactly the same words.
Here is one example.
Direct Speech : He said, “I have eaten a mango.”
Indirect Speech : He said that he had eaten a mango.

The most comprehensive online preparation portal for MBA, Banking and Government exams. Explore a range of mock tests and study material at www.oliveboard.in
