The Lok Sabha has signed off the Finance Bill – 2017 and in this post we bring to you, highlights of the bill along with its repercussions on the economy.
The bill introduces small but significant reform initiatives directed at improving the ease of doing business and boosting anti-corruption initiatives in the economy. The following picture summarizes the main aims of the bill.

The main impacts and the key issues at stake vis-a-vis the Finance Bill – 2017, are as follows:-
1. AADHAR is mandatory for filing income tax returns and PAN
In addition to being linked to a number of public services and subsidies, as per Finance Bill, 2017, it will now be compulsory to have an Aadhaar (from July 1, 2017) in order to file income tax returns and to obtain and retain PAN, or permanent account number.
The main aim is to put curbs on instances of issuing multiple PAN to a single individual. Further, quoting of Aadhaar number would restrict granting of subsidies to only those individuals who are eligible to claim it.
2. Political funding and electoral bonds
There is also an amendment to how companies make donations to political parties. Currently, a company may contribute up to 7.5% of the average of its net profits in the last three financial years, to political parties. The company is required to disclose the amount of contributions made to political parties in its profit and loss account, along with the name of the political parties to which such contribution was made.
The amendments to the Finance Bill, 2017 propose to remove: (i) the limit of 7.5% of net profit of the last three financial years, for contributions that a company may make to political parties, (ii) the requirement of a company to disclose the name of the political parties to which a contribution has been made.
In addition, contributions to political parties will have to be made only through a cheque, bank draft, electronic means, or any other scheme notified by the government to make contributions to political parties. Note that Finance Bill, 2017 contains provisions to introduce electoral bonds to make contributions to political parties. Electoral bonds will be bonds issued by notified banks, for an amount paid through cheque or electronic means.
3. Curbs on cash transactions
In order to reduce generation and circulation of domestic black money the Finance Bill, 2017 had imposed a prohibition on receipt of cash payments of Rs. 3 lakhs and above. The Finance Bill, 2017 originally presented on February 1, 2017 has proposed to amend the threshold limit of cash payments from Rs. 3 lakhs to 2 lakhs.
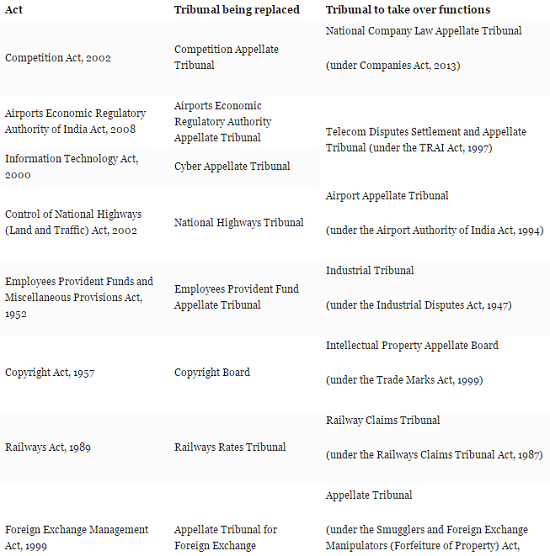
4. Tribunals and appellate tribunals
Certain tribunals are proposed to be replaced, and their functions are proposed to be taken over by existing tribunals under other Acts.
Hope this gives you all the information you need.
All the best!

The most comprehensive online preparation portal for MBA, Banking and Government exams. Explore a range of mock tests and study material at www.oliveboard.in
