Mission Shakti is India’s first successful Anti-Satellite (ASAT) missile test conducted on 27th March 2019. The test was carried out by the Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) from the Dr. APJ Abdul Kalam Island in Odisha.
Why was Mission Shakti ASAT Conducted?
The main objective of Mission Shakti was to demonstrate India’s indigenous capability to destroy satellites in Low Earth Orbit (LEO). This achievement made India the fourth country in the world, after the USA, Russia, and China, to develop and successfully demonstrate such advanced space defence technology.
The test utilized a kinetic-kill approach, where a missile from India’s Ballistic Missile Defence (BMD) program physically intercepted and destroyed a target satellite. The target satellite, Microsat-R, was specifically launched into LEO at an altitude of approximately 283–300 km for this purpose.
What are Anti-Satellite (ASAT) Weapons?
Anti-satellite (ASAT) weapons are designed to destroy, disable, or interfere with satellites in orbit. These weapons are primarily used for defence and strategic purposes, especially to protect national security interests.
Types of ASAT Weapons
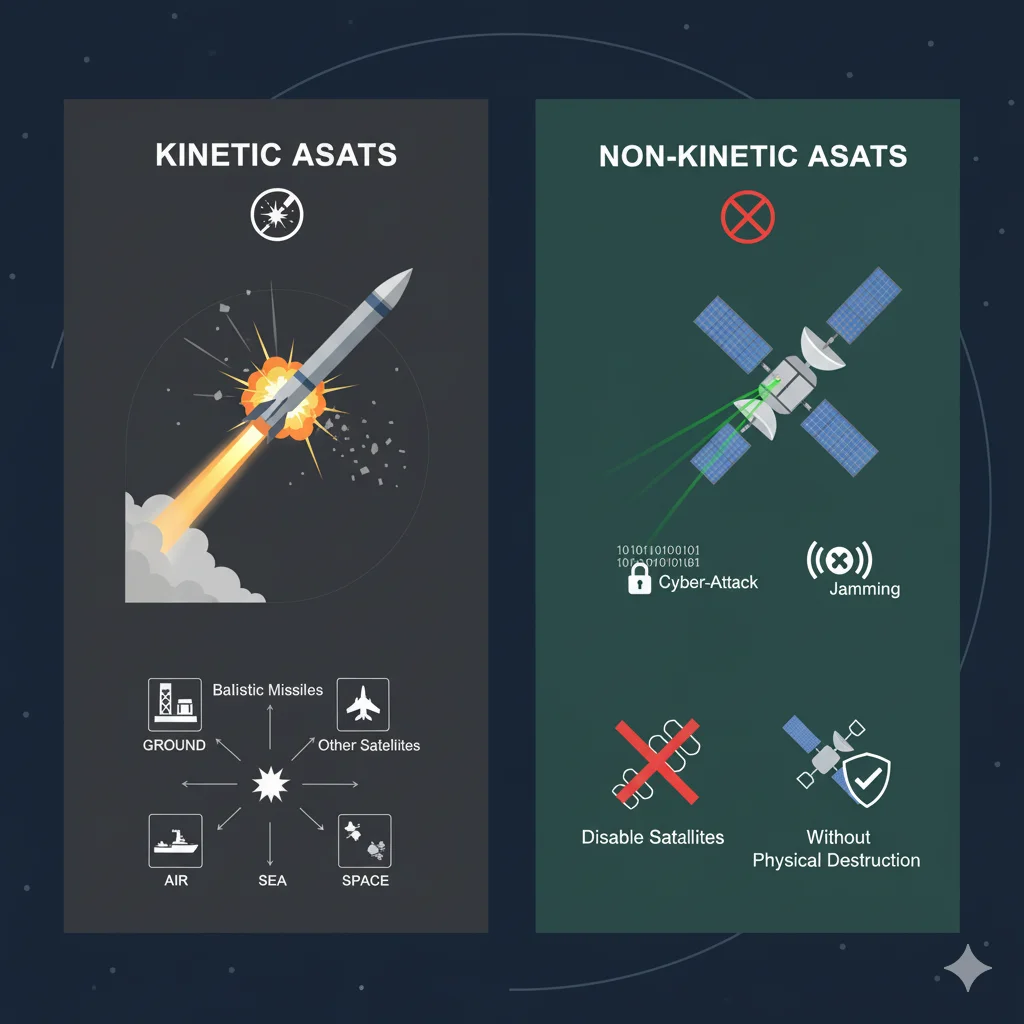
ASAT weapons are broadly classified into two types:
- Kinetic Energy ASATs
- Physically collide with satellites to destroy them.
- Can be launched from ground, air, sea, or space.
- Examples include ballistic missiles, drones, and other satellites.
- Non-Kinetic ASATs
- Use non-physical attacks such as cyber-attacks, jamming, or lasers.
- Disable satellites without physically destroying them.
The Mission Shakti test used the kinetic energy method, where the missile destroyed the target satellite through direct impact.
How did Mission Shakti Work?
The ASAT missile used in Mission Shakti was the Prithvi Delivery Vehicle Mark-II (PDV MK-II). The missile was interceptor-based, designed to collide with a moving satellite in low Earth orbit.
Key features of the test:
- Target satellite: Microsat-R, defunct and launched specifically for the test.
- Altitude of target: ~283–300 km above Earth.
- Impact method: Kinetic energy, destroying the satellite without explosives.
- Outcome: The satellite was neutralized with high precision, showcasing India’s technical and strategic prowess.
Why was ASAT Capability Important for India?
India’s ASAT capability plays a strategic and deterrent role. Some key reasons include:
| Purpose | Details |
| Protecting Critical Infrastructure | – Satellites support navigation, communication, banking, broadcasting, disaster management, and military operations. – An adversary targeting these satellites could cripple national infrastructure. |
| National Security and Strategic Deterrence | – ASAT weapons act as a deterrent against hostile nations and non-state actors. – Knowing India can neutralize satellites discourages attacks on its space assets. |
| Technological Advancement | – Demonstrates India’s growing expertise in missile and space technology. – Enables India to strengthen its Ballistic Missile Defence (BMD) program. |
| Military Applications | – Can interfere with enemy satellites, blind navigation systems, and neutralize potential missile threats. |
How does Mission Shakti Boost India’s Strategic Position?
Mission Shakti positioned India as a credible space power with advanced ASAT capabilities, offering multiple strategic advantages:
- Global Recognition:
- India became the fourth nation to demonstrate ASAT capability.
- Deterrence Against Adversaries:
- Potentially deters threats from countries like China and Pakistan.
- Validation of Defence Technologies:
- The success of Mission Shakti tested and validated India’s BMD technologies, contributing to broader national defence capabilities.
- Space Security:
- Strengthens India’s ability to protect vital space assets, the emerging fourth dimension of warfare.
Get ready to crack government job exams with leading educators
What are the Challenges of ASAT Weapons?
While ASAT capabilities provide strategic benefits, they also present technical, ethical, and operational challenges:
| Concern | Details |
| Space Debris | Kinetic ASAT tests create debris that can threaten satellites; Mission Shakti produced ~45 fragments that decayed within a week; high debris density may cause Kessler Syndrome. |
| Third-Party Satellites | Targeted satellites may not fully disable communications as nations can rely on allied satellites. |
| Weaponization of Space | Could trigger an arms race in space and militarization of outer space. |
| International Laws | India complied with the Outer Space Treaty 1967; kinetic ASAT tests do not involve explosives or WMDs, so no violation. |
How does Mission Shakti Align with India’s Ballistic Missile Defence (BMD) Program?
India’s BMD program, initiated after the Kargil War in 1999, aims to protect against ballistic missile attacks, especially nuclear threats. The Mission Shakti complements BMD by:
- Testing interceptor missile technologies in real-time conditions.
- Demonstrating the ability to neutralize high-speed objects in space.
- Providing a defensive and offensive capability in space warfare scenarios.
The success of Mission Shakti reflects India’s technical maturity in integrating missile defence and space technologies.
What are the Geopolitical Implications of Mission Shakti?
Mission Shakti has significant implications in regional and global geopolitics:
- Deterrence Against China and Pakistan
- Demonstrates India’s counter-space capability, balancing China’s growing space power.
- Signals Pakistan that any missile threat could be neutralized, enhancing strategic stability.
- Influence in Space Governance
- Strengthens India’s position in future space treaties and negotiations.
- Global Space Race
- India’s entry into ASAT technology may encourage other nations to pursue anti-satellite capabilities.
- Collaborative Ventures
- Opens avenues for collaboration with countries like USA, France, and Japan in peaceful space exploration and technology sharing.
How does Mission Shakti Impact Space Security?
Mission Shakti has a direct impact on space security and sustainability:
- Space Debris Management
- Although the test created debris, it was conducted at low altitude to ensure rapid decay.
- Debris management remains a key concern in future ASAT tests.
- Kessler Syndrome Risk
- Collision of debris could trigger a chain reaction, threatening satellites in LEO.
- Peaceful Space Use
- India emphasizes peaceful use of outer space, even while demonstrating ASAT capability.
What are the Alternatives to Kinetic ASAT Weapons?
While kinetic ASATs are effective, alternative methods can achieve satellite neutralization without debris:
- Jamming: Disrupts satellite signals temporarily.
- Cyber Attacks: Hacks or disables satellite systems.
- Directed Energy Weapons: Uses lasers or microwave beams to blind or disable satellites.
Key Takeaways
| Aspect | Key Points |
| Mission Name | Mission Shakti |
| Conducted by | DRDO, with support from ISRO |
| Date & Location | 27th March 2019; Dr. APJ Abdul Kalam Island, Odisha |
| Target | Microsat-R satellite in Low Earth Orbit (~283–300 km) |
| Method | Kinetic-kill ASAT missile (PDV MK-II) |
| Outcome | Successful neutralization of the satellite |
| Significance | India became the 4th country with ASAT capability; strengthened strategic deterrence |
| Strategic Benefit | Protection of satellites, national security, missile defense validation |
| Challenges | Space debris, Kessler Syndrome, weaponization of space |
| Global Impact | Geopolitical recognition, deterrence against adversaries, influence in space treaties |
Questions Based on Mission Shakti ASAT
- When was Mission Shakti conducted?
a) March 15, 2018
b) March 27, 2019
c) April 5, 2019
d) March 27, 2018
e) April 1, 2019 - Which Indian organization led Mission Shakti?
a) ISRO
b) DRDO
c) HAL
d) BEL
e) BARC - What was the target of Mission Shakti?
a) GPS Satellite
b) Microsat-R
c) INSAT-3B
d) RISAT-2
e) Chandrayaan-2 - Which method was used to destroy the satellite?
a) Laser attack
b) Kinetic-kill missile
c) Cyber attack
d) Explosive blast
e) Satellite collision - Which countries have demonstrated ASAT capability?
a) USA, Russia, China, India
b) USA, Russia, France, India
c) USA, China, Japan, India
d) Russia, China, Pakistan, India
e) USA, UK, Russia, India - What is the primary purpose of ASAT weapons?
a) Commercial satellite management
b) Space exploration
c) National security and deterrence
d) Weather forecasting
e) Disaster management - Which missile was used in Mission Shakti?
a) Agni-V
b) Prithvi PDV MK-II
c) BrahMos
d) Akash
e) Nirbhay - What is Kessler Syndrome?
a) A satellite propulsion system
b) Chain reaction of space debris collisions
c) A type of ASAT missile
d) Space treaty regulation
e) A satellite tracking system - Which international treaty governs peaceful use of outer space?
a) Geneva Convention
b) Outer Space Treaty 1967
c) Paris Agreement
d) Missile Technology Control Regime
e) Hague Convention - How does Mission Shakti enhance India’s strategic position?
a) Allows launching satellites faster
b) Strengthens deterrence and protects space assets
c) Reduces need for BMD program
d) Only improves commercial space industry
e) Helps in global climate monitoring
Also Read:
Answer Key:
| Question Number | Correct Answer |
| 1 | b) March 27, 2019 |
| 2 | b) DRDO |
| 3 | b) Microsat-R |
| 4 | b) Kinetic-kill missile |
| 5 | a) USA, Russia, China, India |
| 6 | c) National security and deterrence |
| 7 | b) Prithvi PDV MK-II |
| 8 | b) Chain reaction of space debris collisions |
| 9 | b) Outer Space Treaty 1967 |
| 10 | b) Strengthens deterrence and protects space assets |
- How Some Aspirants Clear Multiple Government Exams: Strategy, Discipline & Exam Psychology
- Crop Diversification Program, Transforming Indian Agriculture
- Government Schemes for NABARD Grade A 2026
- National Dairy Plan Phase 1 and Phase 2, Boosting India’s Dairy Sector
- Mera Gaon Mera Gaurav Scheme, Bridging Lab to Land
- Farmers First Initiative, Empowering Farmers Through Innovation

Hi, I’m Aditi. I work as a Content Writer at Oliveboard, where I have been simplifying exam-related content for the past 4 years. I create clear and easy-to-understand guides for JAIIB, CAIIB, and UGC exams. My work includes breaking down notifications, admit cards, and exam updates, as well as preparing study plans and subject-wise strategies.
My goal is to support working professionals in managing their exam preparation alongside a full-time job and to help them achieve career growth.