Animal husbandry and dairy development form the backbone of rural livelihoods in India. For NABARD Grade A aspirants, these topics are critical as they connect directly to rural development, income generation, and policy implementation. This article provides a detailed understanding of key concepts, trends, and schemes in animal husbandry and dairy development.
Importance of Animal Husbandry in India
India has the largest livestock population in the world, with over 535 million animals as per the latest DAHD estimates. This sector contributes to multiple areas:
- Nutrition: Provides milk, meat, and eggs, helping combat malnutrition.
- Income Generation: Livestock farming supports more than 70% of rural households, particularly small and marginal farmers.
- Employment: Offers secondary and primary employment to nearly 8 crore people.
- Agricultural Productivity: Draught animals support ploughing and transport in rural areas, reducing dependence on mechanization.
Animal husbandry contributes about 25.6% of agricultural GDP, highlighting its economic significance. NABARD’s rural credit policies often focus on livestock financing, dairy cooperative support, and animal health interventions, making it crucial for exam preparation.
Dairy Development in India
India is the world’s largest milk producer, producing over 230 million tonnes annually. The growth of the dairy sector has been driven by:
- White Revolution: Launched in the 1970s to increase milk production via cooperative dairy networks.
- Operation Flood: Helped India achieve self-sufficiency and reduced dependence on imports.
- Technological Advancements: Artificial insemination, scientific breeding, and better feeding practices.
Per capita milk availability has increased from 176 grams/day in 1990 to over 440 grams/day in 2024, improving nutrition for millions. Milk production trends show steady growth, reflecting the effectiveness of government schemes and private-sector participation.
Key Government Schemes
To strengthen animal husbandry and dairy development, several schemes have been launched:
- National Dairy Plan (NDP):
- Objective: Increase milk production and productivity using genetic improvement and better feed.
- Focus Areas: Breeding of high-yielding cows, improved animal nutrition, capacity-building for farmers.
- Dairy Entrepreneurship Development Scheme (DEDS):
- Provides financial assistance up to Rs. 25 lakh for new dairy farms, encouraging private entrepreneurship.
- Promotes establishment of milk processing units and value addition.
- Rashtriya Gokul Mission:
- Focuses on conserving indigenous cattle breeds.
- Promotes better utilization of local breeds to enhance milk quality and farmer income.
- National Programme for Dairy Development (NPDD):
- Aims to enhance milk procurement infrastructure, cold chain management, and marketing.
- Supports cooperative societies and private players to ensure fair milk pricing.
Key Facts and Data
To understand the significance of animal husbandry and dairy development, it is important to look at the latest trends, production statistics, and rural livelihood impact in India.
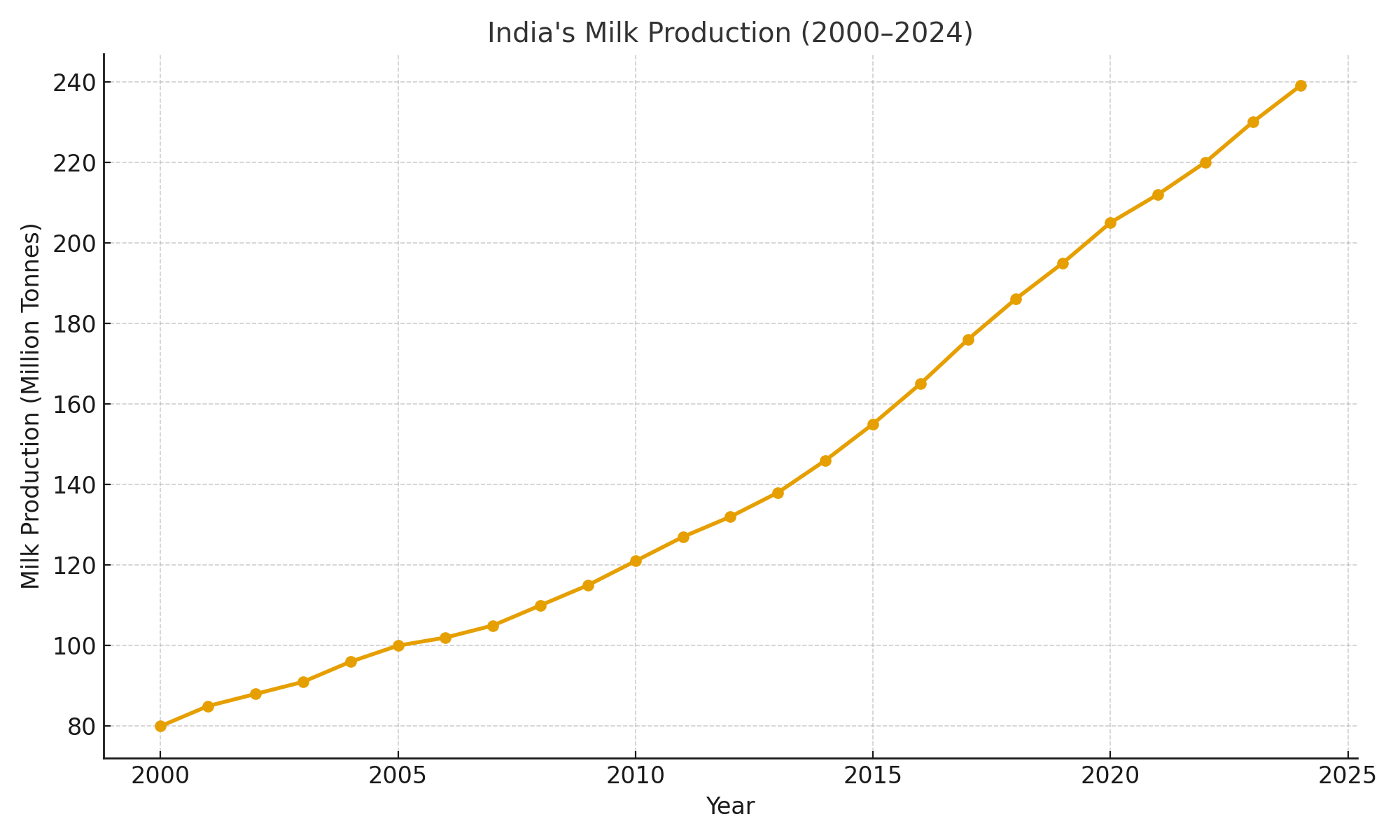
- Milk production increased from 80 million tonnes in 2000 to over 230 million tonnes in 2024.
- India contributes more than 24% of global milk production, ahead of countries like the USA and China.
- The sector employs millions of rural women, who are primary contributors in household dairy activities.
- Smallholder farmers (owning 2–5 animals) account for over 70% of total milk production, highlighting the sector’s decentralized nature.
Challenges in Animal Husbandry and Dairy Development
Despite impressive growth, the livestock and dairy sector faces several challenges that affect productivity, farmer income, and sustainable development, which are crucial for NABARD aspirants to know.
- Low Productivity: Average milk yield per cow is lower compared to global standards.
- Feed and Fodder Shortage: Availability of quality feed is inconsistent in rural areas.
- Veterinary Services Gap: Insufficient access to vaccinations and health care.
- Climate Change Impact: Heat stress and changing rainfall patterns affect productivity.
- Market Access: Farmers often face challenges in selling milk at fair prices due to lack of proper cold chain and transportation.
Why This Topic is Important for NABARD
Understanding animal husbandry and dairy development helps aspirants in multiple ways:
- NABARD focuses on livelihood enhancement, rural credit schemes, and cooperative development, all linked to livestock.
- Questions in Phase 1 and Phase 2 exams often cover trends in milk production, livestock population, and government schemes.
- Analytical questions may require linking dairy development with rural income, women empowerment, or nutrition programs.
FAQs
Animal husbandry is crucial as India has the largest livestock population in the world, contributing to nutrition, income generation, employment, and agricultural productivity. It supports over 70% of rural households and contributes about 25.6% of agricultural GDP.
India is the world’s largest milk producer, producing over 230 million tonnes annually. Key drivers include the White Revolution, Operation Flood, technological advancements like artificial insemination and scientific breeding, and government support for cooperative and private dairy sectors.
Important schemes include:
National Dairy Plan (NDP): Focuses on increasing milk productivity through breeding and better feed.
Dairy Entrepreneurship Development Scheme (DEDS): Provides financial support to new dairy entrepreneurs.
Rashtriya Gokul Mission: Conserves indigenous cattle breeds and improves milk quality.
National Programme for Dairy Development (NPDD): Enhances milk procurement, processing, and marketing infrastructure.
Milk production rose from 80 million tonnes in 2000 to over 230 million tonnes in 2024.
India contributes more than 24% of global milk production.
The sector provides employment to millions of rural women.
Smallholder farmers owning 2–5 animals account for over 70% of total milk production.
Knowledge of animal husbandry and dairy development is essential as NABARD focuses on rural livelihoods, cooperative development, and credit schemes linked to livestock. Questions may cover milk production trends, livestock population, government schemes, and analytical links with rural income, women empowerment, and nutrition programs.
- SEBI IT Officer Syllabus 2026, Exam Pattern, Download PDF

- SEBI Law Officer Recruitment 2026, Download Notification PDF

- SEBI IT Officer Recruitment 2026 Notification, Download PDF

- SEBI Legal Officer Syllabus 2026 & Exam Pattern, Download PDF

- ESI & ARD Practice Questions for NABARD Grade A 2026

- RBI Grade B 2026 Practice Quiz, Download Free PDF

Priti Palit, is an accomplished edtech writer with 4+ years of experience in Regulatory Exams and other multiple government exams. With a passion for education and a keen eye for detail, she has contributed significantly to the field of online learning. Priti’s expertise and dedication continue to empower aspiring individuals in their pursuit of success in government examinations.
