In SSC CGL Tier 2 SSC JSO (Junior Statistical Officer – Paper II), Probability Theory is an important topic in Statistics & Probability. It helps to quantify uncertainty predicting how likely an event is to occur. Questions are mostly conceptual or formula-based, so a clear understanding is key.
1. What is Probability?
Definition
Probability measures the likelihood of occurrence of an event. It always lies between 0 and 1.
P(E)= Total number of possible outcomes/Number of favourable outcomes
| Event Type | Probability Value | Example |
| Certain Event | 1 | Getting a number ≤ 6 on a die |
| Impossible Event | 0 | Getting number 7 on a die |
| Likely Event | Between 0 and 1 | Getting an even number on a die |
Also check out Most Repeated Quantitative Aptitude Questions for SSC CGL Tier 2
2. Key Terms in Probability
Below are the key terms explained:
| Term | Meaning | Example |
| Experiment | Any activity that produces an outcome. | Tossing a coin |
| Sample Space (S) | Set of all possible outcomes. | For one coin → {H, T} |
| Event (E) | Subset of sample space. | Getting Head = {H} |
| Mutually Exclusive Events | Two events cannot occur together. | Getting Head and Tail in one toss |
| Exhaustive Events | All possible outcomes together. | {H, T} for a coin |
| Independent Events | Occurrence of one does not affect another. | Tossing two coins |
| Dependent Events | One event affects the probability of another. | Drawing cards without replacement |
Also check out Most Repeated Quantitative Aptitude Questions for SSC CGL Tier 2
3. Classical or Theoretical Probability

Check out Most Repeated Computer Awareness Questions for SSC CGL Tier 2
4. Complementary Events
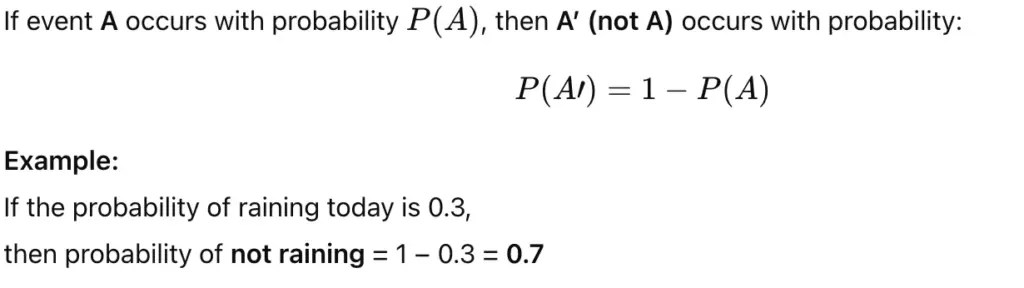
5. Conditional Probability
Definition

Multiplication Theorem of Probability

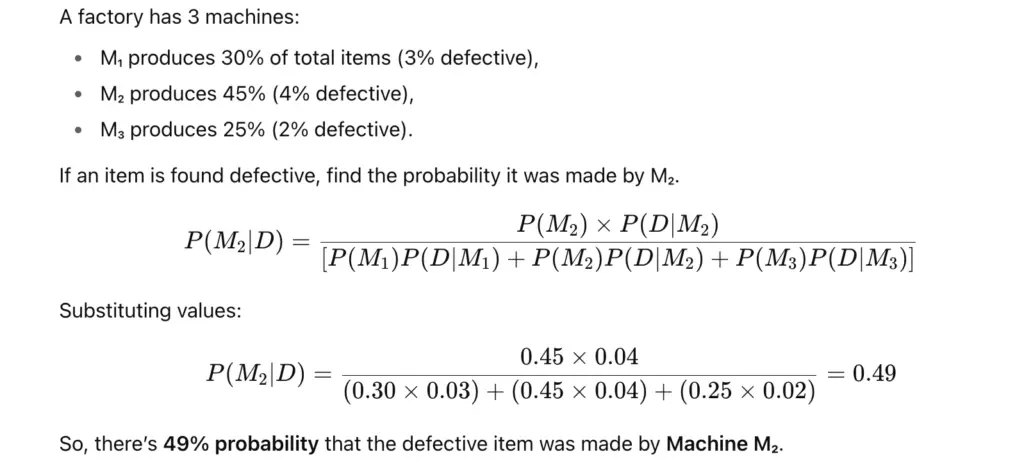
6. Bayes’ Theorem
Definition

Example of Bayes’ Theorem
7. Properties of Probability
Below are the properties of probability:
| Property | Formula / Explanation |
| Probability always lies between 0 and 1 | 0 ≤ P(E) ≤ 1 |
| Probability of entire sample space | P(S) = 1 |
| Probability of impossible event | P(Φ) = 0 |
| Addition Law | P(A ∪ B) = P(A) + P(B) − P(A ∩ B) |
| If A and B are mutually exclusive | P(A ∪ B) = P(A) + P(B) |
Check other SSC JSO related blogs:
Key Takeaways for SSC CGL Tier 2 (JSO)
Below are the key takeaways:
- Probability → measures likelihood of events.
- Conditional Probability → used when one event depends on another.
- Bayes’ Theorem → finds probability of a cause given an outcome.
- Always check whether events are independent or dependent before applying formulas.
- Common exam focus: conditional probability, Bayes’ theorem, addition & multiplication rules.
FAQs
Probability always lies between 0 and 1.
Conditional probability is the probability of an event occurring given that another event has already occurred.
It helps find the probability of a cause when the effect is known.
Independent events do not affect each other, while dependent events influence each other’s outcomes.
Conditional probability and Bayes’ theorem-based numerical questions are most frequently asked.
- SSC CGL पोस्ट प्रेफरेंस फॉर्म 2026, विंडो 9 मार्च से 12 मार्च तक खुली
- SSC CGL Post Preference Form 2026, Window Open from 9th to 12th March
- Important Questions on Fundamental Rights for Railway Exams, Download PDF
- Nitin’s SSC CGL Success Story and His Preparation Strategy
- SSC CGL Tier 2 Weightage of English and Quants, Check Here
- Most Repeated English Questions for SSC CGL Tier 2

I’m Mahima Khurana, a writer with a strong passion for creating meaningful, learner-focused content especially in the field of competitive exam preparation. From authoring books and developing thousands of practice questions to crafting articles and study material, I specialize in transforming complex exam-related topics into clear, engaging, and accessible content. I have first hand experience of 5+ months in SSC Exams. Writing, for me, is not just a skill but a way to support and guide aspirants through their preparation journey one well-written explanation at a time.
