Circle is one of the most important and frequently tested topics in geometry for competitive exams. In this blog, we have provided all the essential concepts, formulas, tricks, solved questions, and more.
What Is Circle in Quantitative Aptitude?
A circle is a set of all points in a plane that are equidistant from a fixed point called the center. The constant distance is called the radius.
Why it appears in exams:
- Fundamental geometric shape with numerous properties.
- Problems involve radius, diameter, chords, arcs, sectors, segments, and tangents.
Skills required:
- Understanding geometric properties and relations.
- Applying formulas related to circumference, area, arc length, and sector area.
- Visualization of 2D figures.
Why Is Circle Important in Competitive Exams?
Circle problems test candidates’ understanding of basic geometric concepts and their ability to apply formulas for perimeter, area, arcs, and sectors, making it a valuable scoring topic.
| Exam | No. of Questions | Difficulty |
| SSC CGL / CHSL | 1–3 | Moderate |
| IBPS PO / SBI PO | 1–2 | Moderate |
| RRB NTPC / Group D | 1–2 | Easy |
| State PSC / Police | 1–2 | Moderate |
Circle Quantitative Aptitude Short Notes
Terms mostly used to solve questions based on circles are as follows:
| Term | Details |
| Radius (r) | Distance from center to any point on the circle |
| Diameter (d) | Twice the radius, longest chord in the circle |
| Circumference | Perimeter of the circle, calculated as 2πr2 \pi r2πr |
| Area | Area covered by the circle, calculated as πr2\pi r^2πr2 |
| Chord | A line segment connecting two points on the circle |
| Arc | A part of the circumference |
| Sector | The area enclosed by two radii and an arc |
| Segment | The area enclosed by a chord and its corresponding arc |
| Tangent | A line that touches the circle at exactly one point |
Quick Circle Revision Summary
Here’s a handy summary of the most important formulas and facts about circles to aid quick memorization.

What Are the Types of Circle Questions in Quantitative Aptitude?
Circle problems can comes in various forms; knowing these types helps in quick recognition and solving.
- Basic perimeter and area problems
- Chord and segment length/area problems
- Sector and arc length questions
- Tangents and properties of tangents
- Coordinate geometry related problems
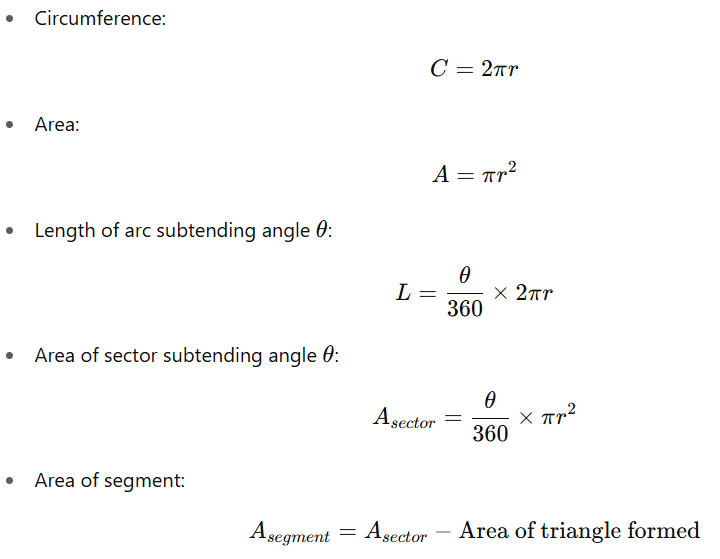
Circle Formulas for Quantitative Aptitude
This section provides the essential formulas that help you solve circle-related problems accurately and quickly.
Circle Tricks for SSC CGL and Other Exams
Follow these tricks to solve circle problems efficiently in competitive exams:
- Remember π≈22/7 or 3.14 for quick calculations.
- Use symmetry properties of circle to simplify problems.
- Visualize sectors and segments to avoid confusion between areas.
- In tangent problems, remember tangent is perpendicular to radius at point of contact.
- Practice applying formulas for arcs and sectors carefully by focusing on the angle subtended.
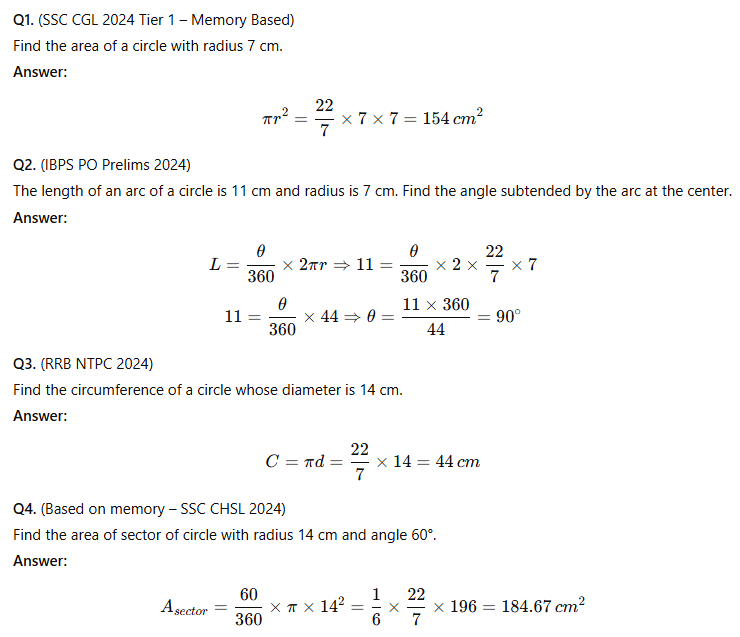
Solved Circle Questions from 2024–25 Exams
Common Mistakes to Avoid while Solving Circle Questions
Common mistakes that students must avoid while solving questions based on the topic of circles are as follows:
- Using wrong value of π\piπ inconsistently.
- Confusing chord length with arc length.
- Forgetting to convert degrees in arc/sector formulas.
- Mixing up sector and segment areas.
- Not applying tangent-radius perpendicularity in tangent problems.
FAQs
Arc is part of circumference, chord is a straight line between two points on circle.
Area enclosed by a chord and the corresponding arc.
Tangent is perpendicular to radius at point of contact.
No, maximum is 360°.
Radius bisects the chord if perpendicular.
- NABARD Development Assistant Exam Analysis 2026, Previous Year Trend
- Monthly Current Affairs 2026 PDF For SSC, Banking, Railways
- RBI Assistant Reasoning Preparation 2026: Complete Strategy
- RBI Assistant Quant Preparation 2026: Complete Strategy Guide
- How to Prepare English for RBI Assistant 2026? Complete Strategy
- Computer Fundamentals for NABARD DA Exam: Free Quiz and PDF

Hi, I’m Aditi. I work as a Content Writer at Oliveboard, where I have been simplifying exam-related content for the past 4 years. I create clear and easy-to-understand guides for JAIIB, CAIIB, and UGC exams. My work includes breaking down notifications, admit cards, and exam updates, as well as preparing study plans and subject-wise strategies.
My goal is to support working professionals in managing their exam preparation alongside a full-time job and to help them achieve career growth.