First Indian Patient Declared Cancer-Free
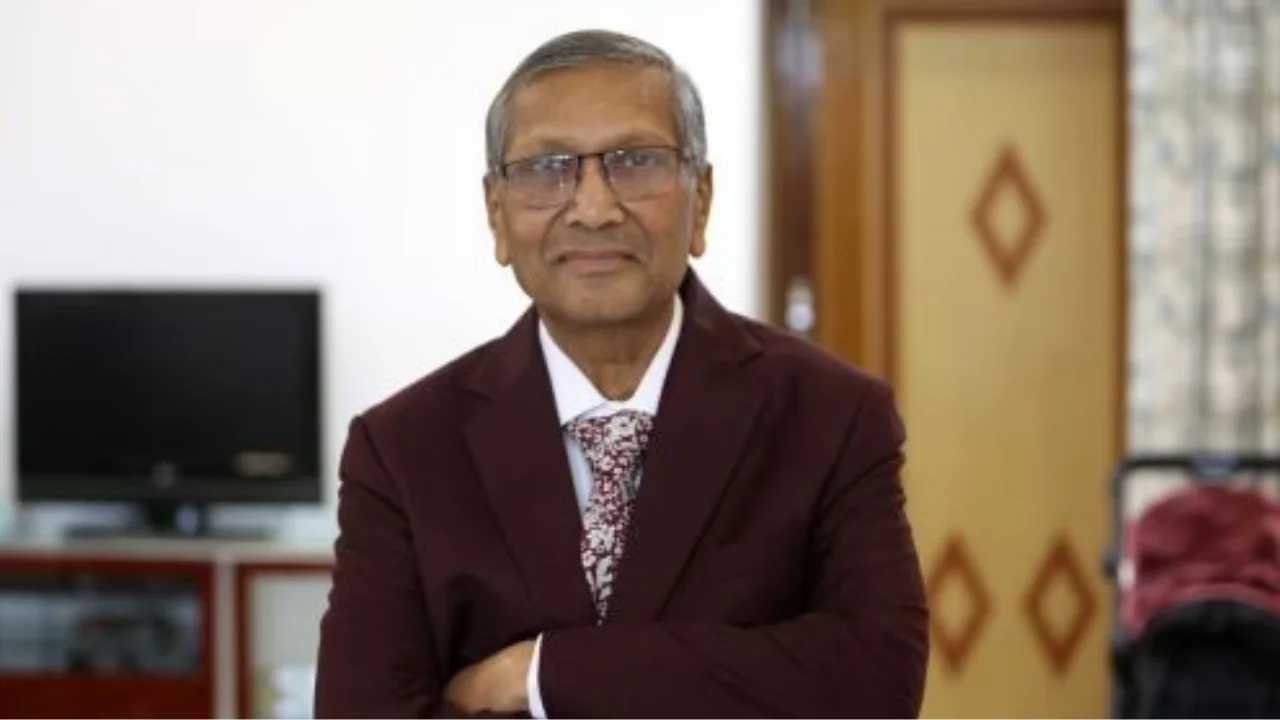
CAR-T cell therapy, approved by India’s drug regulator in November 2023, has proven to be a life-saving treatment for patients battling cancer. Dr. (Col) V K Gupta, a Delhi-based gastroenterologist and former Indian Army officer, became the first patient to be declared “currently free of cancer cells” after undergoing the procedure at Tata Memorial Hospital on February 7. The therapy involves genetically reprogramming a patient’s immune system to target and fight cancer cells. This success marks a significant milestone in the application of advanced medical treatments in India.
What is CAR-T Cell Therapy
CAR-T cell therapy is a revolutionary form of immunotherapy that harnesses the power of a patient’s own immune system to fight cancer. It involves genetically modifying a patient’s T cells (a type of white blood cell) to recognize and destroy specific cancer cells. Here’s how it works:
The Process
- Isolation: T cells are extracted from the patient’s blood through a process called apheresis.
- Modification: In a laboratory, the T cells are engineered to express a chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) on their surface. This CAR is designed to recognize a specific antigen (marker) present in the cancer cells.
- Expansion: The modified T cells, now called CAR-T cells, are multiplied in large numbers in the lab.
- Infusion: The expanded CAR-T cells are infused back into the patient’s bloodstream through an intravenous line.
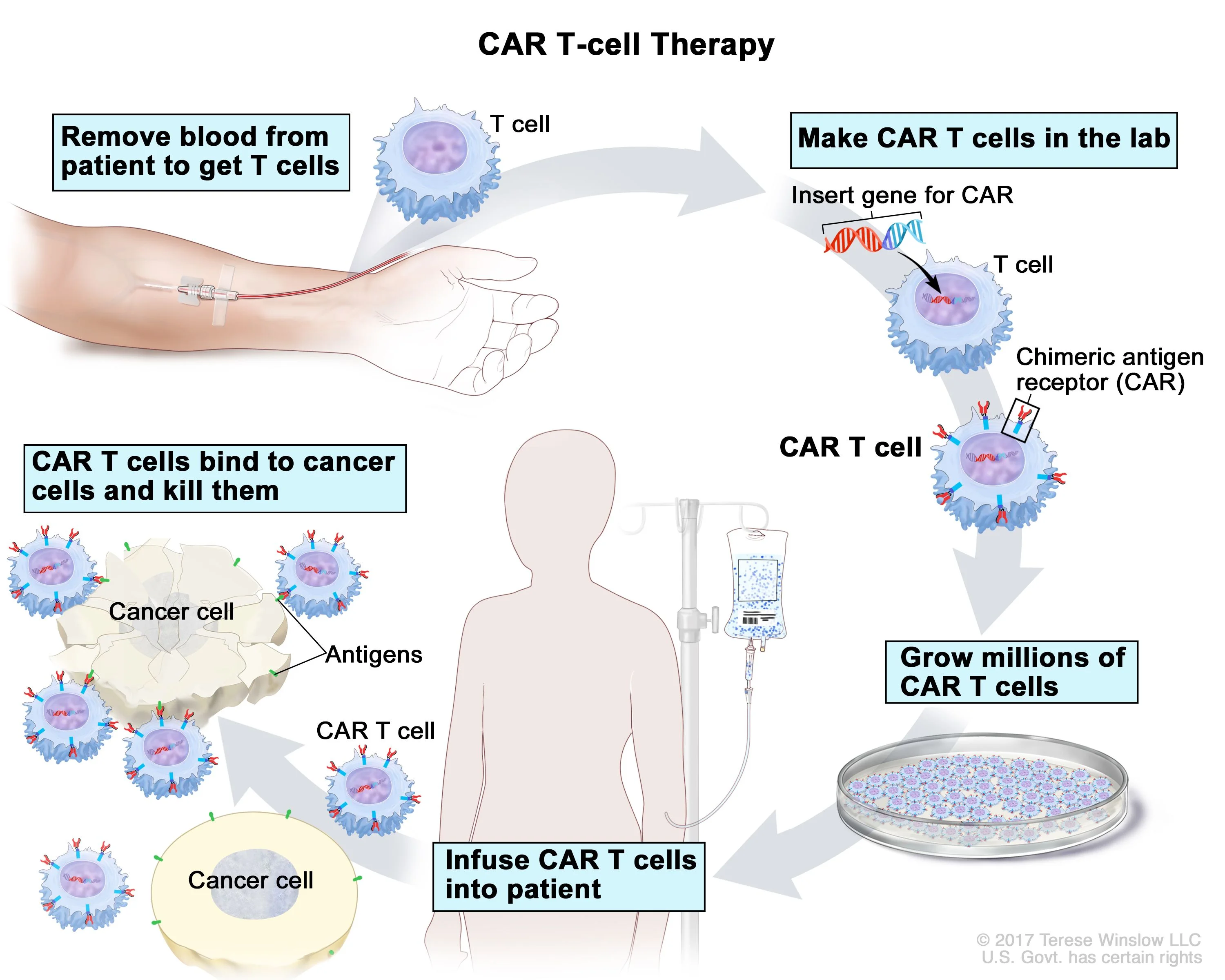
Destroying Cancer Cells
Once infused, the CAR-T cells circulate through the body and bind to the specific antigen on the cancer cells. This binding triggers a powerful immune response:
- Activation: The CAR-T cells become activated and release immune molecules that damage and kill the cancer cells.
- Proliferation: Activated CAR-T cells can multiply further within the body, creating an army of cancer-fighting cells.
- Memory: Some CAR-T cells develop memory, enabling them to recognize and attack the cancer cells if they reappear later.
Advantages of CAR-T Cell Therapy
- Targeted therapy: Unlike traditional chemotherapy or radiation, CAR-T cells specifically target cancer cells, minimizing harm to healthy tissues.
- Living drug: Unlike conventional drugs, CAR-T cells persist in the body, providing long-term protection against cancer relapse.
- Personalized approach: The therapy is tailored to each patient’s specific cancer, making it highly effective in certain cases.
Challenges and Limitations – Side Effects of CAR-T Cell Therapy
- Complex and expensive: The manufacturing process for CAR-T cells is complex and costly, limiting accessibility.
- Side effects: CAR-T cell therapy can cause severe side effects like cytokine release syndrome (CRS) and neurotoxicity, requiring careful monitoring and management.
- Not universally effective: The therapy is not yet effective for all types of cancer and may not be suitable for all patients.
Future of CAR-T Cell Therapy
Despite the challenges, CAR-T cell therapy represents a significant advancement in cancer treatment. Ongoing research is focused on improving its effectiveness, affordability, and accessibility, making it a potentially life-saving option for more patients in the future.
How effective is CAR-T Cell Therapy
The effectiveness of CAR-T cell therapy can vary depending on several factors, including:
Type of cancer: CAR-T cell therapies are currently approved for specific types of blood cancers, particularly acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) and lymphoma. The success rates are generally higher in pediatric ALL compared to other cancers.
Disease stage and patient profile: Patients with less advanced disease and better overall health tend to respond better to CAR-T therapy.
Specific CAR-T design: Different CAR-T cell designs and manufacturing processes can impact their effectiveness.
Overall, CAR-T cell therapy shows promising results for specific cancer types, with complete remission rates ranging from 30% to 80% in some cases. However, it’s important to remember that these therapies are still under development and come with potential risks and limitations.
How CAR-T Cell Therapy is different from other cancer treatments like chemotherapy and radiation
Here’s a breakdown of how CAR-T cell therapy differs from traditional cancer treatments like chemotherapy and radiation:
Target:
- CAR-T: Targets specific cancer cells by recognizing unique proteins on their surface.
- Chemotherapy: Targets rapidly dividing cells, impacting both cancer and healthy cells.
- Radiation: Uses high-energy beams to damage and kill cancer cells in a specific area.
Approach:
- CAR-T: Utilizes the patient’s own immune system to fight cancer.
- Chemotherapy & Radiation: Directly attack cancer cells through chemical agents or radiation beams.
Delivery:
- CAR-T: Requires complex laboratory process to modify T cells and then infuse them back into the patient.
- Chemotherapy & Radiation: Administered through injections, pills, or external beams.
Efficacy:
- CAR-T: Highly targeted and personalized, can lead to high remission rates for specific cancers.
- Chemotherapy & Radiation: Broad-spectrum therapy, is effective for various cancers but can cause widespread side effects.
Side effects:
- CAR-T: Can cause severe side effects like cytokine release syndrome and neurotoxicity, requiring careful monitoring and management.
- Chemotherapy & Radiation: Common side effects include fatigue, nausea, hair loss, and increased risk of infections.
Durability:
- CAR-T: Engineered T cells can persist in the body for months or even years, providing long-term protection.
- Chemotherapy & Radiation: Typically require repeated cycles, and their effects are temporary.
Accessibility:
- CAR-T: Complex and expensive manufacturing process limits widespread access.
- Chemotherapy & Radiation: More readily available but also comes with costs and limitations.
What is NexCAR19
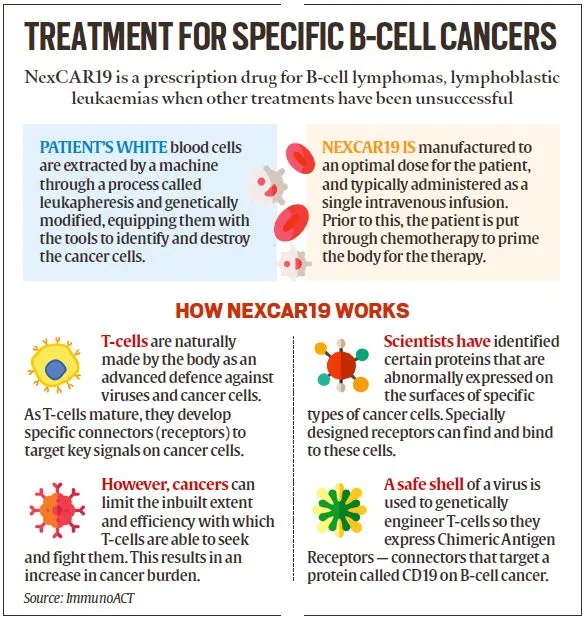
NexCar19, an indigenous CAR-T and gene therapy developed in India by ImmunoACT, represents a significant advancement in cancer treatment. Incubated at IIT Bombay, ImmunoACT’s therapy targets cancer cells with the CD19 protein, acting as a marker for the immune system to identify and eliminate them. This breakthrough positions India among the first developing countries with an indigenous CAR-T and gene therapy platform, showcasing the country’s growing capabilities in cutting-edge medical research and innovation.
Who can get the NexCAR19 Therapy?
The therapy targets individuals with B-cell lymphomas who haven’t responded to standard treatments like chemotherapy, resulting in cancer relapse or recurrence. B-cell lymphoma originates in lymphocytes, white blood cells responsible for producing antibodies to combat infections. These cells are commonly found in lymph nodes and other lymphoid tissues like the spleen.
Patients undergo a straightforward process: they provide a blood sample at their clinic and return 7-10 days later for reinfusion. The blood is genetically modified in the lab to enhance T-cells, which play a crucial role in the immune response. After one cycle of treatment, patients typically recover within two weeks. This streamlined approach offers hope for those facing treatment-resistant B-cell lymphomas, providing a promising avenue for cancer therapy.
Are children eligible for the therapy too?
ImmunoACT has received approval from the Central Drugs Standard Control Organisation (CDSCO) for the therapy’s use in patients aged 15 years and older. Currently, a pediatric trial phase is underway at the Tata Memorial Hospital, conducted in collaboration with IIT-Bombay. This initiative reflects the commitment to expanding the application of the therapy to younger patients, offering a potential breakthrough in the treatment of B-cell lymphomas in this age group.
CAR-T Cell Therapy in India
NexCAR19, developed by ImmunoACT, an incubated company at the Indian Institute of Technology Bombay (IITB) and Tata Memorial Hospital, targets B-cell cancers, including leukemia and lymphoma, by harnessing the body’s immune system.
Approved by the Central Drugs Standard Control Organisation (CDSCO) in October 2023, the therapy is now accessible in over 30 hospitals across more than 10 cities in India. Eligible patients, aged above 15, suffering from B-cell cancers, can avail themselves of this innovative treatment option.
CAR-T Cell Therapy Cost
The current cost of the treatment ranges from Rs 30-40 lakh, and the company aims to bring it down to Rs 10-20 lakh. As technology matures and manufacturing processes improve, there is an expectation that the cost of the therapy will decrease, making it more accessible for a broader range of patients. This commitment aligns to ensure the affordability and widespread availability of this innovative cancer treatment in India.
Dr. (Col) V K Gupta was able to access the CAR-T cell therapy in India at INR 42 lakh ($50,000), which is significantly lower compared to the cost of a similar therapy abroad, where it can go up to INR 4 crore ($480,000). This price difference highlights the potential economic benefits and affordability of the indigenous CAR-T cell therapy developed by ImmunoACT, making advanced cancer treatment more accessible to patients in India.
- Why is The SSC CGL Called a Mini IAS?
- Important Number System Questions for SSC Exams, Practice Here
- Trigonometry Questions For SSC CGL 2025, Solve Important Questions
- How to Prepare for SSC CGL with Full Time Job? Get Complete Guide
- 40 Geometry Formulas PDF – Download Here
- RRB ALP Mock Test 2025 Official Link , Know How to Solve

Hello, I’m Aditi, the creative mind behind the words at Oliveboard. As a content writer specializing in state-level exams, my mission is to unravel the complexities of exam information, ensuring aspiring candidates find clarity and confidence. Having walked the path of an aspirant myself, I bring a unique perspective to my work, crafting accessible content on Exam Notifications, Admit Cards, and Results.
At Oliveboard, I play a crucial role in empowering candidates throughout their exam journey. My dedication lies in making the seemingly daunting process not only understandable but also rewarding. Join me as I break down barriers in exam preparation, providing timely insights and valuable resources. Let’s navigate the path to success together, one well-informed step at a time.