NABARD Grade A Finance Notification
The NABARD Grade A Finance Notification has been released on the official website on 27th July 2024. Out of a total of vacancies, 7 vacancies are out for the Finance discipline. In this blog post, we intend to provide all the necessary information on NABARD Finance Notification, so read out the complete blog.
NABARD Grade A Finance Notification 2024
Applications are invited from Indian citizens for the post of Assistant Manager in Grade ‘A’ for the Finance discipline. The application process has started on the same day as the detailed notification of NABARD is out i.e on 27th July 2024. Download NABARD Grade A Finance Notification for the previous year below.

NABARD Grade A Finance Officer 2024 – Important Dates
The NABARD Grade A Notification 2024 is out for 17 disciplines. The schedule for the NABARD Grade A Finance officer exam is provided below :
| Events | Important Dates |
| NABARD Grade A Finance Officer Notification Release Date | 27th July 2024 |
| NABARD Grade Finance Officer Application Start Date | 27th July 2024 |
| NABARD Grade A Finance Officer Application End Date | 15th August 2024 |
| NABARD Grade A Finance Officer (RDBS) – Phase 1 Prelims Exam Date | 1st September 2024 |
| NABARD Grade A Finance Officer – Phase 2 (Mains) Exam Date | 19th October 2024 (Tentative) |
NABARD Grade A Finance Vacancies 2024
The vacancies for NABARD Grade ‘A’ AM (RDBS) – Finance are provided below.
| Category | 2024 Vacancies | Previous Year Vacancies |
| Unreserved | 3 | 3 |
| OBC | 1 | 5 |
| SC | 1 | 4 |
| ST | 1 | 1 |
| EWS | 1 | 2 |
| Total | 7 | 15 |
NABARD Grade A Finance Notification 2024 – Direct Link to Apply
The application window will remain open till 15th August 2024 and the candidates must apply for the post without waiting. This is because during the last days of application, due to some technical errors or high traffic, the server crashes down. Use the direct link given below to apply for NABARD Grade A Finance Officer.
Direct Link to Apply for NABARD Finance Officer
NABARD Grade A Finance Eligibility Criteria
The candidates will have to meet all the eligibility criteria as mentioned in the subsections.
NABARD Grade A Finance Eligibility – Age Limit
The candidate must be between 21 and 30 years of age which means that the candidate must have been born not earlier than 02-07-1994 and not later than 01-07-2003 as of 1st July 2024.
Upper Age Limit Relaxation
Check out the below table to know the age relaxation provided to different category candidates:
| Category | Age Relaxation |
| OBC | 3 years |
| 1. SC/ST 2. Ex-servicemen 3. Emergency Commissioned Officers/Short Service Commissioned Officers 4. Children/family members of victims died in the 1984 riots | 5 years |
| PWBD 1. General 2. OBC 3. SC/ST | 10 years 13 years 15 years |
NABARD Grade A Finance Eligibility – Educational Qualification
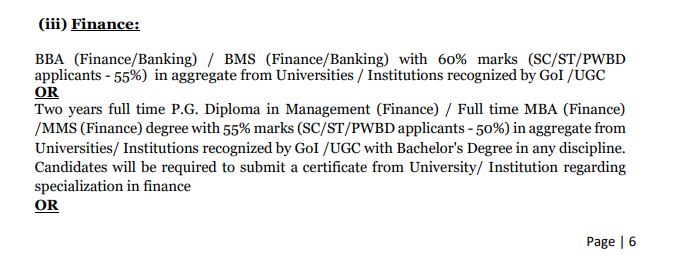
- BBA (Finance/Banking) / BMS (Finance/Banking) with 60% marks (SC/ST/PWBD applicants – 55%) in aggregate from Universities / Institutions recognized by GoI /UGC OR
- Two years full-time P.G. Diploma in Management (Finance) / Full-time MBA (Finance) /MMS (Finance) degree with 55% marks (SC/ST/PWBD applicants – 50%) in aggregate from Universities/ Institutions recognized by GoI /UGC with a Bachelor’s Degree in any discipline. Candidates will be required to submit a certificate from a University/ Institution regarding specialization in finance OR
- Bachelor of Financial and Investment Analysis with 60% marks (SC/ST/PWBD applicants -55%) in aggregate from University/ Institution recognized by GoI /UGC OR
- Bachelor’s degree in any discipline from a recognized University/Institution with Membership of the Institute of Chartered Accountants of India (ICAI) OR CFA Institute. OR
- Bachelor’s degree in any discipline from a recognized University/Institution with Membership of the Institute of Cost Accountants of India (ACMA/FCMA) & ICWA.
NABARD Grade A Finance Exam Pattern
The selection will be in three Phases as furnished below:
- Phase 1 (Preliminary Examination) – 200 Marks
- Phase 2 (Mains Examination) – 200 Marks
- Phase 3 (Interview) – 50 marks
NABARD Grade A Finance Prelims Exam Pattern 2024
The Prelims Exam Pattern of NABARD Grade ‘A’ Assistant Manager – Finance is given below :
| Name of the Test | No. of Questions | Max Marks |
| Test of Reasoning | 20 | 20 |
| English Language | 30 | 30 |
| Computer Knowledge | 20 | 20 |
| Quantitative Aptitude | 20 | 20 |
| Decision Making | 10 | 10 |
| General Awareness | 20 | 20 |
| Eco & Soc. Issues (with focus on Rural India) | 40 | 40 |
| Agriculture & Rural Development with an Emphasis on Rural India | 40 | 40 |
| Total | 200 | 200 |
Important Notes for the Phase 1 Exam (Prelims)
- Qualifying Section – Test of Reasoning, English Language, Computer Knowledge, Quantitative Aptitude, Decision Making.
- Merit Section – General Awareness, Eco & Soc. Issues (with focus on Rural India), Agriculture & Rural Development with Emphasis on Rural India.
- Shortlisting of the candidates for the Main exam will be based on marks scored in the Merit section only.
NABARD Grade A Finance Mains Exam Pattern 2024
The Mains exam pattern of NABARD Grade A Finance Officer (Assistant Manager Exam) is given below :
| Paper | Subject | Type of Paper | Number of Qs | Marks | Duration | Remarks |
| Paper- I | General English | Online Descriptive | 3 | 100 | 90 minutes | Descriptive Answers to be typed using keyboard |
| Paper-II | Finance | Objective | 30 | 50 | 30 minutes | – |
| Paper-II | Finance | Descriptive Type | 6 You will be required to attempt 4 questions [2 of 15 marks each] | 50 | 90 Minutes | Descriptive Answers to be typed using keyboard either in English or Hindi (Remington and Inscript keyboards) |
The calling ratio to qualify for the main examination and interview would be a maximum of
1:25 and 1:3, respectively.
Negative Marking
- There will be a penalty for wrong answers marked by the candidate.
- For every wrong answer marked, 1/4th of the marks assigned to that question will be deducted as a penalty in Phase-I and Phase-II.
- Cut-offs in Phase-I and Phase-II may be applied in two stages:
- On scores in individual tests
- On Total Score
NABARD Grade A Finance Syllabus
NABARD Grade A Phase 1 (prelims) examination and Phase 2 (mains) examination syllabus are given below:
NABARD Grade A Finance Prelims Syllabus 2024
Check out the detailed syllabus below:
| Name of Section | Topics asked |
| Reasoning Ability | 1. Puzzles & Seating arrangement 2. Syllogism 3. Data sufficiency 4. Statement-based questions (Verbal reasoning) 5. Inequality 6. Coding-Decoding 7. Input-Output 8. Blood relations 9. Miscellaneous Questions |
| Quantitative Aptitude | 1. Data Interpretation 2. Quadratic Equations 3. Number Series 4. Simplification/ Approximation 5. Data Sufficiency 6. Arithmetic Questions 7. Quantity Comparisons 8. Mathematical Inequalities |
| English Language | 1. Reading Comprehension 2. Sentence improvement 3. Cloze test 4. Spotting the errors 5. Fill in the blanks 6. Sentence rearrangement 7. Para Jumbles 8. New pattern questions |
| General Awareness | Majorly includes questions from current affairs – Banking, Finance, Insurance, Appointments, Awards and Honours, Sports, Schemes, and National and International Events. |
| Computer Knowledge | It various topics like Networking, Input-output devices, DBMS, MS Office, Internet, History of computers & generations, and Shortcuts. |
Economic and Social Issues
The ESI is one of the most important subjects to excel if you want to clear the NABARD Grade A Exam.
| Name of Section | Topics asked |
| Nature of Indian Economy | 1. Structural and Institutional features 2. Economic Underdevelopment 3. Opening up the Indian Economy 4. Globalization 5. Economic Reforms in India 6. Privatization |
| Inflation | Trends in Inflation & their Impact on National Economy and Individual Income. |
| Poverty Alleviation and Employment Generation in India | Rural and Urban Measurement of Poverty Poverty Alleviation Programmes of the Government |
| Population Trends | Population Growth and Economic Development Population Policy in India |
| Agriculture | 1. Characteristics / Status 2. Technical and Institutional changes in Indian 3. Agriculture 4. Agricultural performance 5. Issues in Food Security in India 6. Non-Institutional and Institutional Agencies in rural credit |
| Industry | 1. Industrial and Labour Policy 2. Industrial performance 3. Regional Imbalance in India’s Industrial Development 4. Public Sector Enterprises |
| Rural banking and financial institutions in India | Reforms in the Banking/ Financial sector. |
| Globalization of Economy | 1. Role of International Funding Institutions 2. IMF & World Bank 3. WTO 4. Regional Economic Cooperation |
| Social Structure in India | 1. Multiculturalism 2. Demographic trends 3. Urbanization and Migration 4. Gender Issues- Joint family system 5. Social Infrastructure 6. Education 7. Health and Environment |
| Education | 1. Status & System of Education 2. Socio-Economic Problems associated with Illiteracy 3. Educational relevance and educational wastage 4. Educational Policy for India |
| Social Justice | Problems with scheduled castes and scheduled tribes Socio-economic programmes for scheduled castes and scheduled tribes and other backward classes. |
| Positive Discrimination in favour of the underprivileged | 1. Social Movements 2. Indian Political Systems 3. Human Development |
Agriculture and Rural Development
This is the section of which the students are scared. But we have created ebooks for free to help you out with this section.
| Name of Section | Topics asked |
| Agriculture | 1. Definition, meaning, and its branches 2. Agronomy: Definition, meaning, and scope of agronomy 3. Classification of field crops 4. Factors affecting crop production 5. Agro Climatic Zones 6. Cropping Systems: Definition and types of cropping systems 7. Problems of dry land – Seed production, seed processing, seed village 8. Meteorology: weather parameters, crop-weather advisory 9. Precision Farming 10. System of Crop Intensification 11. Organic farming |
| Soil and Water Conservation | 1. Major soil types 2. Soil fertility 3. Fertilizers 4. Soil erosion 5. Soil conservation 6. Watershed management |
| Water Resource | 1. Irrigation Management 2. Types of irrigation 3. Sources of irrigation 4. Crop-water requirement 5. Command area development 6. Water conservation techniques 7. Micro-irrigation 8. Irrigation pumps 9. Major, medium, and minor irrigation. |
| Farm and Agri-Engineering | 1. Farm Machinery and Power 2. Sources of power on the farm- human, animal, mechanical, electrical, wind, solar, and biomass, biofuels 3. Water harvesting structures 4. Farm Ponds 5. Agro-Processing 6. Controlled and modified storage, of perishable food storage, godowns, bins, and grain silos |
| Plantation & Horticulture | 1. Definition, meaning, and its branches 2. Agronomic practices and production technology of various plantation and horticulture crops 3. Post-harvest management, value, and supply chain management of Plantation and Horticulture crops. |
| Animal Husbandry | 1. Farm animals and their role in the Indian economy 2. Animal husbandry methods in India 3. Common terms pertaining to different species of livestock 4. Utility classification of breeds of cattle Introduction to common feeds and fodders, their classification, and utility 5. Introduction to the poultry industry in India (past, present, and future status) 6. Common terms pertaining to poultry production and management 7. The concept of mixed farming and its relevance to the socio-economic conditions of farmers in India 8. Complimentary and obligatory nature of livestock and poultry production with that of agricultural farming. |
| Fisheries | 1. Fisheries resources Management and exploitation – freshwater, brackish water, and marine 2. Aquaculture- Inland and marine 3. Biotechnology Post-harvest technology 4. Importance of fisheries in India 5. Common terms pertaining to fish production. |
| Forestry | 1. Basic concepts of Forest and Forestry 2. Principles of silviculture, forest mensuration, forest management, and forest economics 3. Concepts of social forestry, agroforestry, joint forest management 4. Forest policy and legislation in India, India State of Forest Report 2015 5. Recent developments under the Ministry of Environment, Forest, and Climate Change |
| Agriculture Extensions | 1. Its importance and role, methods of evaluation of extension programs 2. Role of Krishi Vigyan Kendra (KVK) in the dissemination of Agricultural technologies |
| Ecology and Climate Change | 1. Ecology and its relevance to man, natural resources, sustainable management, and conservation 2. Causes of climate change, GreenHouse Gases (GHG), major GHG emitting countries, climate analysis 3. Distinguish between adaptation and mitigation 4. Climate change impact on agriculture and rural livelihoods 5. Carbon credit, IPCC, UNFCCC, CoP meetings 6. Funding mechanisms for climate change projects 7. Initiatives by Govt of India, NAPCC, SAPCC, and INDC. |
| Present Scenario of Indian Agriculture and Allied activities | 1. Recent trends 2. Major challenges in agriculture measures to enhance 3. Viability of agriculture 4. Factors of Production in agriculture 5. Agricultural Finance and Marketing 6. Impact of Globalization on Indian Agriculture and issues of Food Security 7. Concept and Types of Farm Management. |
| Rural Development | 1. Concept of Rural Area 2. Structure of the Indian Rural Economy 3. Importance and role of the rural sector in India 4. Economic, Social, and Demographic Characteristics of the Indian rural economy 5. Causes of Rural Backwardness 6. Rural population in India 7. Occupational structure 8. Farmers, Agricultural Laborers, Artisans, Handicrafts, Traders, Forest dwellers/tribes, and others in rural India 9. Trends of change in rural population and rural workforce 10. Problems and conditions of rural labour 11. Issues and challenges in Hand-looms 12. Panchayati Raj Institutions – Functions and MGNREGA, NRLM – Aajeevika, Rural Drinking water 13. Working Programmes, Swachh Bharat, Rural Housing, PURA, and other rural development programs |
NABARD Grade A Finance Mains Syllabus 2024
| Paper-I – English Topics |
| Essay, Précis writing, Comprehension, and Business/Office Correspondence |
| Paper-II – Syllabus |
| FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING 1.1 Meaning; Objectives; Basic Accounting; Principles, Concepts, and Conventions; Limitations of Financial Accounting 1.2 Preparation of Financial Statements – Nature of Financial Statements; Capital and Revenue Expenditure; Trading Account; Profit and Loss Appropriation Account and Balance Sheet; Limitation of Financial Statements 1.3 Analysis and Interpretation of Financial Statements – Tools of Financials Statements analysis; Ratio Analysis – different types of ratios; Advantages and Limitations of ratio analysis. 1.4 Depreciation: Reserves and Provisions – Meaning; Need to provide Depreciation; Methods of providing depreciation; Provisions and Reserves; Choice of Methods; Objectives of Depreciation Policy. 1.5 Inventory Valuation: Nature and Importance of Inventory Valuation; Types of Inventory Systems; Methods of Inventory valuation; choice of Method. 1.6 Developments in Accounting – Interim Reporting – Segment Reporting – Value-added statement – Corporate Social Reporting – Human Resource Accounting – Accounting for Intangible Assets – Accounting for Financial Instruments – Environmental Accounting – Inflation Accounting. 1.7 Statement of Sources and Application of Funds – Meaning of Funds, The distinction between Funds and Cash; Preparation of Fund Flow Statement; Analysis of flow of funds; Utility of Fund Flow Statement; Preparation of cash flow statement; Utility of cash Flow Statement. 1.8 Preparation of Final Accounts of Banking, Insurance Companies – Basel III & Prudential Norms like Capital Adequacy Ratio, Non-Performing Assets – Provisions therefore for Banks and Financial Institutions. MANAGEMENT ACCOUNTING 2.1 Meaning and scope of Management Accounting; Financial Accounting vs. Management Accounting; Role of Management Accounting; Function and Position of Controller. 2.2 Variable Costing – Fixed costs and Variable Costs; Distinctions between variable costing and absorption costing; application of variables costing as a technique; Differential costing and decision making. 2.3 Marginal costing – Cost volume profit analysis, Profit Planning, Break-even analysis, Break-even Point, and Break-even chart. 2.4 Methods of costing – job costing – Contract costing – Batch Costing – Process costing – Unit costing – Operation costing and Operating costing. 2.5 Cost of capital – Cost of different sources of finance –Weighted average cost of capital – Marginal cost of capital – Concepts of operating and financial leverage – Capital Structure patterns – Designing optimum capital structure – Different sources of finance -Long, medium, and short-term finance. 2.6 Money market and their operations 2.7 Business valuations – Mergers, Acquisitions, and corporate restructuring 2.8 Budgetary control – Meaning and objectives; operation of Budgeting system; types of Budgets; Preparation of Sales Budget; Production Budget, Cash Budget, Master Budget; Flexible Budgeting; Zero Budgeting. 2.9 Standard Costing –Meaning of Standard costing; the distinction between Standard Costing and Budgeting Control; Advantages of Standard costing; Setting up of Standards; Variance Analysis – Material, labour, and Overheads. 2.10 Management Control System: distinction between strategic planning, Operational Control and Management control System; Responsibility Accounting; Transfer Pricing; Tools of Control – Residual Income and Return on Investment; Performance Budgeting; Economic Value added. 2.11 Appraisal of firms – Objectives, Uniform costing; Ratio Based Comparison; Credit Rating; Risk Assessment. 2.12 Appraisal of Projects – Methods of appraisal – preparation of project report –Economic, Technical, Financial Feasibility – Techniques for evaluation of projects like Pay Back Method, Discounted Cash Flow, Net Present Value, Internal Rate of Return, etc. – Sensitivity analysis in capital budgeting – Impact of inflation in capital budgeting – Risk analysis in capital budgeting – Social cost-benefit analysis – Simulation and decision tree analysis. 2.13 Working Capital Management: Factors affecting working Capital requirements; Assessment of Working Capital; Inventory Management; Receivable Management; Cash Management; Method of Financing working capital; different forms of bank credit; working capital and Banking Policy AUDITING 3.1 Auditing – Nature and scope – Audit Process – Objectives of audit – basic principles governing an audit – Types of audit – Relationship of auditing with other subjects – Internal Audit and External Audit – Audit & Inspection 3.2 Planning and programming of Audit – Division of work; supervision and review of audit notes and working papers; planning the flow of audit work. 3.3 Conduct of Audit – Audit Programme; Audit Note Book; Working Papers and Audit files. 3.4 Internal Control – Internal Control, Internal Check, Internal Audit and Concurrent Audit. 3.5 Vouching – General consideration vouching of payments and receipts; Vouching of payment into and out of Bank; Vouching of Goods on consignment, Sale on an approval basis, Empties, Sale under the hire-purchase system, and various types of allowances to customers. 3.6 Verification – Meaning; General principles; Verification of Cash in hand and Cash at Bank; Verification and Valuation of Investments and Inventories; Loans Bills Receivables; Freehold and Leasehold property; Debtors, Plant and Machinery; Verification of different liabilities. 3.7 Audit of Limited Company – Statutory requirements under the Companies Act 2013 – Audit of branches – Joint Audit – Concepts of true and fair materiality and audit risk in the context of audit of companies. 3.8 Dividends and divisible profits – financial, legal, and policy considerations with special reference to depreciation – Audit reports – Qualification and Notes on accounts –Special report on offer documents. 3.9 Audit under income tax and indirect taxes – Special features of audit of banks, Insurance companies, cooperative societies, and Non-banking Financial Companies – Audit of incomplete records – Special audit assignments like audit of bank borrowers – Inspection of special entities like banks, financial institutions, etc. – Investigation including due diligence. 3.10 Concept of Cost Audit, Management Audit, Operational Audit, Environmental Audit and Energy Audit. 3.11 Audit under computerized environments – Computer Auditing – Specific problems of EDP audit – need for a review of internal control especially procedure controls and facility controls – techniques of audit of EDP output – use of computers for internal and management audit purposes – test packs – computerized audit programme – involvement of the auditor at the time of setting up the computer system BBA (BANKING & FINANCE) 4.1 Advance Technology in Banking (ATM, Internet Banking, etc.) – Auditing – Business Communication Skills – Business Ethics and Ethos – Business Laws – Banking Theory and Practice – Corporate Law – Counter Operations, Savings Bank, Current Account and Remittances 4.2 Data Base Management System – Financial Management – Fundamentals of Computers -Income Tax -International Banking – Legal Aspects of Banking – Loans (Housing, Vehicle, Consumer and Personal loans, etc) Managerial Economics – Marketing Information 4.3 System – Merchant Banking & Financial Services – Organization and Management – Organization Theory and Behaviour – Principles & Practices of Banking – Principles and Practices of Management – Quantitative Techniques – Research Methodology – Resource Mobilization and Marketing of Banking Services – Statistic for Management – 4.4 Strategic Credit Management – Treasury & Risk Management Topics like Basic Business Statics, Introduction to modern business, Basic business communication, Business Laws, Introduction to computers, Communication, and soft skills, microeconomics, 4.5 Organizational behavior, operation research, Basic accounting, Macroeconomics, etc BMS (FINANCE & BANKING) 5.1 Foundation of Human Skills – Introduction of Financial Accounts – Business Law – Business Statistics – Business Communication 5.2 Principles of Management I – Introduction to Computers – Business Environment – Industrial Law – Computer Applications in Business 5.3 Managerial Economics I – Business Mathematics – Introduction of Cost Accounting – Environmental Management -Management Accounting – Managerial Economics II – Marketing Management – Business Aspects in Banking & Insurance – Production Management & Materials Management – Strategic Management – Productivity and Quality Management 5.4 Direct & Indirect Taxes – Export-Import Procedures & Documentation – Cooperatives & Rural Markets – Research Methods in Business – Public Relations Management – Human Resource Management – Service Sector Management – Financial Management Elements of Logistics 5.5 Management – Business Ethics & Corporate Social Responsibility Elective I: – Special Studies in Marketing – Special Studies in Finance – E-Commerce – Project Work – Entrepreneurship & Management of SME – Operation Research – International Finance- 5.6 Indian Management – Thoughts & Practices – International Marketing |
NABARD Grade A Finance Notification 2024 FAQs
The NABARD Grade A Finance Notification is out on 27th July 2024.
The NABARD Grade A Finance Application Dates are 27th July 2024 and 15th August 2024 inclusive of both dates.
The candidates with Bachelor’s or Master’s degree in relevant discipline are eligible.
Yes, the third phase of the selection process is the Interview and you will have to clear all three phases to get finally selected.
For SC/ST/PwBD, it is Rs 150 and for others, it is Rs 800.
- CCI Last Minute Revision Plan for 8th July 2025, Check Tips
- Effective Study Strategies for the PFRDA Grade A Statistics
- PFRDA Grade A Lifestyle in 2025, Their Growth and Benefits
- PFRDA Grade A Exam Date 2025, Check Complete Exam Schedule
- PFRDA Grade A Salary 2025, Check In Hand Salary
- PFRDA Grade A Syllabus & Exam Pattern 2025, Detailed

Hello there! I’m a dedicated Government Job aspirant turned passionate writer & content marketer. My blogs are a one-stop destination for accurate and comprehensive information on exams like Regulatory Bodies, Banking, SSC, State PSCs, and more. I’m on a mission to provide you with all the details you need, conveniently in one place. When I’m not writing and marketing, you’ll find me happily experimenting in the kitchen, cooking up delightful treats. Join me on this journey of knowledge and flavors!
