Tiger Reserves in India 2024
There are currently 54 tiger reserves in India, as of January 2024. These reserves are managed by the National Tiger Conservation Authority (NTCA) under Project Tiger, a flagship wildlife conservation program launched in 1973. India is home to over 80% of the world’s wild tigers, making these reserves crucial for the survival of this magnificent species.
List of all Tiger Reserves in India
| S.No. | Tiger Reserve | Year of Creation | State | Total Area (sq. km) |
| 1 | Bandipur | 1973–74 | Karnataka | 1,456.30 |
| 2 | Corbett | 1973–74 | Uttarakhand | 1288.31 |
| 3 | Kanha | 1973–74 | Madhya Pradesh | 2,051.79 |
| 4 | Manas | 1973–74 | Assam | 2,837.10 |
| 5 | Melghat | 1973–74 | Maharashtra | 2,768.52 |
| 6 | Palamau | 1973–74 | Jharkhand | 1,129.93 |
| 7 | Ranthambore | 1973–74 | Rajasthan | 1,411.29 |
| 8 | Similipal | 1973–74 | Odisha | 2750.00 |
| 9 | Sunderbans | 1973–74 | West Bengal | 2,584.89 |
| 10 | Periyar | 1978–79 | Kerala | 925.00 |
| 11 | Sariska | 1978–79 | Rajasthan | 1,213.34 |
| 12 | Buxa | 1982–83 | West Bengal | 7,57.90 |
| 13 | Indravati | 1982–83 | Chhattisgarh | 2,799.07 |
| 14 | Nagarjunsagar-Srisailam | 1982–83 | Andhra Pradesh | 3,296.31 |
| 15 | Namdapha | 1982–83 | Arunachal Pradesh | 2,052.82 |
| 16 | Dudhwa | 1987–88 | Uttar Pradesh | 2,201.77 |
| 17 | Kalakad-Mundanthurai | 1988–89 | Tamil Nadu | 1,601.54 |
| 18 | Valmiki | 1989–90 | Bihar | 899.38 |
| 19 | Pench | 1992–93 | Madhya Pradesh | 1,179.63 |
| 20 | Bandhavgarh | 1993–94 | Madhya Pradesh | 1,536.93 |
| 21 | Tadoba-Andhari | 1993–94 | Maharashtra | 1,727.59 |
| 22 | Dampa | 1994–95 | Mizoram | 988.00 |
| 23 | Panna | 1994–95 | Madhya Pradesh | 1,598.10 |
| 24 | Bhadra | 1994–95 | Karnataka | 1,064.29 |
| 25 | Pench | 1998–99 | Maharashtra | 741.22 |
| 26 | Nameri | 1999–2000 | Assam | 464.00 |
| 27 | Pakke | 1999–2000 | Arunachal Pradesh | 1,198.45 |
| 28 | Satpura | 1999–2000 | Madhya Pradesh | 2,133.30 |
| 29 | Mudumalai | 2007 | Tamil Nadu | 688.59 |
| 30 | Achanakmar | 2008–09 | Chhattisgarh | 914.01 |
| 31 | Anamalai | 2008–09 | Tamil Nadu | 1,479.87 |
| 32 | Dandeli-Anshi (Kali) | 2008–09 | Karnataka | 1,097.51 |
| 33 | Kaziranga | 2008–09 | Assam | 1,173.58 |
| 34 | Nagarhole | 2008–09 | Karnataka | 1,205.76 |
| 35 | Parambikulam | 2008–09 | Kerala | 643.66 |
| 36 | Sanjay-Dubri | 2008–09 | Madhya Pradesh | 1,674.50 |
| 37 | Satkosia | 2008–09 | Odisha | 963.87 |
| 38 | Udanti-Sitanadi | 2008–09 | Chhattisgarh | 1,842.54 |
| 39 | Sahyadri | 2009–10 | Maharashtra | 1,165.57 |
| 40 | Biligiri Ranganatha Temple | 2010–11 | Karnataka | 574.82 |
| 41 | Kawal | 2012–13 | Telangana | 2,015.44 |
| 42 | Mukandra Hills | 2013–14 | Rajasthan | 759.99 |
| 43 | Nawegaon-Nagzira | 2013–14 | Maharashtra | 1,894.94 |
| 44 | Sathyamangalam | 2013–14 | Tamil Nadu | 1,408.40 |
| 45 | Amrabad | 2014 | Telangana | 2,611.39 |
| 46 | Bor | 2014 | Maharashtra | 816.27 |
| 47 | Pilibhit | 2014 | Uttar Pradesh | 730.25 |
| 48 | Rajaji | 2015 | Uttarakhand | 1075.17 |
| 49 | Kamlang | 2016 | Arunachal Pradesh | 783.0 |
| 50 | Orang | 2016 | Assam | 492.46 |
| 51 | Srivilliputhur – Megamalai | 2021 | Tamil Nadu | 1,016.57 |
| 52 | Ramgarh Vishdhari | 2022 | Rajasthan | 1,501.89 |
| 53 | Ranipur Wildlife Sanctuary | 2022 | Uttar Pradesh | 529.36 |
| 54 | Veerangana Durgavati | 2023 | Madhya Pradesh | 1414.006 |
All Tiger Reserves in India Map 2024
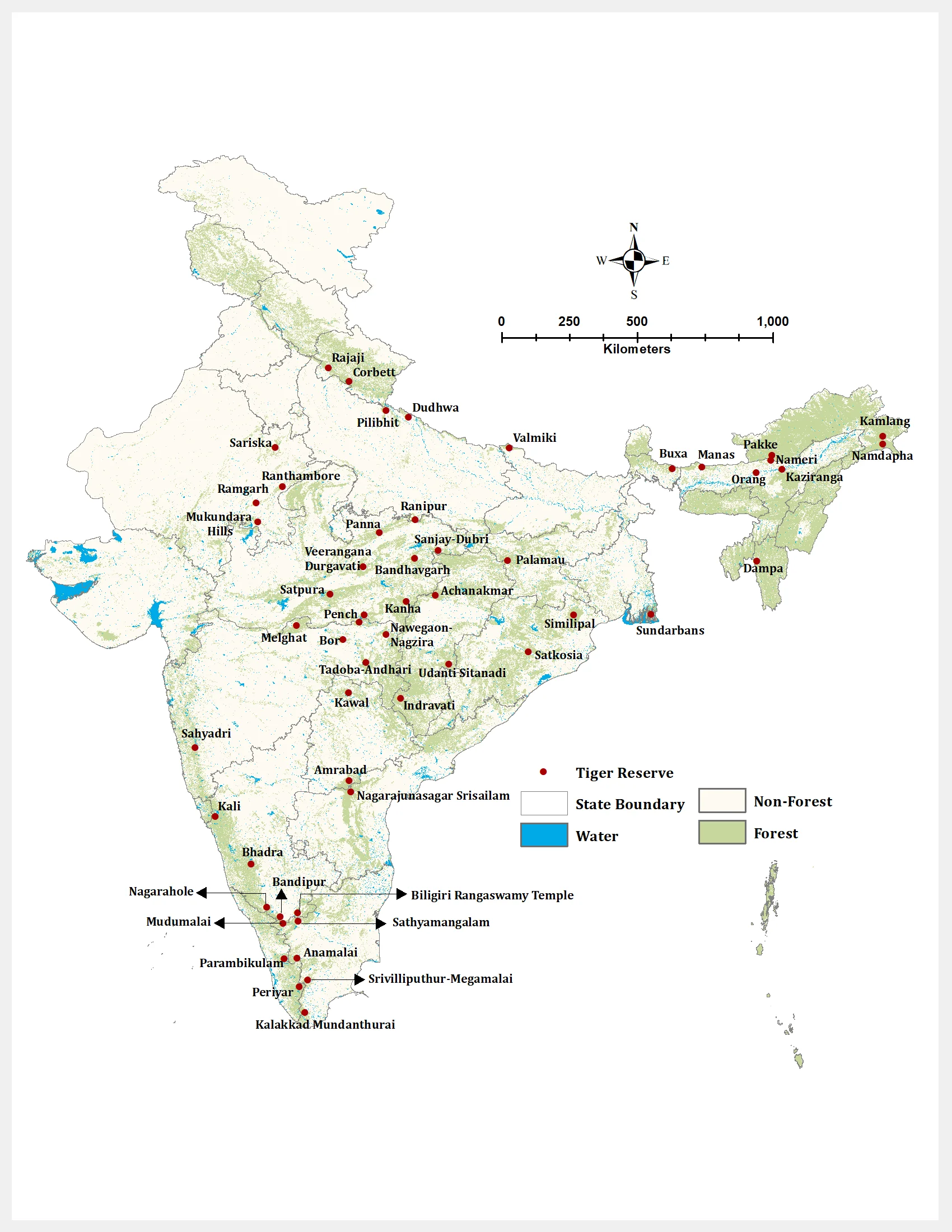
Statewise List of all Tiger Reserves in India
| S.No. | State | No. of TR |
| 1 | Andhra Pradesh | 01 |
| 2 | Arunachal Pradesh | 03 |
| 3 | Assam | 04 |
| 4 | Bihar | 01 |
| 5 | Chhattisgarh | 03 |
| 6 | Jharkhand | 01 |
| 7 | Karnataka | 05 |
| 8 | Kerala | 02 |
| 9 | Madhya Pradesh | 07 |
| 10 | Maharashtra | 06 |
| 11 | Mizoram | 01 |
| 12 | Odisha | 02 |
| 13 | Rajasthan | 04 |
| 14 | Tamil Nadu | 05 |
| 15 | Telangana | 02 |
| 16 | Uttar Pradesh | 03 |
| 17 | Uttrakhand | 02 |
| 18 | West Bengal | 02 |
| Total | 54 |
Most Famous Tiger Reserves in India
Here are some of the most famous tiger reserves in India:
- Ranthambore Tiger Reserve, Rajasthan: This reserve is known for its high tiger density and stunning scenery. It is also home to a variety of other wildlife, including leopards, sloth bears, and crocodiles.
- Jim Corbett National Park, Uttarakhand: This park is the oldest national park in India and was established in 1936. It is a UNESCO World Heritage Site and is known for its diverse wildlife, including tigers, elephants, and deer.
- Kanha National Park, Madhya Pradesh: This park is home to a large population of tigers and is also known for its beautiful sal forests. It is a popular destination for wildlife enthusiasts.
- Periyar Tiger Reserve, Kerala: This reserve is located in the Western Ghats and is home to a variety of wildlife, including tigers, elephants, and gaur. It is also a popular destination for trekking and boating.
- Sunderbans Tiger Reserve, West Bengal: This reserve is located in the Sundarbans delta, which is the world’s largest mangrove forest. It is home to a unique population of tigers that have adapted to living in a saltwater environment.
These are just a few of the many tiger reserves in India. Each reserve has its unique characteristics and wildlife. If you are interested in learning more about tiger reserves, I recommend visiting the website of the National Tiger Conservation Authority.
First Tiger Reserve in India – Jim Corbett National Park
The title of “First Tiger Reserve in India” belongs to the Jim Corbett National Park, originally known as Hailey National Park. It was established in 1936, long before the official launch of Project Tiger in 1973, which led to the creation of the country’s extensive network of tiger reserves.
Located in the Nainital district of Uttarakhand, Jim Corbett National Park became a protected area primarily due to the efforts of the legendary wildlife conservationist Jim Corbett. It played a crucial role in pioneering tiger conservation in India and served as a model for future reserves.
Interesting Facts about Jim Corbett National Park
- It is named after the famous British hunter-turned-conservationist Jim Corbett, who played a crucial role in protecting tigers in the region.
- The park is home to a diverse range of wildlife, including tigers, leopards, elephants, deer, and over 500 species of birds.
- It offers a variety of ecotourism activities, such as jeep safaris, elephant rides, and birdwatching.
- The park is a UNESCO World Heritage Site, recognized for its outstanding natural beauty and ecological importance.
The Latest Tiger Reserve in India – Veerangana Durgavati Tiger Reserve
The title of “latest tiger reserve” in India goes to Veerangana Durgavati Tiger Reserve, established on September 20, 2023, in Madhya Pradesh. This reserve marks the 54th tiger reserve in the country and contributes significantly to the ongoing efforts to protect the majestic Bengal tiger.
Located in the Durg district of Madhya Pradesh, the reserve spans an area of 1,052.32 square kilometers. It boasts a rich biodiversity, including tigers, leopards, sloth bears, chital, sambhar, nilgai, and over 200 species of birds.
The establishment of the Veerangana Durgavati Tiger Reserve was a significant step towards tiger conservation in India. It provides a much-needed haven for tigers and their prey and strengthens the existing network of tiger reserves in the country.
Why Tigers are Important?
The importance of tigers extends far beyond their majestic beauty and captivating presence. Here are some key reasons why tigers are vital:
Ecological Importance
- Apex predator: Tigers are at the top of the food chain, keeping prey populations in check. This prevents overgrazing and maintains the balance of the ecosystem, ensuring healthy vegetation and thriving plant communities.
- Indicator species: Their presence indicates a healthy and functioning ecosystem, as they require diverse and undisturbed habitats. Protecting tigers often means protecting a wide range of other species and the entire ecosystem they inhabit.
- Umbrella species: Protecting tiger habitats often benefits many other species living alongside them, as these reserves provide safe havens for various plants and animals. This contributes to overall biodiversity and the health of the planet.
Economic Importance
- Ecotourism: Tigers are a major draw for wildlife tourism, generating significant revenue for local communities and contributing to economic development. This can provide alternative income sources and encourage conservation efforts.
- Jobs and livelihoods: Tiger conservation creates jobs in areas like park management, research, and tourism, providing valuable income and opportunities for local people.
Cultural Significance
- Spiritual and symbolic importance: Tigers hold deep cultural significance in many Asian countries, featuring prominently in mythology, folklore, and art. They are often revered for their strength, power, and beauty.
- Cultural heritage: Tigers have been woven into the cultural fabric of many communities for centuries, preserving traditional knowledge and practices related to their conservation and coexistence.
Global Impact
- Climate change mitigation: Healthy tiger ecosystems play a crucial role in carbon sequestration and regulating climate patterns. Protecting these habitats contributes to mitigating the effects of climate change.
- Public health: Tigers can act as reservoirs for certain diseases, but their conservation can help prevent zoonotic spillover events, protecting human health.
Overall, tigers are not just magnificent creatures; they play a vital role in maintaining healthy ecosystems, supporting local economies, and enriching our cultural heritage. Their conservation is crucial not only for their survival but also for the well-being of our planet and its inhabitants.
Project Tiger
Project Tiger is a flagship wildlife conservation program launched by the Indian government in 1973 to protect the endangered Bengal tiger. It is considered one of the most successful tiger conservation initiatives in the world and has played a crucial role in reversing the decline of tiger populations in India.
Objectives
- Increase tiger population: The primary objective is to increase the tiger population in India and prevent its extinction.
- Protect tiger habitats: This involves establishing and managing tiger reserves, buffer zones, and corridors to provide secure habitat for tigers and their prey.
- Reduce threats: The project addresses poaching, habitat loss, and human-wildlife conflict through patrolling, anti-poaching measures, and community involvement.
- Raise awareness: Project Tiger also focuses on raising public awareness about the importance of tiger conservation and promoting responsible ecotourism.
Key Achievements
- Increased tiger population: Since its inception, Project Tiger has led to a significant increase in the tiger population in India. The latest tiger census, conducted in 2018, estimated a population of 2,603-3,346 individuals, up from just 400 in the early 1970s.
- Establishment of tiger reserves: Currently, there are 54 tiger reserves across India, providing protected habitat for tigers and other wildlife.
- Improved anti-poaching measures: Project Tiger has implemented intensive anti-poaching measures, including patrolling, informant networks, and camera traps, leading to a significant decline in poaching activities.
- Community involvement: The project encourages local communities to participate in conservation efforts through initiatives like ecotourism and wildlife awareness programs.
Challenges
- Habitat loss: Despite the successes, habitat loss and fragmentation due to agriculture, infrastructure development, and other human activities remain major threats to tigers.
- Human-wildlife conflict: As tiger populations increase, encounters with humans are becoming more frequent, leading to conflict and loss of life for both tigers and people.
- Poaching: While poaching has decreased, it remains a threat, particularly in some areas.
- Funding limitations: Sustaining the long-term success of Project Tiger requires continuous funding, which can be a challenge.
Overall, Project Tiger is a remarkable success story in tiger conservation. However, ongoing efforts are crucial to address remaining challenges and ensure the continued survival and recovery of the Bengal tiger in India.
International Tiger Day 2024
International Tiger Day is coming up on July 29th, 2024. It’s a crucial opportunity to raise awareness about the plight of these magnificent creatures and advocate for their conservation.
International Tiger Day serves as a platform to:
- Raise awareness: Educate people about the importance of tigers and the threats they face.
- Promote conservation efforts: Encourage support for initiatives protecting tigers and their habitats.
- Celebrate successes: Recognize the progress made in tiger conservation and inspire continued efforts.
- IBPS AFO Bank Wise Vacancy 2025 Out, Check Complete List
- SSC JE Previous Year Question Papers, Download the Free PDF
- IBPS AFO Bank Preference List 2025, Get Participating Banks List
- IBPS AFO Documents Required for Interview 2025, Complete List
- IBPS AFO Books 2025, Check Complete List of IBPS AFO Books
- IBPS AFO Full Form, Know Everything on AFO Full Form
FAQs – Tiger Reserves in India 2024
Ans. At present, there are 54 Tiger Reserves in India.
Ans. The title of “First Tiger Reserve in India” belongs to the Jim Corbett National Park, originally known as Hailey National Park. It was established in 1936.
Ans. The title of “latest tiger reserve” in India goes to Veerangana Durgavati Tiger Reserve, established on September 20, 2023, in Madhya Pradesh. This reserve marks the 54th tiger reserve in the country.
Ans. Project Tiger is a significant wildlife conservation initiative introduced by the Indian government in 1973 to safeguard the endangered Bengal tiger. It stands out as one of the most successful tiger conservation programs globally, contributing significantly to the recovery of tiger populations in India.

Hello, I’m Aditi, the creative mind behind the words at Oliveboard. As a content writer specializing in state-level exams, my mission is to unravel the complexities of exam information, ensuring aspiring candidates find clarity and confidence. Having walked the path of an aspirant myself, I bring a unique perspective to my work, crafting accessible content on Exam Notifications, Admit Cards, and Results.
At Oliveboard, I play a crucial role in empowering candidates throughout their exam journey. My dedication lies in making the seemingly daunting process not only understandable but also rewarding. Join me as I break down barriers in exam preparation, providing timely insights and valuable resources. Let’s navigate the path to success together, one well-informed step at a time.






