The Memory Organization topic in SSC CGL Tier 2 Computer Awareness checks your understanding of how data is stored, managed, and retrieved in a computer system. Questions are mostly conceptual and direct, so having clarity on types of memory and their functions will help you score easily. This article covers SSC CGL Tier 2 Memory Organization, including types of memory, primary vs secondary memory, memory hierarchy, storage devices, and key revision points.
SSC CGL Tier 2 Memory Organization Syllabus Coverage
In SSC CGL Tier 2, questions on Memory Organization usually come from:
- Types of Memory (Primary, Secondary, Cache, Virtual)
- Storage Devices (Hard Disk, SSD, Optical Media)
- Memory Hierarchy
- Characteristics of Memory (Volatile, Non-Volatile, Speed, Cost)
Types of Computer Memory
Memory in a computer is broadly divided into two categories: Primary (Main Memory) and Secondary (Storage Memory). Primary memory is directly accessible by the CPU, while secondary memory stores data permanently.
| Type of Memory | Description | Examples |
| Primary Memory | Fast, volatile memory used for processing. | RAM, Cache |
| Secondary Memory | Permanent storage, slower than primary. | Hard Disk, SSD, DVD |
| Cache Memory | Very high-speed memory between CPU and RAM. | L1, L2, L3 Cache |
| Virtual Memory | Portion of secondary storage used as extended RAM. | Swap Space in OS |
Primary vs Secondary Memory
To answer SSC CGL questions easily, you should know the clear difference between Primary and Secondary Memory.
| Feature | Primary Memory | Secondary Memory |
| Speed | Very Fast | Slower |
| Volatility | Volatile (data lost when power off) | Non-volatile |
| Access | Directly accessed by CPU | Needs Input/Output operations |
| Cost | Expensive | Cheaper |
| Capacity | Small in size (GBs) | Large (GBs to TBs) |
Also check out: SSC CGL Typing Test Errors to minimize your errors in Data Entry Speed Test.
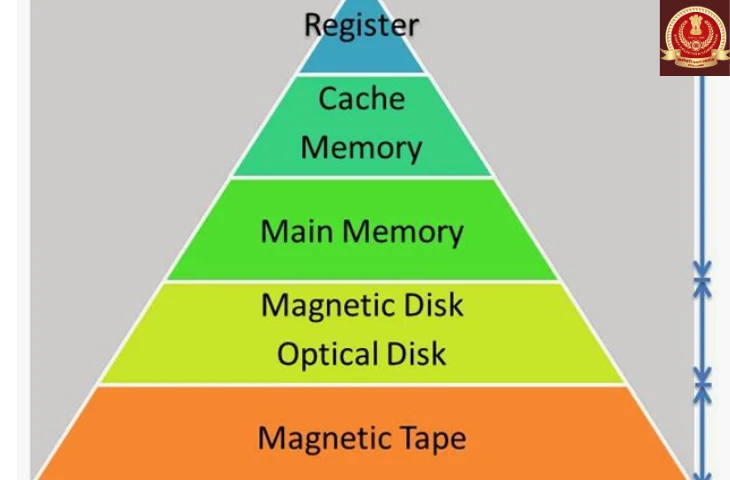
Memory Hierarchy (Speed & Cost)
Memory is organized in a hierarchy based on speed, cost, and capacity.
| Level | Memory Type | Speed | Cost | Capacity |
| Top | CPU Registers | Fastest | Very High | Very Small |
| High | Cache Memory | Very Fast | High | Small |
| Middle | RAM (Main Memory) | Fast | Medium | Moderate |
| Low | Secondary Storage | Slow | Low | Very Large |
The higher you go in the hierarchy, the faster but costlier the memory is.
Storage Devices and Examples
Storage devices are part of secondary memory and are commonly asked in exams.
| Device Type | Examples | Nature |
| Magnetic Storage | Hard Disk Drives (HDD), Floppy Disks | Non-volatile |
| Optical Storage | CD, DVD, Blu-Ray | Non-volatile |
| Solid-State Storage | SSD, Pen Drive, Memory Card | Non-volatile |
Key Takeaways
Below are the key points for quick revision:
- RAM is volatile, while ROM and Hard Disk are non-volatile.
- Cache memory is faster than RAM.
- Virtual memory is created by OS to extend RAM.
- Registers are the fastest memory in a computer.
- SSC CGL mostly asks direct difference-based or abbreviation-based questions.
FAQs
Q1. What is Memory Organization in SSC CGL Tier 2?
Ans. It tests your understanding of how data is stored, managed, and retrieved in a computer system.
Ans. Primary (RAM, Cache), Secondary (HDD, SSD, Optical), Cache, and Virtual memory.
Ans. Primary memory is fast, volatile, directly accessed by CPU; secondary memory is slower, non-volatile, and used for permanent storage.
Ans. Memory hierarchy organizes memory by speed, cost, and capacity, with registers at the top and secondary storage at the bottom.
Ans. Hard Disk, SSD, CD/DVD, Pen Drive, and Memory Cards.
- Average Problems for SSC Exams, Practice Questions with Solutions
- SSC CGL Previous Year General Awareness Questions in Quiz Format
- Top 100 SSC CGL General Awareness Questions, Download PDF
- 1000 SSC CGL General Knowledge Questions, Attempt Now
- IBPS PO vs SSC CGL vs RBI Assistant: Complete Comparison
- SSC CGL vs RBI Assistant: Salary Job Profile Comparison 2026 Guide

I’m Mahima Khurana, a writer with a strong passion for creating meaningful, learner-focused content especially in the field of competitive exam preparation. From authoring books and developing thousands of practice questions to crafting articles and study material, I specialize in transforming complex exam-related topics into clear, engaging, and accessible content. I have first hand experience of 5+ months in SSC Exams. Writing, for me, is not just a skill but a way to support and guide aspirants through their preparation journey one well-written explanation at a time.