Alzheimer’s Treatment Potential
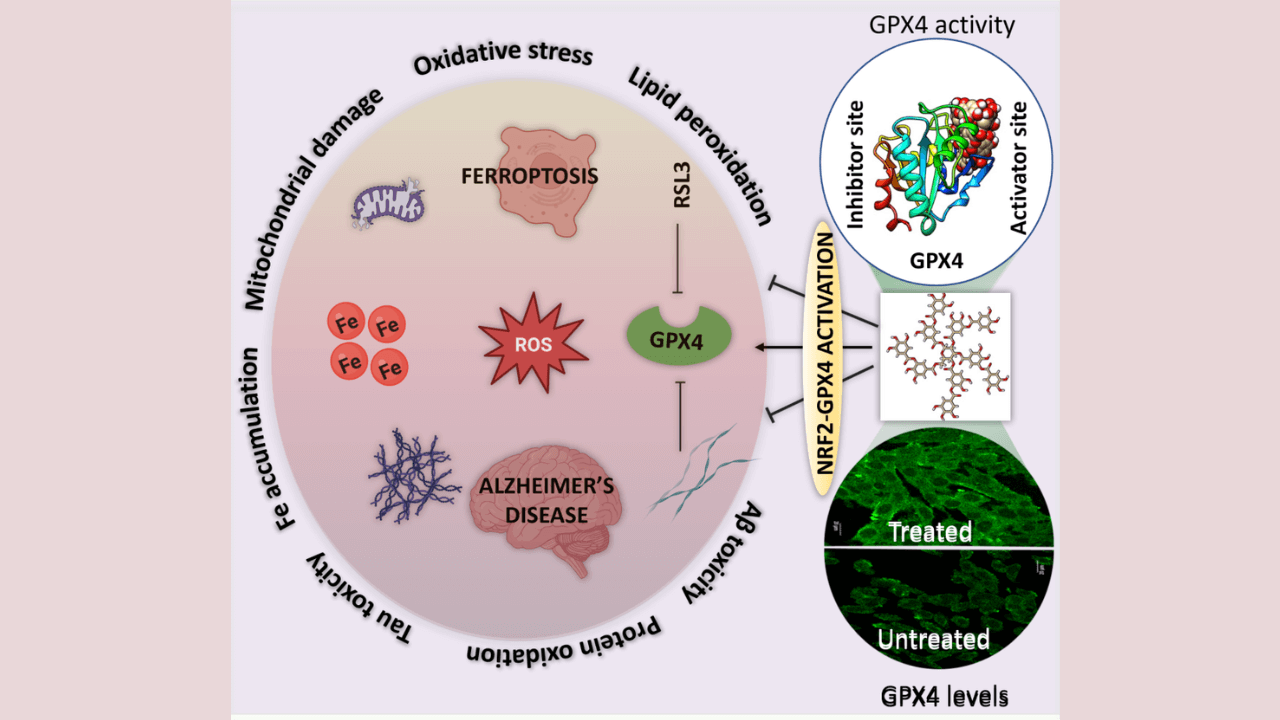
Alzheimer’s Treatment Potential: In a groundbreaking development, scientists have uncovered the therapeutic potential of naturally occurring plant-based polyphenols (PPs), such as tannic acid found in trees like Chestnut and Oak, to revolutionize the battle against Alzheimer’s disease (AD). This pervasive neurodegenerative ailment, characterized by progressive memory and cognitive deterioration, has remained enigmatic despite years of dedicated research, with no definitive cure in sight. The breakthrough discovery centers around ferroptosis, an iron-dependent form of programmed cell death that significantly contributes to AD development. This innovative approach introduces the activation and elevation of the antioxidant enzyme glutathione peroxidase 4 (GPX4) as a pivotal mechanism for countering ferroptosis in AD.
Unlocking Nature’s Potential: Natural Polyphenols
Researchers from the Jawaharlal Nehru Centre for Advanced Scientific Research (JNCASR), an autonomous institute under the Department of Science and Technology (DST), have unveiled the immense potential of natural polyphenols (PPs) as a groundbreaking therapeutic agent with dual capabilities to alleviate ferroptosis and AD. This pioneering approach encompasses inhibiting protein aggregation, reducing oxidative stress, restoring mitochondrial function, and suppressing ferroptosis. Remarkably, tannic acid (TA), a natural polyphenol, emerges as a potent activator and enhancer of GPX4, presenting an advanced strategy to combat AD by modulating the GPX4-ferroptosis-AD axis.
A New Frontier in Drug Development
Published in the journal Chemical Sciences, this study propels research toward ferroptosis inhibitors, opening new vistas for drug development. The discovery of TA as a GPX4 activator with the potential to counter Aβ-induced ferroptosis signifies a groundbreaking advancement. By unraveling the intricate interplay between AD and ferroptosis, this research not only addresses neurological challenges but also advances scientific knowledge, paving the way for innovative therapeutic avenues in neurodegenerative diseases.
Promise for the Future: Alzheimer’s Treatment Potential
This novel approach not only holds promise for Alzheimer’s disease but also introduces a potential breakthrough for tackling other neurodegenerative diseases. By exploring the role of ferroptosis and the activation of GPX4 in various neurological disorders, researchers can unlock new avenues for treatment and offer hope to millions of patients worldwide. This multidimensional strategy offers a ray of optimism in the otherwise challenging landscape of neurodegenerative disease research.
- SIDBI Grade B Notification 2025 Out For 26 Manager Post
- SSC CGL Tier 2 Weightage of English and Quants, Check Here
- 7 Tips for Staying Motivated during SSC CGL Exam Preparation
- General Science Question for SSC CGL Exam, Attempt Here
- SIDBI Grade B Syllabus & Exam Pattern 2025, Download PDF