Today marks the ninth anniversary of the successful implementation of the Pradhan Mantri Jan Dhan Yojana (PMJDY), which is the National Mission for Financial Inclusion.
The inception of PMJDY was announced by Prime Minister Shri Narendra Modi during his Independence Day speech on 15th August 2014. The program was officially launched on 28th August 2014, and during its launch, the Prime Minister likened the event to a festival, celebrating the emancipation of the underprivileged from a destructive cycle.
Since its initiation, PMJDY has played a crucial role in promoting financial inclusion and providing access to various financial services for millions of individuals across the nation. The scheme has contributed significantly to empowering the economically marginalized sections of society by offering them access to banking facilities, insurance, pension schemes, and direct benefit transfers.
Biggest Financial Inclusion Program in the World
The Ministry of Finance has consistently been at the forefront of promoting financial inclusivity and aiding disadvantaged and economically underprivileged sectors through its initiatives focused on financial inclusion. Financial Inclusion (FI) is a key strategy that fosters fair and comprehensive growth while ensuring accessible financial services are provided at reasonable costs to vulnerable demographics, including those with lower incomes and weaker socio-economic backgrounds who often lack access to essential banking services.
Financial Inclusion serves as a means to integrate the savings of economically disadvantaged individuals into the formal financial system. This approach not only enables these individuals to securely save their earnings but also offers them a channel to send money to their families residing in rural areas, liberating them from the grip of exploitative moneylenders.
About the Pradhan Mantri Jan Dhan Yojana (PMJDY)
Pradhan Mantri Jan Dhan Yojana (PMJDY) is a comprehensive initiative aimed at achieving financial inclusion on a national scale. Its primary objective is to provide easy access to essential financial services to all individuals, particularly those who have been historically excluded from the formal banking system. This mission encompasses a range of financial services including opening banking and savings accounts, facilitating remittances, extending credit facilities, offering insurance options, and enabling access to pension plans, all of which are made available at affordable rates.
Objectives
- Ensure access of financial products & services at an affordable cost
- Use of technology to lower cost & widen reach
Basic Tenets
- Banking the unbanked – Opening of basic savings bank deposit (BSBD) account with minimal paperwork, relaxed KYC, e-KYC, account opening in camp mode, zero balance & zero charges
- Securing the unsecured – Issuance of Indigenous Debit cards for cash withdrawals & payments at merchant locations, with free accident insurance coverage of Rs. 2 lakhs
- Funding the unfunded – Other financial products like micro-insurance, overdraft for consumption, micro-pension & micro-credit
6 Pillars of PMJDY

- Universal access to banking services – Branch and BC
- Basic savings bank accounts with an overdraft facility of Rs. 10,000/- to every eligible adult
- Financial Literacy Programme– Promoting savings, use of ATMs, getting ready for credit, availing insurance and pensions, using basic mobile phones for banking
- Creation of Credit Guarantee Fund – To provide banks some guarantee against defaults
- Insurance – Accident cover up to Rs. 1,00,000 and life cover of Rs. 30,000 on account opened between 15 Aug 2014 to 31 January 2015
- Pension scheme for the Unorganised sector
New features
The Government decided to extend the comprehensive PMJDY program beyond 28.8.2018 with some modifications

- Focus shifted from ‘Every Household’ to Every Unbanked Adult’
- RuPay Card Insurance – Free accidental insurance cover on RuPay cards increased from Rs. 1 lakh to Rs. 2 lakhs for PMJDY accounts opened after 28.8.2018.
- Enhancement in overdraft facilities: OD limit doubled from Rs 5,000/- to Rs 10,000/-; OD up to Rs 2,000/- (without conditions) with an increase in upper age limit for OD from 60 to 65 years
Important approach adopted in PMJDY based on experience
Accounts opened are online accounts in the core banking system of banks, in place of the earlier method of offline accounts opening with technology lock-in with the vendor
- Inter-operability through RuPay debit card or Aadhaar-enabled Payment System (AePS)
- Fixed-point Business Correspondents
- Simplified KYC / e-KYC in place of cumbersome KYC formalities
Impact
- The Pradhan Mantri Jan Dhan Yojana (PMJDY) has laid the groundwork for economic initiatives that prioritize the well-being of people.
- It serves as the starting point for numerous significant programs such as direct benefit transfers, COVID-19 financial assistance, PM-KISAN, enhanced wages through MGNREGA, and life and health insurance coverage.
- Between March 2014 and March 2020, half of the newly opened bank accounts were PMJDY accounts.
- During the initial 10 days of the nationwide lockdown, more than 20 crore women holding PMJDY accounts received Rs 500 per month for three months through Direct Benefit Transfer (DBT).
- The COVID-19 pandemic highlighted the rapid and seamless nature of Direct Benefit Transfers (DBTs) in empowering and financially securing vulnerable segments of society.
- A key advantage is that DBTs via PMJDY accounts ensure that every rupee is channeled to its intended recipient, preventing any systemic leakages.
PMJDY has effectively integrated the unbanked population into the banking system, expanding India’s financial infrastructure and bringing financial inclusion within reach of nearly every adult.
Achievements under PMJDY- As of 16th August’23
PMJDY Accounts
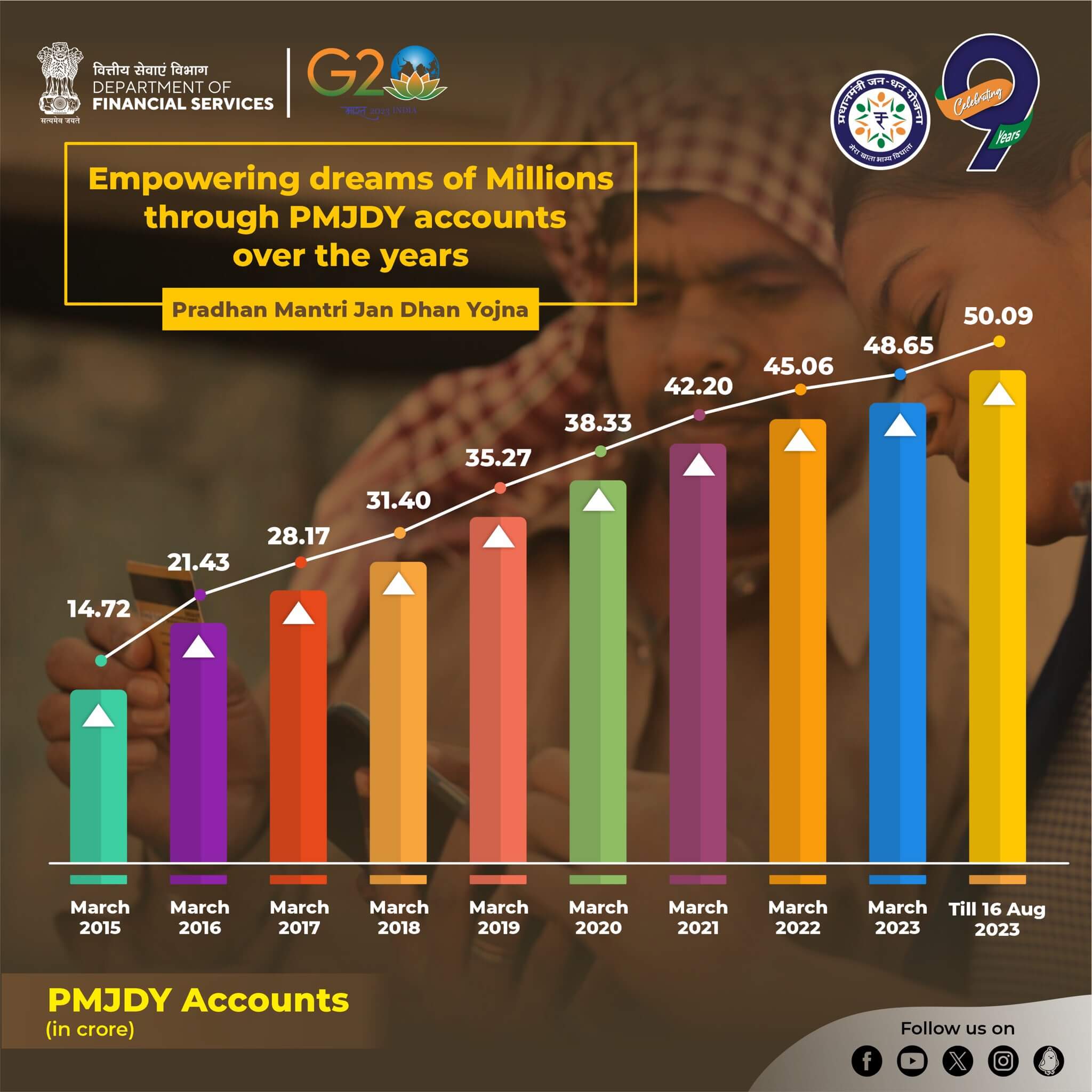
As of 9th August, the number of total PMJDY Accounts is 50.09 crore; 55.6% (27.82 crores) Jan-Dhan account holders are women, and 66.7% (33.45 crores) Jan Dhan accounts are in rural and semi-urban areas
Deposits Under PMJDY Accounts
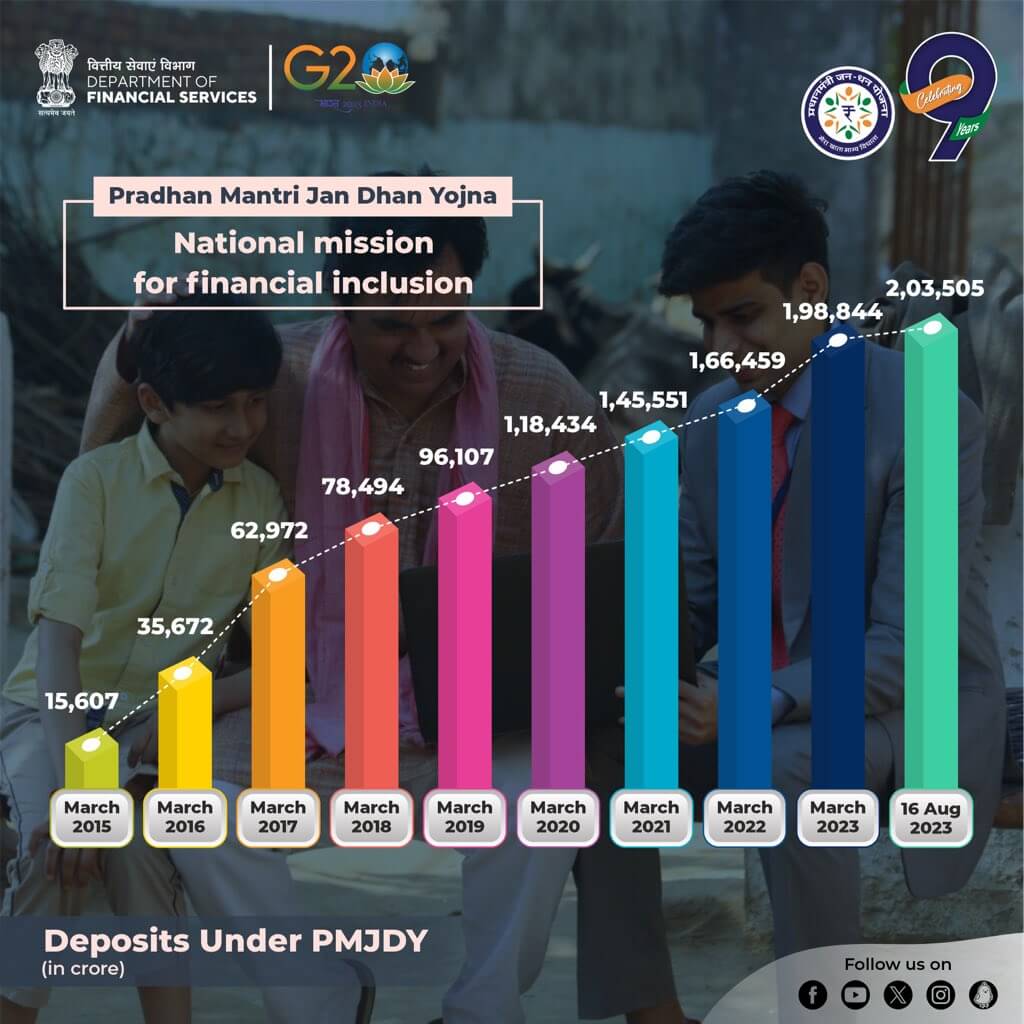
Total deposit balances under PMJDY Accounts stand at Rs. 2,03,505 crore
- Deposits have increased about 13 times with an increase in accounts 3.34 times (Aug’23 / Aug’15)
Average Deposit per PMJDY Account
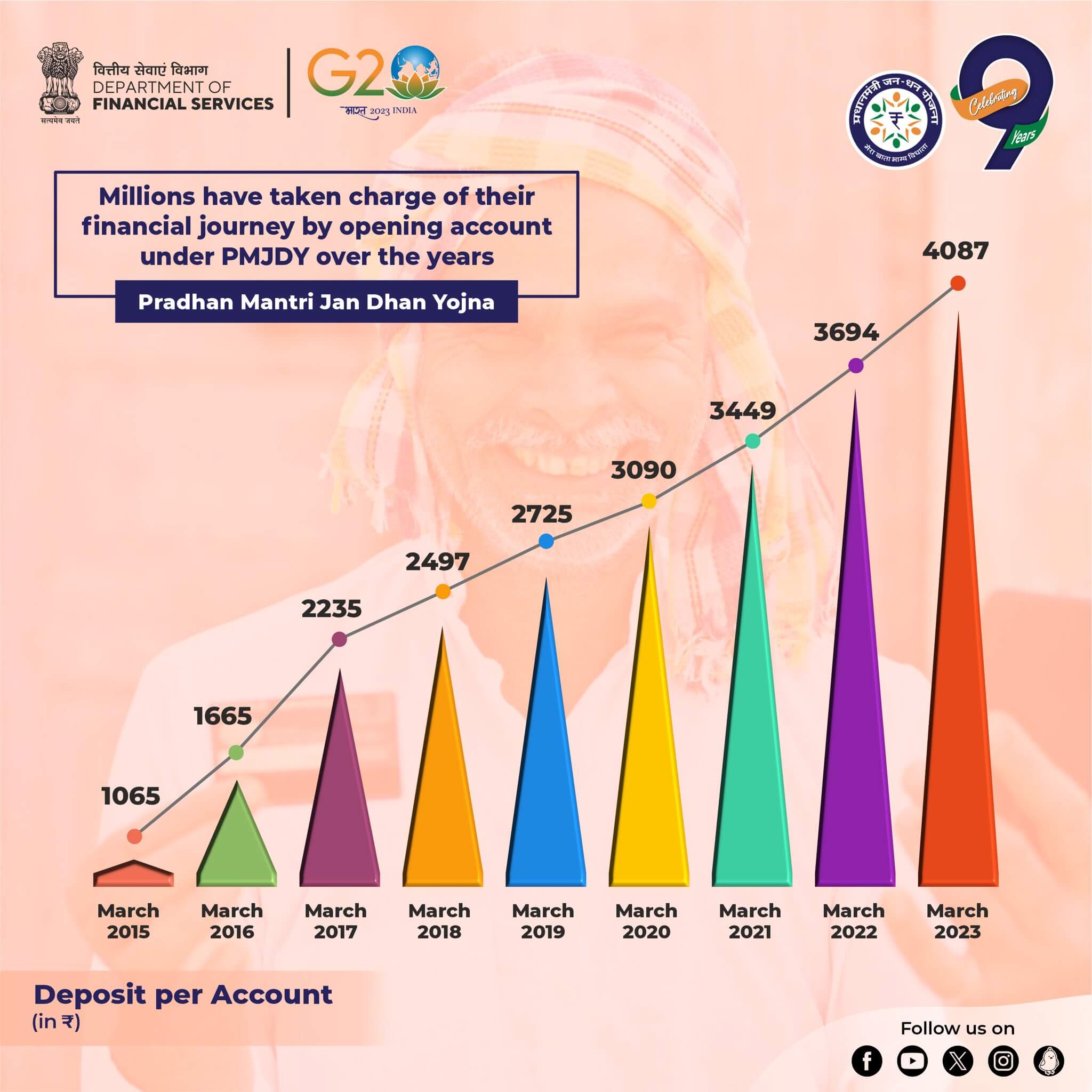
The average deposit per account is Rs. 4,063 as of 16.08.2023
- Avg. Deposit per account has increased over 3.8 times over August 15
- An increase in the average deposit is another indication of increased usage of accounts and inculcation of saving habits among account holders
RuPay Card issued to PMJDY account holders
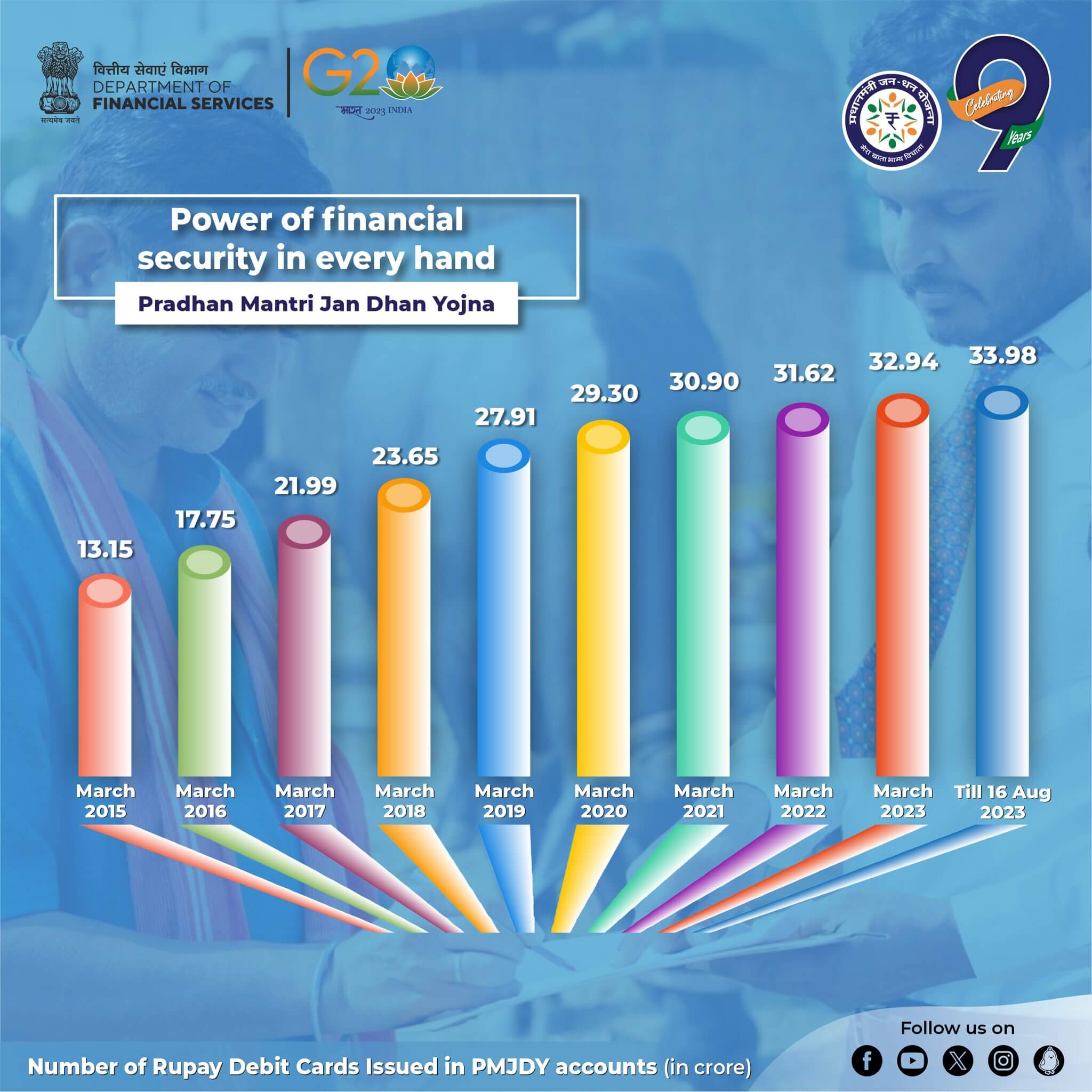
Total RuPay cards issued to PMJDY account holders: 33.98 crore
- The number of RuPay cards & their usage has increased over time
Jan Dhan Darshak App (JDD App)
The Jan Dhan Darshak (JDD) App is a mobile application designed to offer citizens a user-friendly platform for locating various banking touchpoints across the country.
- These touch points include bank branches, ATMs, Banking Correspondents (BCs), and Indian Post Payment Banks, among others.
- The app has successfully mapped over 13 lakh banking touchpoints, providing an extensive network for easy access.
- The Jan Dhan Darshak App is aimed at providing convenient facilities to individuals based on their specific needs and preferences.
- Additionally, the web version of the app can be accessed via the link http://findmybank.gov.in.
- Furthermore, this application serves the purpose of identifying villages that are yet to be covered by banking outlets within a 5 km radius.
- Once these villages are identified, concerned State Level Bank Committees (SLBCs) allocate them to various banks for the establishment of banking outlets.
- This initiative has led to a significant reduction in the number of villages without access to banking services.
As of July 2023, the Jan Dhan Darshak (JDD) app has successfully mapped a total of 6.01 lakh villages. Among these, an impressive 5,99,468 villages, which account for about 99.7% of the total mapped villages, have been covered by banking outlets. These outlets include bank branches, Banking Correspondents (BCs), and Indian Post Payment Banks (IPPB) located within a radius of 5 km. This achievement signifies substantial progress in ensuring access to banking services for a large portion of rural areas in the country.
Towards ensuring smooth DBT transactions
Banks have reported that approximately 6.26 crore account holders under the Pradhan Mantri Jan Dhan Yojana (PMJDY) are beneficiaries of the government’s direct benefit transfer (DBT) across various schemes. To ensure timely delivery of these benefits to eligible recipients, the concerned department actively collaborates with the DBT Mission, the National Payments Corporation of India (NPCI), banks, and other relevant ministries to identify and address avoidable factors that may lead to DBT failures.
Digital transactions
The widespread distribution of over 33.98 crore RuPay debit cards through PMJDY, along with the deployment of 79.61 lakh Point of Sale (PoS) and mobile PoS (mPoS) machines, as well as the introduction of mobile-based payment systems like Unified Payments Interface (UPI), has significantly boosted digital transactions. The total number of digital transactions has surged from 1,471 crore in the fiscal year 2017-18 to 11,394 crore in the fiscal year 2022-23. In particular, UPI-based financial transactions have grown from 92 crore in FY 2017-18 to an impressive 8,371 crore in FY 2022-23. Likewise, the overall count of RuPay card transactions at both PoS terminals and e-commerce platforms has risen from 67 crore in FY 2017-18 to 126 crore in FY 2022-23.
- Weekly Current Affairs 2025 PDF For Bank, SSC, UPSC Exams
- Unsung Heroes of India: 10 Unknown Freedom Fighters You Should Know
- 26 December Current Affairs 2023 in English
- Daily Current Affairs 2025, Check Today’s Current Affairs
- April Month Current Affairs 2024, Download PDF
- June Month Current Affairs 2024, Download PDF

Hello, I’m Aditi, the creative mind behind the words at Oliveboard. As a content writer specializing in state-level exams, my mission is to unravel the complexities of exam information, ensuring aspiring candidates find clarity and confidence. Having walked the path of an aspirant myself, I bring a unique perspective to my work, crafting accessible content on Exam Notifications, Admit Cards, and Results.
At Oliveboard, I play a crucial role in empowering candidates throughout their exam journey. My dedication lies in making the seemingly daunting process not only understandable but also rewarding. Join me as I break down barriers in exam preparation, providing timely insights and valuable resources. Let’s navigate the path to success together, one well-informed step at a time.






