Temple architecture is an important subject of Art and Culture part of syllabus of UPSC civil services prelims 2018. UPSC has asked around 12-15 questions for history over the last 5 years on an average, which includes the art and culture component. This shows the value of preparing Arts and culture well. While preparing Arts and Culture one of the First topics which comes is Temple Architecture. We thereby bring you notes to help you cover and revise the Temple Architecture topic under Art and Culture for UPSC civil services prelims 2018.
To go through the strategy to cover complete Art and culture please click here.

Temple Architecture Styles can be divided into 3 types.
1 – Dravida Style – This style is associated with the Temples from South India. The Vimana in Dravida Style of Temple Architecture is Pyramidical Elevation of Towers.
2 – Nagara Style – The style is related to the Temples found in North India. The distinctive feature of this style is that the shikhara/Vimana is curvilinear shaped.
3 – Vesara Style – The temples build with a Mixture of Dravida and Nagara Styles of Temple Architecture are called as Vesara Style of Temples. These can mainly be seen in Karnataka region.

-
Dravida Style of Temple Architecture:
This Style predominantly developed in the 7-8th century AD under the Pallava’s and Cholas in South India.
Characteristics:
- The Temples are enclosed by a compound wall.
- The entrance gateway called as Gopuram is in the centre of the Front wall.
- The Garbhagriha is square shaped which is topped by a pyramidical Tower called as Vimana.
- The Shikhara in South India, which is an octagonal cupola, is equivalent to Kalash of North India.
- A Temple tank of Fresh water is within the enclosed structure of the Temple.
- A pillared wall called a Mandapa, precedes the Garbhagriha and the Vimana.
- The Pillars and Vimana storeys are decorated by sculpting of images of Dwarpalas (door keepers)
- Over the period of time the height of the Goparam’s kept on increasing and in the Vijayanagara period the Goparam’s had almost become bigger than the Vimana’s
Examples of Temples build in Dravida Style of Temple architecture:
- Brihedeshwara Temple at Tanjore built by Rajarajeshwara Chola
- Shore Temple ot Mahabalipuram built by Narasimhavarman II (Pallava King)
- Meenakshi- Sundareswara temple at Madurai built by Nayaka Rulers
- Kailashnath Temple at Kanchipuram built by Narasimhavarman II (Pallava King)

-
Nagara Style of Temple Architecture:
This Style of Temple Architecture is seen in temples built in North India.
Characteristics:
- The Temple complex is not enclosed.
- The Garbhagriha (Inner Sanctum) is topped by a Shikhara which is curvilinear shaped.
- The Mandapa (main hall) are of different types called as Ardhamandapa, Mandapa and Mahamandapa. Based on their sizes.
- There is a Stone disc type structure called as amalaka at the top of the Temple.
- Amalaka is Topped by a Kalasha which is the highest point of the Shikara as well as the entire temple.
- There is also an Anatarala, which is transition area between the Garbhagriha and the Mandapa.
- The walls and pillars of the temple are decorated by sculpted images of river goddesses and mithuna images.
The entire Temple complex is build on a stone platform with steps leading to it.
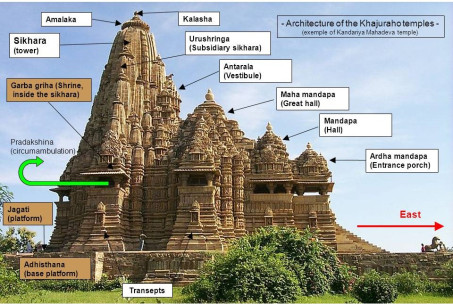
Examples of Temples build in Nagara Style of Temple architecture:
- Kandariya Mahadeva Temple at Khajuraho, built by Chandela rulers
- Sun Temple at Modhera, Gujrat built by Solanki Rulers
- Sun Temple at Konark, built by Narasimhadeva I of the Eastern Ganga Dynasty
- Jagannatha temple at Puri, built by Eastern Ganga Dynasty rulers

-
Vesara Style of Temple Architecture:
These style is also called as the Deccan style as most of the temples of this Temple architecture style are found in Deccan region.
Characteristics:
- It is a hybridized style formed by combining features of both Dravida and Nagara Style of Temple architecture.
- This style had Spire shaped Shikhara inspired by Nagara style
- The Mandapa is designed in Dravidian style which is a pillared hall
- The Shikhara and Mandapa are joined by antarala
- Pradakshina path – ambulatory path way around Sanctum Sanctorum (Garbhagriha) is not present.
- The Pillars, ceiling and door frames are very intricately carved.
Examples of Temples build in Vesara Style of Temple architecture:
- Lad Khan temple at Aihole, Karnataka, built by the Kings of the Chalukya Dynasty
- Virupaksha temple at Pattadakkal, built by Loka-Mahadevi, the Queen of the Chalukya king Vikramaditya II
- Kailshnatha Temple at Ellora, built by Rahstrakuta rulers
- Hoyasaleswara temple at Halebid, by the Hoyasala king Vishnuvardhan.
We hope this is helpful in your preparation of Temple Architecture topic of Art and Culture for UPSC Civil services prelims 2018.
All the best!!!

The most comprehensive online preparation portal for MBA, Banking and Government exams. Explore a range of mock tests and study material at www.oliveboard.in
