The JAIIB 2026 notification has been released, and the May 2026 exam cycle will begin on 3rd May 2026. Professionals planning to appear for the exam should start their preparation early. Previous year papers are especially useful, as they provide insights into the types of questions asked, important topics, and help candidates practice completing the paper within the 2-hour time frame.
Download JAIIB 2025 Previous Year Question Papers PDF
Below, we have provided the JAIIB previous year question papers for 2023, 2024, and 2025. Professionals can download these papers and practice, as each paper comes with the correct answers to all questions.
JAIIB previous year question papers for the November 2025 cycle exam, Download PDF
Candidates can download the IIBF JAIIB previous year question papers for the November 2025 cycle through the direct link provided below and take their JAIIB 2026 exam preparation to the next level.
| JAIIB Papers | Link to Download |
| JAIIB November 2025 AFM Paper | Download PDF |
| JAIIB November 2025 IE and IFS Paper | Download PDF |
| JAIIB November 2025 PPB Paper | Download PDF |
| JAIIB November 2025 RBWM Paper | Download PDF |
JAIIB previous year question papers for the May 2025 cycle exam, Download PDF
Candidates can download the IIBF JAIIB previous year question papers for the May 2025 cycle through the direct link provided below:
| JAIIB May Papers | Link to Download |
| JAIIB May 2025 AFM Paper | Download PDF |
| JAIIB May 2025 IE and IFS Paper | Download PDF |
| JAIIB May 2025 PPB Paper | Download PDF |
| JAIIB May 2025 RBWM Paper | Download PDF |
Download JAIIB May 2024 past year paper free PDF
Professionals can download the IIBF JAIIB May-June 2024 papers through the direct link provided below:
| Paper | Download Link |
| JAIIB IE & IFS May 2024 Paper | Download Here |
| JAIIB PPB May 2024 Paper | Download Here |
| JAIIB AFM May 2024 Paper | Download Here |
| JAIIB RBWM May 2024 Paper | Download Here |
JAIIB October 2023 previous year paper PDF
Candidates can download the IIBF JAIIB previous year question papers for the October 2023 cycle through the direct link provided below:
| Paper Name | Download Link |
| JAIIB October 2023 IE and IFS Paper | Download PDF |
| JAIIB October 2023 PPB Paper | Download PDF |
| JAIIB October 2023 AFM Paper | Download PDF |
| JAIIB October 2023 RBWM Paper | Download PDF |
JAIIB May 2023 past year paper free PDF
Candidates can download the IIBF JAIIB previous year question papers for the May 2023 cycle through the direct link provided below:
| Paper Name | Download Link |
| JAIIB May 2023 IE and IFS Paper | Download PDF |
| JAIIB May 2023 PPB Paper | Download PDF |
| JAIIB May 2023 AFM Paper | Download PDF |
| JAIIB May 2023 RBWM Paper | Download PDF |
Which are the important topics for JAIIB IE and IFS based on previous year question paper analysis?
Preparing for the JAIIB IE & IFS exams requires focusing on most repeated topics, numericals, and case studies. The most repeated and scoring modules include Committees, RBI Regulations, Insurance & Pension Schemes, Economic Reforms, Microfinance/MSME, Finance, SDGs, and Numericals.
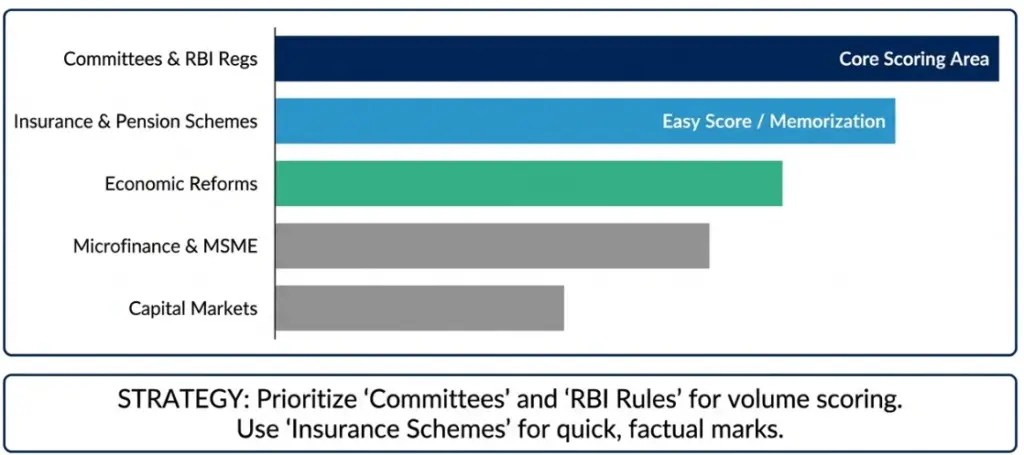
Which committees and banking reforms are frequently asked in IE and IFS papers?
Committees are very high-yield areas. Questions are usually about the committee’s name, sector focus, recommendations, and implementation impact.
| Committee / Topic | Key Focus Area | Frequency / Observations |
| Narsimha Committee I & II (1991 & 1998) | Banking sector reforms, reduction of NPAs, introduction of Liquidity Adjustment Facility (LAF), strengthening prudential norms | Extremely frequent; almost every paper includes questions on NPA management, LAF, and prudential norms |
| Malhotra Committee | Insurance sector reforms, establishment of IRDA, regulation of Life & Non-Life insurance, framework for private insurance companies | Frequently asked in insurance-related questions; often linked to policy implementation |
| B Committee | MSME financing, venture capital promotion, financial inclusion for small industries | Repeated in IE exams; scoring if recommendations remembered |
| Dr. Krishna Swamy / MV Nair Committee | Priority Sector Lending (PSL) targets for agriculture, MSME, housing, education, social infrastructure | Very frequent; usually 1–2 questions per paper |
| Hilton Young Commission (1926) | Establishment of Reserve Bank of India, structure, and functions | Occasionally asked; high-scoring if remembered |
| Other RBI Committees (e.g., Monetary Policy Committee, Credit Information Companies, Development Financial Institutions) | Regulatory framework, composition of MPC, strengthening DFIs, credit information reporting | Frequently conceptual questions in IE and RBI-related exams |
Which RBI and banking regulation topics are most repeated in IE and IFS past papers?
RBI regulations and banking rules form the core of frequently tested questions. Questions are mostly conceptual or direct.

| Topic | Key Points | Frequency |
| SLR / CRR / Repo Rate / LAF | SLR – Section 24 of Banking Regulation Act 1949; CRR – Section 42 of RBI Act 1934; Repo rate, LAF purpose and mechanism | Almost always 2–3 questions per paper; direct definitions, regulatory sections, or purpose |
| Priority Sector Lending (PSL) | Targets for agriculture, MSME, education, housing, renewable energy, weaker sections | Repeated across nearly all IE and IFS exams; questions on sector allocation and compliance |
| Microfinance / NBFCs / MFIs | RBI regulations, loan limits, borrower eligibility, income ceiling | Often 2–3 questions per paper; numerical or scenario-based |
| Universal Bank Concept | Definition of a full-service bank and services offered | Occasionally asked; scoring if conceptual clarity is strong |
Also Check: JAIIB IE and IFS Exam Analysis
Which insurance and pension schemes are mostly asked in the JAIIB IE and IFS exam?
Insurance and pension schemes are easy to score with knowledge of age limits, premiums, coverage, and contribution rates.
| Scheme / Topic | Key Features | Frequency |
| EPFO / EPF | Employee retirement savings, employer & employee contribution rates (minimum salary, % contribution) | 3 to 4 questions per paper; focus on contribution percentages and salary limits |
| PMSBY (Pradhan Mantri Suraksha Bima Yojana) | Accidental death/disability insurance, age 18–70 years, annual premium Rs 20 | Frequently asked every cycle; focus on age, premium, and coverage |
| PMJJBY (Pradhan Mantri Jeevan Jyoti Bima Yojana) | Life insurance coverage, age 18–50 years, annual premium Rs 330 | Usually 1–2 questions per paper |
| Atal Pension Yojana (APY) | Government-backed pension, age 18–40 years, monthly pension Rs 1000–5000 depending on contribution | Very high-yield topic; commonly tested |
| Insurance Ombudsman | Claims resolution mechanism; maximum claim: Life Rs 30 lakh, Banking Rs 20 lakh | Frequently asked; conceptual and numerical questions |
| Other Schemes | PM Jeevan Jyoti, PM Suraksha Bima | Occasionally asked; questions focus on age, premium, and coverage |
Which economic reforms and macroeconomics topics are commonly asked in IE and IFS previous year papers?
Questions focus on LPG reforms, GDP/GVA, fiscal deficit, monetary indicators. Numericals are usually simple formula-based.
| Topic | Key Points | Frequency |
| LPG Reforms (1991) | Liberalization, Privatization, Globalization | Always 1–2 questions per paper; mostly conceptual |
| GDP / GVA at Basic Prices | Formula: GVA + Taxes – Subsidies; sectoral contributions | 1–2 questions per paper; simple numerical |
| Fiscal Deficit | Government expenditure – revenue | Usually 1 question per paper; simple calculation |
| Velocity of Money | Nominal GDP ÷ Money Supply | 1 question per paper |
| Demand & Supply Curves | Conceptual understanding: Demand inverse, Supply positive | Frequently asked; usually conceptual |
Which finance, capital market, and investment topics frequently appear in the exam?
Moderate-frequency topics; scoring if definitions, regulatory framework, and limits are clear.
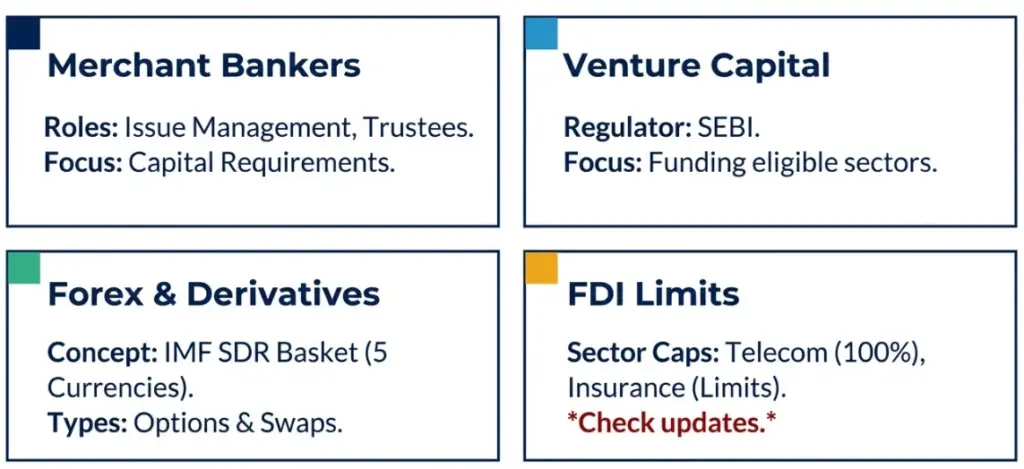
| Topic | Key Points | Frequency |
| Merchant Bankers | Categories, minimum capital, trustee responsibilities | 1–2 questions per paper; conceptual |
| Venture Capital Fund | Regulated by SEBI; investment norms and eligible sectors | Frequently repeated |
| Derivatives / Options / Forex / Currency Basket | Conceptual understanding; currency basket – IMF SDR 5 currencies | Occasionally numerical; usually conceptual |
| FDI Limits | Sector-wise limits (Telecom 100%, Insurance, etc.) | Repeated in recent papers; regulatory updates |
| Credit Information Companies | Regulatory authority, role in reporting credit information | Occasionally; mostly conceptual |
Which development, sustainability, microfinance, and MSME topics are important for the exam?
These topics appear with medium frequency, and while some are optional, they are scoring if well-prepared. The key topics to focus on are as follows:
| Topic | Key Points | Frequency |
| Sustainable Development Goals (SDG) | 17 Goals; sectors prioritized for development | 1–2 questions per cycle |
| Sunrise Sectors | Recognized sectors for investment and priority allocation | Occasionally asked; scoring if known |
| Microfinance / Grameen Model | Prof. Muhammad Yunus, Bangladesh model; MFI loan limits, borrower income ceiling | Frequently repeated |
| MSME Financing & Venture Capital | Investment and capital limits; regulatory guidelines | 1–2 questions per paper |
Which numerical and formula-based questions appear in the JAIIB IE and IFS papers?
Light, formula-based, and scoring numericals appear across Economic Reforms, Insurance, Pension, PSL, GDP/GVA, Fiscal Deficit.
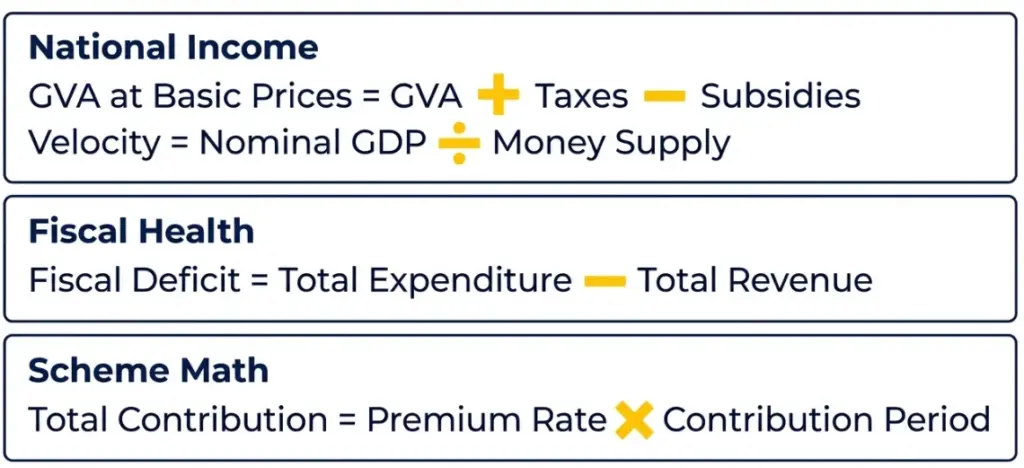
| Topic | Formula | Frequency |
| GDP / GVA at Basic Prices | GVA + Taxes – Subsidies | 1–2 questions per paper |
| Fiscal Deficit | Total Expenditure – Total Revenue | 1 question; straightforward |
| Velocity of Money | Nominal GDP ÷ Money Supply | 1 question per paper |
| Insurance / EPFO / Pension Contributions | Premium × Contribution | 2–3 small numericals per paper |
| Credit Score / Population Coverage | Direct calculation; scenario-based | 1 question |
What type of case study questions are mostly asked in IE and IFS?
Case study questions are typically situational, applied, and linked to banking operations, microfinance, MSME, PSL, or insurance schemes. They test your ability to apply concepts, calculate limits, or decide eligibility based on the scenario. Most questions are short, scoring, and require formula application or rule-based reasoning.
| Type of Case Study | Example | What is Tested |
| PSL / Priority Sector Lending Cases | A bank has to allocate loans to agriculture, MSME, or housing sectors | Knowledge of PSL sectors, limits, and eligibility |
| Microfinance / MFI Eligibility | Household income ≤3 lakh; borrower applies for a loan | Understanding of microfinance regulations, borrower eligibility |
| Insurance / Pension Schemes | An applicant wants PMSBY, PMJJBY, or APY; calculate premium, coverage, or eligibility | Premium calculation, age limits, contribution, coverage |
| MSME / Venture Capital Funding | Company seeks MSME registration or venture capital funding | Knowledge of investment / capital limits, government schemes |
| Numerical Case Studies | Compute GVA, fiscal deficit, or velocity of money for a hypothetical scenario | Formula application, light numerical calculation |
| Banking Regulation / RBI Guidelines | Bank compliance scenario – CRR, SLR, repo rate, or LAF application | Regulatory knowledge, section application |
Also watch the JAIIB IE and IFS Previous Year Paper Discussion:
| Video Link | Video Link |
| JAIIB PYP Part 1 | JAIIB PYP Part 2 |
JAIIB PPB important topics based on PYP analysis
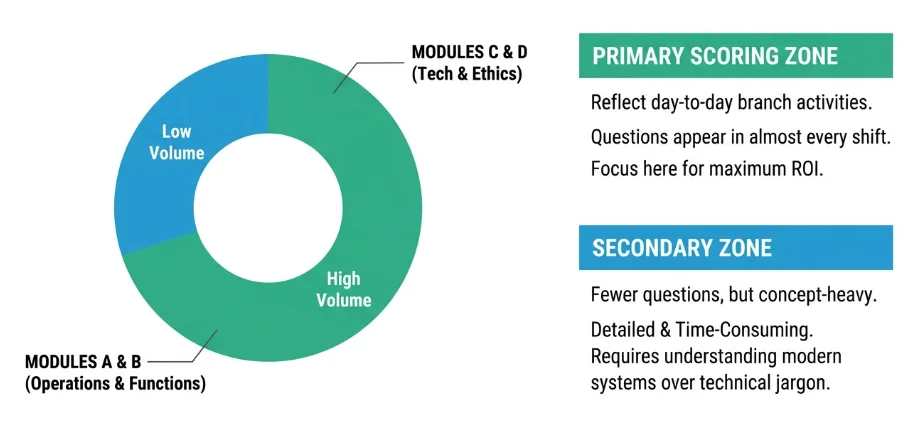
The JAIIB PPB paper has clearly moved towards longer, concept-based, and case-study questions. Instead of testing only direct theory, the exam now checks whether a banker can understand real-life situations such as account operations, lending rules, and legal duties. Based on previous year paper trends, Modules A and B still carry the highest weightage, while Modules C and D have fewer questions but they are usually more detailed and take more time. Smart preparation means focusing on important repeated topics instead of trying to memorise the whole syllabus.
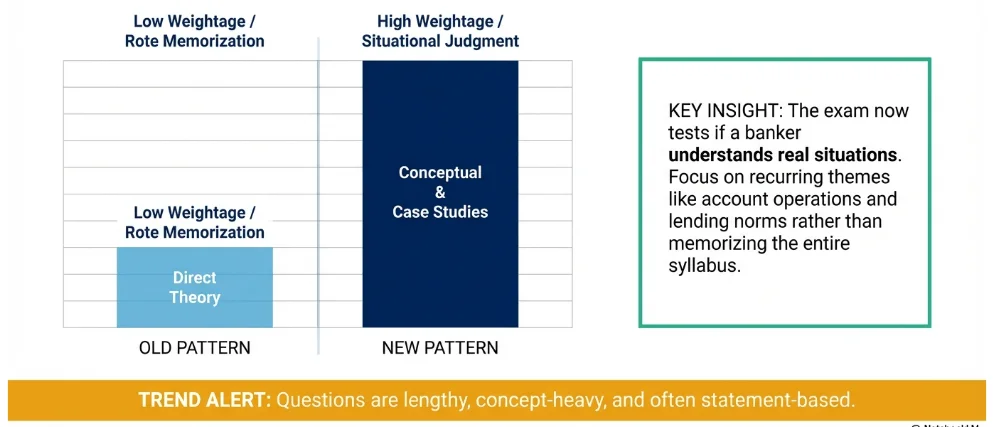
What banking operations and customer relationship topics are asked repeatedly in PPB paper?
Previous year papers show that operational banking topics appear in almost every shift because they reflect day-to-day branch activities. Questions are usually statement-based and require understanding the legal relationship between banker and customer. Candidates should focus on concepts that involve authority, liability, and account handling procedures.
| Topic Area | Detailed Focus Areas | Why It Is Important in the Exam |
| Minor Accounts | Understand the definition of a minor under the Indian Majority Act, restrictions on minors entering contracts, rules related to opening savings accounts for minors, and liability issues when a minor is involved in partnership accounts. | Many case-based questions test whether a banker knows the legal limitations of minors and how banks should protect themselves from contractual risk. |
| Joint Accounts | Learn the operational instructions such as Either or Survivor, Former or Survivor, Jointly, and Anyone or Survivor. Also focus on account closure rights, cheque signing authority, and procedures after the death of an account holder. | Questions often describe practical scenarios where candidates must identify who has the authority to operate or close the account. |
| HUF Accounts | Study the legal status of a Hindu Undivided Family, the powers and responsibilities of the Karta, and how liability works for family members. | HUF questions test conceptual clarity because many bankers confuse ownership and management rights within the family structure. |
| Mandate vs Power of Attorney | Understand the difference between limited authority given through a mandate and broader legal authority granted through a Power of Attorney, including duration, revocation, and legal implications. | Statement-based MCQs frequently compare features of both documents to check legal understanding. |
| Garnishee and Attachment Orders | Learn the process banks follow when they receive court orders, including freezing accounts, handling lien amounts, and priority of claims. | These topics appear in legal case studies where candidates must decide how a bank should respond to legal instructions. |
Also Check: JAIIB Exam Pattern
Which credit and loan product concepts appear most in PPB PYPs?
Credit and lending topics remain a major scoring area in PPB because they represent core banking functions. Questions are mostly conceptual but may include small calculations or regulatory limits. Understanding the logic behind RBI guidelines is more useful than memorising numbers alone.
| Topic Area | Detailed Focus Areas | Why It Is Important in the Exam |
| Priority Sector Lending (PSL) | Study sector-wise targets, sub-targets, housing loan eligibility limits based on population categories, and the treatment of shortfalls through RIDF deposits with NABARD. | PSL questions are frequently repeated and often appear as multi-statement questions requiring deep conceptual clarity. |
| MSME Classification | Understand how MSMEs are classified based on investment in plant and machinery and annual turnover limits, and know the differences between Micro, Small, and Medium enterprises. | Direct definition-based questions and application-based scenarios are commonly asked. |
| NPA Norms | Learn the classification of assets into standard, sub-standard, doubtful, and loss assets, along with provisioning requirements and special treatment for agricultural advances. | Questions often test whether candidates can apply NPA rules to practical lending situations. |
| Agricultural Loan Rules | Focus on the “two harvest seasons but not exceeding two years” rule for identifying NPAs in crop loans and how seasonal factors affect classification. | Appears in conceptual MCQs and sometimes within longer credit case studies. |
| Working Capital Assessment | Understand the Tandon Committee’s second method, the Nayak Committee’s turnover method, and basic working capital calculations. | Numericals based on these methods are frequently reported in tougher shifts. |
Which banking technology topics should be focused on in PPB Module C?
Module C may have fewer questions compared to other modules, but they are often concept-heavy and require understanding of modern banking systems. Candidates should focus on how technology is applied in real banking processes rather than technical jargon.
| Topic Area | Detailed Focus Areas | Why It Is Important in the Exam |
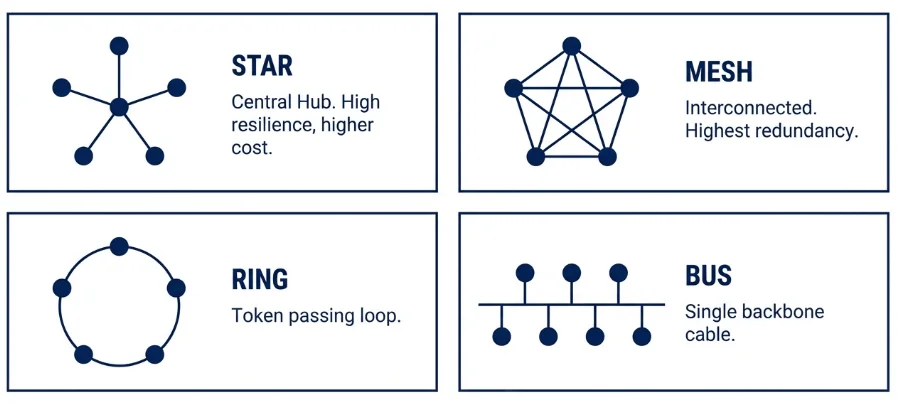
| Network Topologies | Learn the structure and characteristics of Star, Mesh, Ring, and Bus topologies, including advantages, disadvantages, and real-life usage in banking networks. | These questions are repeated frequently and are usually conceptual rather than technical. |
| Payment Systems | Understand the features, settlement timings, transaction limits, and use cases of NEFT, RTGS, UPI, IMPS, and the role of the National Financial Switch (NFS). | Comparison-based questions test practical understanding of digital payment channels. |
| Cheque Truncation System (CTS 2010) | Study image-based clearing, security features, and how CTS improves cheque processing efficiency. | Practical technology questions related to cheque clearing are common. |
| Digital Innovations | Learn the basics of Blockchain, Central Bank Digital Currency (CBDC), and their purpose in modern banking systems. | Recent exam trends show increasing focus on new technology concepts. |
| Cloud Computing and Security | Understand data storage, risk management, and the importance of cyber security controls in banking operations. | Statement-based questions test awareness of digital risks and safety practices. |
Which regulatory and legal framework topics are frequently tested?
Legal awareness is essential in PPB because bankers are expected to understand customer rights and bank liabilities. Many questions describe real legal situations and ask candidates to identify the correct rule or section.
| Law / Regulation | Detailed Focus Areas | Why It Is Important in the Exam |
| Negotiable Instruments Act | Focus on Section 138 related to dishonour of cheques, Section 85 related to protection provided to the paying banker, and the concept of Holder in Due Course. | These sections appear regularly because they directly relate to cheque operations. |
| Holder in Due Course | Understand the rights, protections, and conditions required for someone to become a holder in due course. | Questions test whether candidates understand legal ownership and transferability of instruments. |
| Banking Ombudsman Scheme | Study the complaint process, award limits, and authority of the Ombudsman in resolving customer disputes. | Appears in customer protection and ethics-related questions. |
| Consumer Protection Act | Learn the role of the Central Consumer Protection Authority and how customer grievances are handled. | Conceptual questions test awareness of customer rights and regulatory responsibilities. |
What numericals and case studies dominate recent PPB exams?
Recent PPB paper analysis clearly shows an increase in lengthy case studies, especially in tougher shifts. These questions are usually worth two marks and require careful reading, logical thinking, and application of rules.
| Case Study / Numerical Area | Detailed Focus Areas | Why It Is Important in the Exam |
| Operating Cycle Calculations | Understand how to calculate inventory period, receivable period, payable period, and total operating cycle duration. | Appears in numerical questions that test financial understanding. |
| Current Ratio and Financial Ratios | Learn formulas for Current Assets, Current Liabilities, and ratio interpretation used in credit analysis. | Basic calculations are frequently included in tougher exam shifts. |
| NPA Provisioning | Study how provisioning percentage changes based on asset category and the value of available security. | Practical lending scenarios require applying RBI norms. |
| Locker Liability Cases | Understand the bank’s responsibility in case of negligence and the compensation rule of up to 100 times the annual locker rent. | High-weightage case studies are commonly asked. |
| Banker–Customer Relationships | Learn legal relationships such as Bailor–Bailee, Lessor–Lessee, and Agent–Principal in different services. | Candidates must identify the correct relationship from real-life examples. |
| Indemnity and Bank Guarantees | Study procedures for issuing duplicate Demand Drafts, executing indemnity bonds, and types of bank guarantees. | Application-based questions test operational and legal awareness. |
What are the JAIIB AFM important topics based on PYP analysis?
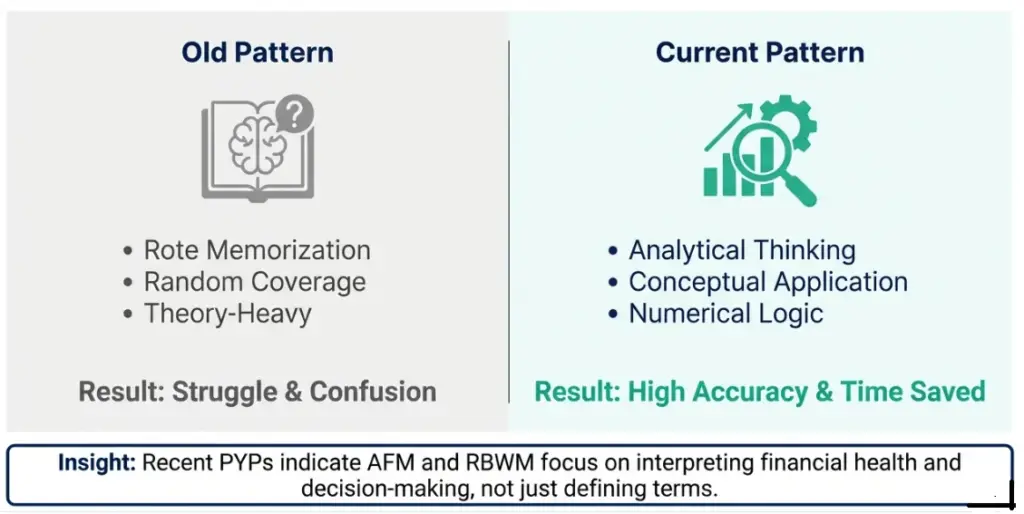
Based on the JAIIB AFM previous year paper analysis, a clear pattern emerges candidates who rely only on memorisation struggle, while those who understand concepts and practise numericals manage the paper more confidently.
Recent memory-based questions indicate that the AFM exam is becoming more analytical, with strong focus on Accounting Standards, financial decision-making, banking accounts, and ratio interpretation. Instead of covering everything randomly, focusing on repeatedly asked themes helps improve accuracy and saves valuable exam time.

Why are Accounting Standards and journal entries repeatedly asked in AFM paper?
Accounting Standards and journal entries are asked frequently because they test practical accounting understanding. The examiner checks whether you know how financial transactions are actually recorded and reported, not just the theory behind them.
| Topic | What the exam focuses on | How you should prepare |
| Accounting Standards such as AS 2, AS 3, AS 9, AS 10, AS 19, AS 26 | Questions usually check valuation rules, revenue recognition timing, treatment of leases, and classification of tangible or intangible assets through conceptual or statement-based formats. | Prepare short notes explaining the purpose of each standard, understand recognition rules, and practice identifying correct accounting treatment in real situations. |
| Journal Entries | Many questions involve passing entries for prepaid expenses, share forfeiture, purchase of assets on credit, and security premium adjustments. | Focus on debit and credit logic using Real and Personal account rules and practise full entry formats instead of memorising isolated examples. |
| Classification of Accounts | Candidates must identify whether an account is personal or real before attempting entries. | Revise basic account categories with examples from companies, banks, and asset transactions to avoid confusion during numericals. |
Also Check: JAIIB Paper Wise Exam Date 2026
How important are Bond valuation and Time Value of Money numericals in AFM?
Numerical questions may form a smaller portion of the paper, but they are scoring areas if formulas and concepts are clear. Most calculations are direct applications of financial management principles.
| Numerical Area | What examiners test | How you should prepare |
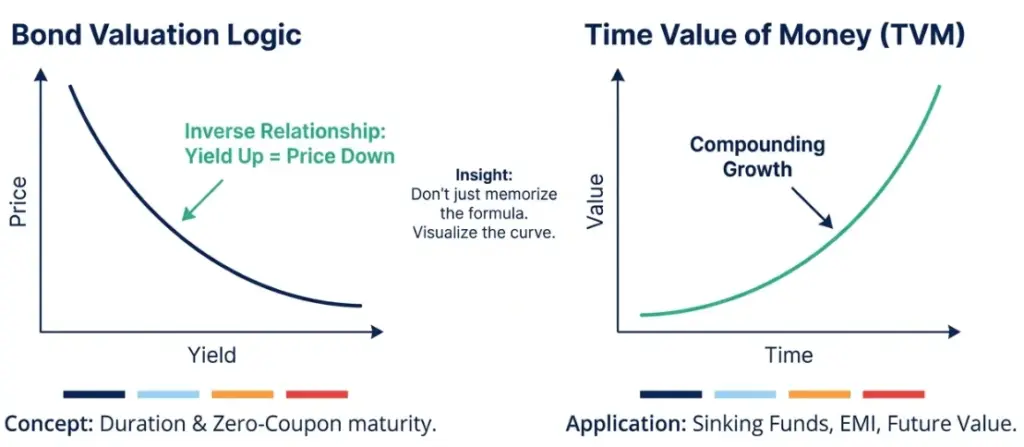
| Bond Valuation and YTM | Questions test the inverse relationship between bond price and yield, along with concepts like duration and zero-coupon bond maturity. | Understand the reasoning behind price movements and practise simple yield and duration questions rather than complex calculations only. |
| Annuity and Time Value of Money | Candidates are asked to calculate future value or present value in scenarios like sinking funds or EMI calculations. | Maintain a clear formula sheet and solve multiple practice questions to improve speed and accuracy. |
| Depreciation Methods | Focus is on WDV method and Sum of Years Digit method and their impact on asset value. | Learn step-by-step calculation logic so you can handle both conceptual and numerical variations in the exam. |
What role do Banking Company Accounts and Company Law concepts play in AFM?
Banking and company law topics connect accounting knowledge with regulatory frameworks, which is why they appear regularly in AFM exams. These areas usually involve conceptual clarity and structured formats.
| Area Covered | What examiners expect | How you should prepare |
| Banking Company Accounts | Understanding of balance sheet format, Profit and Loss structure, and schedules such as Schedule 10 and Schedule 18. | Study the structure of banking financial statements and revise how items are grouped under different schedules. |
| Company Law Rules | Questions test knowledge of membership requirements, share capital rules, and provisions like Section 52 related to security premium. | Link company law sections with accounting treatment so that concepts become easier to remember during revision. |
| Share Capital Concepts | Over-subscription, premium utilisation, and allotment adjustments are common themes. | Practise journal entries related to share capital from past questions to build confidence. |
Also Check: JAIIB AFM Exam Analysis
Which Ratio Analysis and Working Capital topics appear most in AFM PYPs?
Ratio analysis and working capital questions test your ability to interpret financial health, not just calculate numbers. These areas are usually straightforward if fundamentals are clear.
| Topic | What the exam focuses on | How you should prepare |
| Current Ratio and Quick Ratio | Candidates must calculate liquidity ratios and interpret whether the company’s financial position is stable. | Remember that liquid assets exclude stock and prepaid expenses and practise solving ratios from simple balance sheet data. |
| Debt Equity Ratio | Questions analyse leverage and financial risk through conceptual understanding of borrowed funds and owner’s equity. | Understand the meaning behind the ratio rather than only memorising formulas. |
| Working Capital Assessment | Tandon Committee and Nayak Committee methods are used to test understanding of permissible bank finance. | Study practical banking examples so that you can apply formulas easily in case-study questions. |
What special “trap” concepts and niche areas should you revise before the JAIIB AFM exam?
AFM papers often include small conceptual questions that look easy but are designed to test attention to detail. Revising these niche areas can help avoid unnecessary mistakes.
| Niche Concept | What you should remember | How you should prepare |
| GST Penalties and Regulatory Numbers | Questions may check specific penalty rates such as interest charged annually, which candidates often confuse. | Maintain a quick revision list of important regulatory figures and limits. |
| Dormant Company Definition | The exam may test whether you understand that a dormant company is one that is not actively carrying business operations. | Revise definitions with examples so you can recognise tricky wording in options. |
| Zero-Coupon Bonds | A key concept is that the duration of a zero-coupon bond equals its maturity period. | Add such small conceptual facts to your final revision notes for quick recall. |
JAIIB RBWM important topics based on PYPs analysis
The JAIIB RBWM paper has evolved into a concept-driven and application-focused exam where understanding banking products, customer handling, government schemes, and wealth concepts matters more than memorising facts. Previous year paper (PYP) analysis shows that Modules B and D carry strong weightage, while numericals, case studies, and statement-based questions test clarity of concepts. Topics like PMAY, retail loans, marketing frameworks, and regulatory limits appear repeatedly, making them essential for focused preparation.
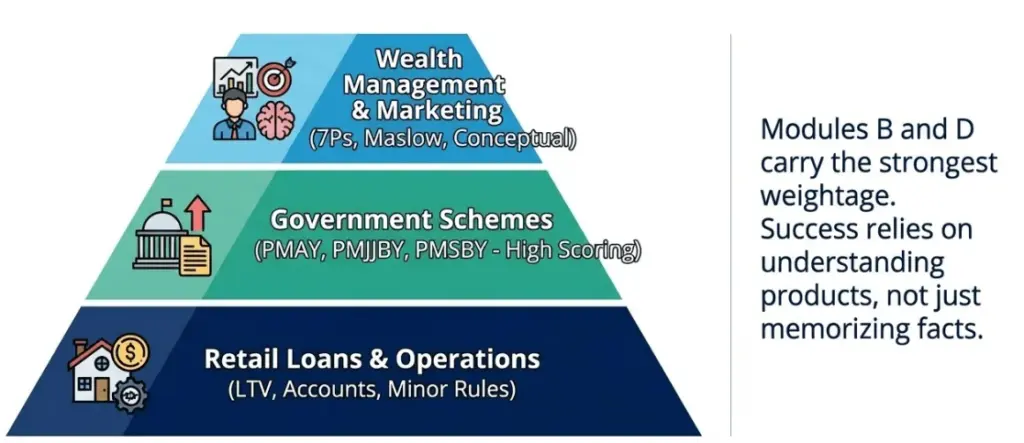
What government schemes and social security topics are frequently asked in JAIIB RBWM?
Government schemes are one of the most scoring areas in RBWM because questions are often direct but detail-oriented. Candidates are expected to remember eligibility criteria, subsidy rates, age limits, and premium details. Questions from PMAY, PMJJBY, and PMSBY are commonly asked in both theory and case-based formats.
| Topic Area | Detailed Explanation |
| PMAY income categories | Questions often test the classification of beneficiaries under Economically Weaker Section (EWS), Low Income Group (LIG), and Middle Income Groups. Candidates should understand that EWS covers annual income up to ₹3 lakh, while LIG includes income between ₹3 lakh and ₹6 lakh. |
| Interest subsidy structure | The exam frequently asks about subsidy percentages offered under PMAY. For example, EWS and LIG categories receive a higher subsidy compared to MIG-I and MIG-II. Understanding why these slabs exist helps answer conceptual questions. |
| PMJJBY scheme details | This life insurance scheme is asked through age eligibility, premium amount, and waiting period. Candidates should remember that it targets financially vulnerable customers and has a fixed annual premium structure. |
| PMSBY coverage | Questions focus on accidental insurance coverage, age eligibility, and the fact that there is no waiting period. The scheme’s low premium is often highlighted in comparison-based questions. |
Also Check: List of Central and State Gov. Schemes
Which retail loan products and banking operations topics have high weightage?
Retail loans and customer account operations form the backbone of RBWM. Questions usually check practical knowledge such as LTV ratios, minor account rules, education loan security requirements, and BSBD account limits. These areas are scoring because many questions are rule-based.
| Topic Area | Detailed Explanation |
| Home loan LTV ratios | Candidates must understand how loan eligibility changes with property value. For smaller loans, banks may finance a higher percentage of the property cost, while higher value loans require more borrower contribution to reduce risk. |
| Education loan security norms | The exam often asks about security requirements depending on loan size. Smaller loans generally do not require collateral, while higher loan amounts involve third-party guarantees or tangible security to protect the bank’s interest. |
| Minor account operations | Questions focus on age eligibility for independent operation and signing authority. Candidates should know that banks allow minors above a certain age to operate accounts with specific limits to ensure safety. |
| BSBD and small accounts | Limits related to maximum balance, annual credits, and withdrawals are commonly asked. These accounts are designed for financial inclusion and therefore have controlled transaction limits. |
Also Check: JAIIB registration Process here
What marketing and wealth management concepts are repeatedly tested in RBWM paper?
Marketing and wealth management topics are highly conceptual but scoring when understood clearly. The exam frequently includes questions on marketing mix models, customer segmentation, and investment services like PMS. These topics also appear in case studies that test real-world banking scenarios.
| Topic Area | Detailed Explanation |
| Marketing mix framework | Candidates should clearly understand the difference between the traditional 4Ps (Product, Price, Place, Promotion) and the extended 7Ps used in service industries, which include People, Process, and Physical Evidence. |
| Product Life Cycle stages | Questions often ask candidates to identify the stage of a product such as Introduction, Growth, Maturity, or Decline. Understanding customer demand and competition at each stage helps answer scenario-based questions. |
| Portfolio Management Services (PMS) | The exam checks knowledge of minimum investment limits and regulatory requirements for providers. PMS is positioned as a specialised wealth solution aimed at high-net-worth customers. |
| Customer need analysis | Concepts such as Maslow’s Hierarchy are used to connect financial products with customer motivations. Candidates should learn how banking products align with different need levels. |
Which numericals, case studies, and regulatory details should you prioritise for RBWM preparation?
As per the JAIIB RBWM paper analysis the numerical questions and regulatory concepts together contribute a significant portion of marks. The exam expects candidates to apply formulas, interpret financial ratios, and understand legal frameworks like SARFAESI and DRT procedures. These areas require practice along with conceptual clarity.
| Topic Area | Detailed Explanation |
| Time value of money calculations | Questions may involve Present Value, Future Value, and rules such as Rule of 72 or Rule of 144. Understanding the logic behind compounding helps solve questions faster. |
| Financial ratios in retail banking | Ratios like Fixed Income Obligation Ratio (FIOR), Net Profit Margin, and Return on Assets are used to evaluate customer eligibility and business performance. Candidates should focus on interpretation rather than memorisation. |
| Capital gains and indexation | Long-term and short-term capital gain calculations are asked through case scenarios. Knowledge of Cost Inflation Index and holding period rules is important. |
| SARFAESI and CERSAI timelines | Regulatory questions often check awareness of registration deadlines, penalty implications, and borrower rights under recovery laws. |
| DRT and customer liability rules | Candidates should know threshold limits for approaching the Debt Recovery Tribunal and understand liability caps in unauthorised electronic transactions. |
JAIIB Memory Based Paper MCQs
JAIIB Memory Based Paper MCQs are based on past exam trends to help candidates practice effectively. These questions cover key topics from all modules, providing a realistic exam experience.
Module: IE & IFS (Indian Economy & Indian Financial System)
Check out a few questions from JAIIB IE&IFS Paper and do not forget to check out JAIIB IE&IFS Preparation Strategy.
1. What is the primary objective of monetary policy in India?
a) Control inflation
b) Regulate foreign exchange
c) Promote employment
d) Reduce fiscal deficit
Answer: a) Control inflation
2. What is the current base year for GDP calculation in India?
a) 2004-05
b) 2011-12
c) 2014-15
d) 2020-21
Answer: b) 2011-12
3. Which of the following is NOT a function of the Reserve Bank of India?
a) Issuing currency
b) Supervising non-banking financial companies
c) Setting fiscal policy
d) Managing foreign exchange
Answer: c) Setting fiscal policy
4. What does CRR stand for in banking?
a) Cash Reserve Ratio
b) Credit Risk Ratio
c) Current Reserve Requirement
d) Cash Revenue Rate
Answer: a) Cash Reserve Ratio
5. Which financial market instrument is used for short-term borrowing by governments?
a) Treasury Bills
b) Corporate Bonds
c) Mutual Funds
d) Equity Shares
Answer: a) Treasury Bills
Module: PPB (Principles and Practices of Banking)
Check out a few questions from JAIIB PPB Paper and do not forget to check out JAIIB PPB Preparation Strategy.
1. Identify the incorrect statements:
- Private Ltd restricts the right to transfer its shares but permit invitation to public
to subscribe for any of its securities. - A subsidiary company of another company that is not a private company is
deemed to be public company, even if registered as a private company. - A company in which fifty per cent or more of the shares are held by any one or
more of the Central/ State Governments, including a subsidiary of such a
company is called a Government Company.- A. I only
- B. II and III only
- C. III only
- D. II and I only
Ans: B
2. Mr. Rajat, a farmer residing in a rural area, has his savings account in a bank branch that is being taken over by another bank. He wants to understand how the transfer will affect his account. What happens to the terms of the contract governing deposit accounts when a bank branch is taken over by another bank in rural and semiurban centers?
a) The terms of the contract are renegotiated with the new bank branch
b) The terms of the contract are decided by the regulatory authority
c) The terms of the contract are invalidated
d) The terms of the contract remain the same as agreed with the original bank
Branch
Ans: D
3. What is the procedure for handling shortages and excesses in cash balances at
a bank branch?
a) Shortages are recovered from the Suspense Account, and excesses are credited to
the Sundry Deposit Account.
b) Shortages are immediately recovered from the responsible staff, and excesses are
debited to the Suspense Account.
c) Shortages are recovered on the same day from the responsible staff, and excesses
are credited to the Cash Officer/Head Cashier/Cashier.
d) Shortages are debited to the Suspense Account, and excesses are credited to the
responsible staff.
Ans: A
4. Which of the following instruments is a negotiable instrument under the NI Act, 1881?
a) Fixed Deposit Receipt
b) Cheque
c) Bank Guarantee
d) Savings Certificate
Answer: b) Cheque
5. What does CASA stand for in banking?
a) Current Account Savings Account
b) Credit and Savings Account
c) Cash and Savings Access
d) Consolidated Account Savings Analysis
Answer: a) Current Account Savings Account
Module: AFM (Accounting & Financial Management for Bankers)
Check out a few questions from JAIIB AFM Paper and do not forget to check out JAIIB AFM Preparation Strategy.
1. Which financial statement shows the assets and liabilities of a company?
a) Profit and Loss Statement
b) Balance Sheet
c) Cash Flow Statement
d) Trial Balance
Answer: b) Balance Sheet
2. What is the accounting term for allocating the cost of tangible assets over their useful life?
a) Depreciation
b) Amortization
c) Capitalization
d) Valuation
Answer: a) Depreciation
3. In double-entry bookkeeping, which of the following is a debit entry?
a) Increase in revenue
b) Decrease in expense
c) Increase in assets
d) Decrease in liabilities
Answer: c) Increase in assets
4. What does the term “contingent liability” refer to?
a) A liability that is guaranteed
b) A liability that depends on a future event
c) A liability recorded in the Profit and Loss statement
d) A liability that is settled immediately
Answer: b) A liability that depends on a future event
5. The formula for calculating Return on Equity (ROE) is:
a) Net Income / Total Assets
b) Net Income / Shareholder’s Equity
c) Gross Profit / Total Sales
d) Total Liabilities / Shareholder’s Equity
Answer: b) Net Income / Shareholder’s Equity
Module: RBWM (Retail Banking & Wealth Management)
Check out a few questions from JAIIB RBWM Paper and do not forget to check out JAIIB RBWM Preparation Strategy.
1. What is the main feature of a term deposit?
a) Unlimited withdrawals
b) Higher interest rate than savings accounts
c) Instant liquidity
d) No minimum deposit requirement
Answer: b) Higher interest rate than savings accounts
2. What is the primary purpose of mutual funds?
a) To provide loans
b) To pool resources for diversified investments
c) To facilitate online banking
d) To provide insurance coverage
Answer: b) To pool resources for diversified investments
3. As per Income Tax Act, repayment of FD proceeds:
- Applies to the bank as a whole, not branch-wise.
- Must be by A/c Payee cheque/draft/credit if maturity proceeds ≥ ₹20,000.
- Applies to deposits held singly or jointly at a branch.
- Cash repayment is allowed for amounts < ₹20,000.
Which are correct?
- A. 1, 2, 3
- B. 2, 3, 4
- C. 1, 3
- D. 1, 2, 3, 4
Answer: a) 1, 2, 3
4. What is the tenure for the Public Provident Fund (PPF) account?
a) 5 years
b) 10 years
c) 15 years
d) 20 years
Answer: c) 15 years
5. Which of the following statements are true?
- Banks may allow loans up to 80–90% of
FD value. - Interest charged on loan is higher than FD
interest rate. - Advances against third-party deposits are
encouraged by banks. - Advances against minors’ deposits jointly
with guardians may be permitted.
Which are correct?
- A. 1, 2, 4
- B. 2, 3, 4
- C. 1, 3
- D. 1, 2, 3, 4
Answer: a) 1, 2, 4
Why should professionals practise and revise JAIIB previous year papers?
Practising previous year papers (PYPs) is crucial for working professionals because of limited preparation time and the evolving exam pattern and syllabus. Key benefits include:
- Spot high-weightage questions: Identify topics that appear every year, like NPA rules, PSL limits, EPF/APY contributions, PMAY eligibility, and RBI regulations.
- Master multi-statement questions: Previous papers show how PPB and RBWM exams ask multiple statements per question, requiring precise understanding.
- Familiarity with case studies: Learn how real banking situations like minor accounts, loan defaults, or insurance claim calculations are framed in exams.
- Practice formula-based numericals: Repeated calculations on fiscal deficit, GVA, bond valuation, and working capital appear across IE, AFM, and PPB.
- Recognise tricky “trap” questions: Past papers reveal subtle wording in areas like zero-coupon bonds, dormant companies, or GST penalties, helping avoid mistakes.
FAQs
It is a set of questions from the actual JAIIB exam, recalled by candidates.
They help understand exam patterns and commonly asked questions.
There are four papers: IE & IFS, PPB, AFM, and RBWM.
We have interlinked the subject wise memory based papers in the blog above.
- JAIIB Practice Book, Download the JAIIB Genius Free eBoook
- PPB Memory Based Questions for JAIIB 2026, Download PDF
- 100 Expected PPB Questions for JAIIB Exam 2026, Download PDF
- JAIIB 2026 PPB 50 Most Repetitive MCQs, Download PDF
- Balance Sheet Equation Notes, Important for JAIIB AFM 2026
- JAIIB Study Material 2026, Download Subject Wise Notes

Hi, I’m Aditi. I work as a Content Writer at Oliveboard, where I have been simplifying exam-related content for the past 4 years. I create clear and easy-to-understand guides for JAIIB, CAIIB, and UGC exams. My work includes breaking down notifications, admit cards, and exam updates, as well as preparing study plans and subject-wise strategies.
My goal is to support working professionals in managing their exam preparation alongside a full-time job and to help them achieve career growth.
