Understanding the organization of a computer is a an important topic for the Computer Awareness section in SSC CGL Tier 2 Paper 1. It helps you answer questions related to computer components, working, and memory organization. This blog contains the details about the computer components, CPU, memory types, input/output devices, ports, backup devices, and tips for SSC CGL Tier 2, with easy tables and pointers for quick revision.
What is Computer Organization?
Computer organization refers to the structure and interconnection of the main components of a computer. It explains how different parts of the system work together to perform tasks efficiently. In SSC CGL Exam for Tier 2 stage, questions may test your understanding of CPU, memory, input/output devices, and data flow under the head of Computer Organization.
What are the Main Components of a Computer?
A computer has three main components: Input Devices, Central Processing Unit (CPU), and Output Devices.
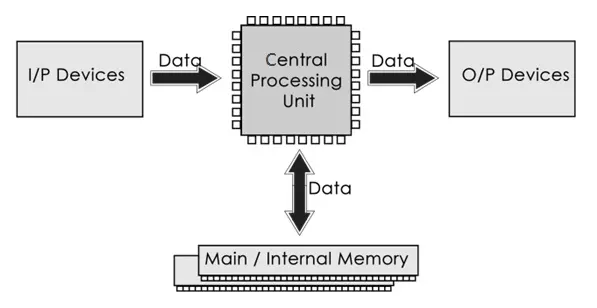
| Component | Function | Examples |
| Input Devices | Allow users to enter data into the computer | Keyboard, Mouse, Scanner |
| Central Processing Unit (CPU) | Processes instructions and performs calculations | ALU, Control Unit, Registers |
| Output Devices | Display or produce results from the computer | – |
What is a Central Processing Unit (CPU)?
The Central Processing Unit (CPU) is the brain of the computer, responsible for processing instructions and performing calculations.
- Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU): Performs all calculations and logical operations.
- Control Unit (CU): Directs the flow of data and instructions within the computer.
- Registers: Small, fast storage locations used to temporarily hold data and instructions.
SSC CGL Tier 2 Tip: Focus on CPU components and their functions; questions often ask about ALU, CU, and registers.
Check out SSC CGL Tier 2 Paper 1 Tips to have a strategic approach before the exam.
What are Input and Output Devices?
Input and Output Devices are components that allow a computer to receive data from the user and provide results back.
| Type | Function | Examples |
| Input Devices | Used to enter data into the computer | Keyboard, Mouse, Scanner, Microphone |
| Output Devices | Used to display or produce results from the computer | Monitor, Printer, Speakers |
Want to solve computer awareness questions to get a good hold on the subject? Solve 100 Computer Awareness Questions for SSC Exams by downloading this E-book for free.
Memory Organization
Memory is where a computer stores data and instructions for processing. It is divided into different types:
- Primary Memory (RAM, ROM): Fast memory used while the computer is running programs.
- Secondary Memory (HDD, SSD): Permanent storage for files and data.
- Cache Memory: Very fast, small memory that keeps frequently used data for quick access.
Also check out: SSC CGL Typing Test Errors to minimize your errors in Data Entry Speed Test.
Differences between RAM, ROM, and cache
The table below highlights the main differences between RAM, ROM, and Cache memory, focusing on their speed, purpose, and usage:
| Memory Type | Full Form | Speed | Purpose | Volatility | Example Use |
| RAM | Random Access Memory | Fast | Temporarily stores data and instructions while programs run | Volatile | Running applications, active processes |
| ROM | Read-Only Memory | Slow | Stores permanent instructions and system firmware | Non-volatile | Booting the computer, BIOS |
| Cache | Cache Memory | Very Fast | Stores frequently accessed data for quick retrieval | Volatile | Speeding up CPU processing |
Check Out SSC CGL Computer Awareness Blog for the overall information about the section.
What are Ports and Connections?
Ports and Connections are interfaces that allow external devices to connect to a computer for data transfer or communication.
- USB: Used to connect devices like pen drives, keyboards, and mice for data transfer.
- HDMI: Connects monitors or TVs to display video and audio from the computer.
- Ethernet: Allows wired internet or network connections for data communication.
- Audio jack: Connects headphones, speakers, or microphones for sound input and output.
What are Backup Devices?
Backup Devices are used to store additional copies of important data to prevent loss.
| Backup Device | Function | Example Use |
| External Hard Drives | Stores large amounts of data externally | Backup of documents, photos, videos |
| Pen Drives | Portable storage for quick data transfer | Carrying small files or documents |
| Cloud Storage | Online storage accessible from anywhere | Backup of files on Google Drive, Dropbox, OneDrive |
Why Computer Organization is Important for SSC CGL Tier 2
Computer organization is an important topic for SSC CGL Tier 2 as it forms the foundation of computer awareness, helps you answer questions accurately, improves understanding of hardware-software interaction, and strengthens problem-solving skills for technical questions.
Key Takeaways:
Below is the list of key takeaways about Computer Organization for SSC CGL Tier 2:
- Understanding computer organization helps answer SSC CGL Tier 2 computer awareness questions accurately
- Key components to focus on include CPU, ALU, CU, registers, input/output devices, and memory types
- Memory organization knowledge, including differences between RAM, ROM, and cache, is important for speed and purpose questions
- Awareness of ports, connections, and backup devices aids in questions on data transfer and storage
- Helps improve understanding of how hardware and software interact in a computer system
- Enhances problem-solving skills for technical and application-based questions in Tier 2
FAQs
Ans. Computer organization refers to the structure and arrangement of a computer’s components and how they work together to perform tasks efficiently.
Ans. It forms the basis of the Computer Awareness section, helping you answer questions on CPU, memory, input/output devices, and system operations correctly.
Ans. The main components are Input Devices, Central Processing Unit (CPU), and Output Devices.
Ans. The CPU processes instructions, performs calculations, and controls the flow of data within the computer through its ALU, Control Unit, and Registers.
Ans. The main types are Primary Memory (RAM, ROM), Secondary Memory (HDD, SSD), and Cache Memory.
- Average Problems for SSC Exams, Practice Questions with Solutions
- SSC CGL Previous Year General Awareness Questions in Quiz Format
- Top 100 SSC CGL General Awareness Questions, Download PDF
- 1000 SSC CGL General Knowledge Questions, Attempt Now
- IBPS PO vs SSC CGL vs RBI Assistant: Complete Comparison
- SSC CGL vs RBI Assistant: Salary Job Profile Comparison 2026 Guide

I’m Mahima Khurana, a writer with a strong passion for creating meaningful, learner-focused content especially in the field of competitive exam preparation. From authoring books and developing thousands of practice questions to crafting articles and study material, I specialize in transforming complex exam-related topics into clear, engaging, and accessible content. I have first hand experience of 5+ months in SSC Exams. Writing, for me, is not just a skill but a way to support and guide aspirants through their preparation journey one well-written explanation at a time.
