India’s G20 Presidency marked a significant moment in the country’s rise as a global economic power. For aspirants of UPSC, RBI Grade B, SEBI, and other competitive exams, understanding India’s G20 leadership is important because it connects international diplomacy, trade, growth, and digital finance. Knowing the Presidency’s theme, priorities, and economic indicators helps frame strong answers in economics and international relations papers.
Latest Official Data
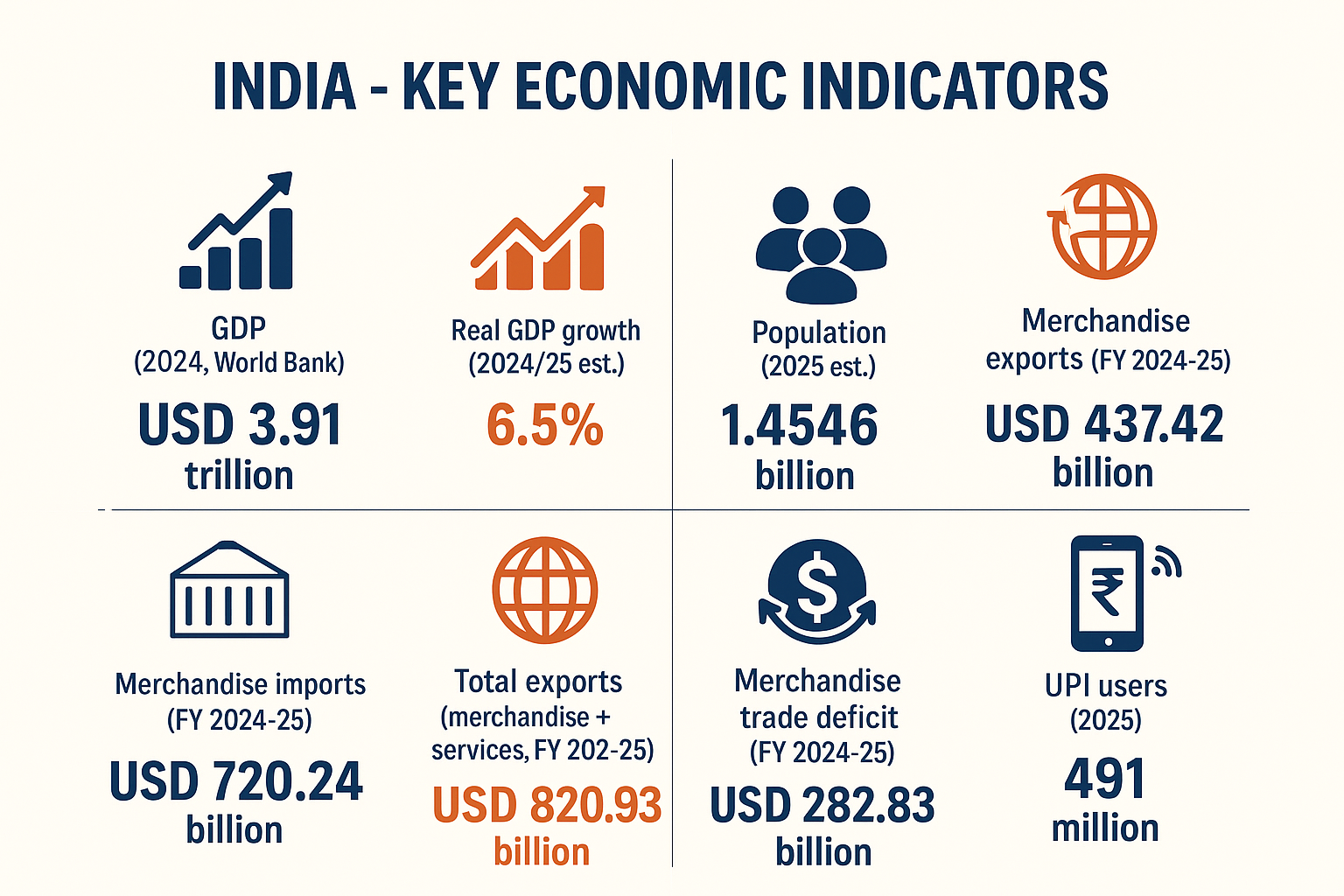
India has emerged as one of the fastest-growing major economies. Below are some key indicators that highlight its economic role:
India – Key Economic Indicators
| Indicator | Value | Units |
| GDP (2024, World Bank) | USD 3.91 trillion | USD |
| Real GDP growth (2024/25 est.) | 6.5% | Percent |
| Population (2025 est.) | 1.4546 billion | People |
| Merchandise exports (FY 2024-25) | USD 437.42 billion | USD |
| Merchandise imports (FY 2024-25) | USD 720.24 billion | USD |
| Total exports (merchandise + services, FY 2024-25) | USD 820.93 billion | USD |
| Merchandise trade deficit (FY 2024-25) | USD 282.83 billion | USD |
| FDI ranking (2024, UNCTAD) | 15th | Rank |
| UPI users (2025) | 491 million | People |
India’s G20 Presidency (2023), Theme, Priorities and Outcomes
India chaired the G20 in 2023 under the theme “One Earth · One Family · One Future.” This theme emphasized inclusivity, sustainability, and global cooperation.
Key priorities and outcomes:
- Climate & Energy: Commitment to triple global renewable energy capacity by 2030.
- Finance & Development: Strengthening multilateral development banks (MDBs) and creating pipelines of investible projects.
- Digital Public Infrastructure (DPI): Showcasing UPI and Aadhaar as models for global digital cooperation.
- Start-up20: Launching a dedicated platform for entrepreneurship and innovation within the G20 framework.
- Global South Focus: Advocating for inclusive growth and amplifying the voices of developing economies.
The Presidency not only gave India global visibility but also positioned it as a bridge between developed and developing nations.
India’s evolving Global Economic role
India’s global economic role is expanding rapidly, backed by strong growth, a large market, and digital innovation. However, challenges like trade imbalances and external vulnerabilities remain. To understand India’s position, it is useful to look at both its strengths and constraints side by side.
| Strengths | Constraints |
| Rapid Growth: With a GDP of ~USD 3.91 trillion and growth of 6.5%, India is one of the fastest-growing major economies. | High Trade Deficit: Merchandise imports (USD 720.24B) far exceed exports (USD 437.42B). |
| Large Market: A population of 1.45 billion provides a strong base for consumption-driven growth. | Export Dependence: Heavy reliance on services; merchandise exports need diversification. |
| Digital Leadership: UPI, Aadhaar, and CoWIN showcase India’s leadership in digital public infrastructure. | Geopolitical Risks: Global tensions and energy dependencies pose challenges. |
| Global Investment Hub: Ranked 15th in FDI inflows, India is becoming a preferred investment destination. | – |
What India achieved at G20 that strengthens its global economic role?
India leveraged the G20 Presidency to showcase its economic, digital, and diplomatic leadership.
- Agenda-setting: Renewable energy, DPI, and investment pipelines became central topics.
- Digital Showcase: UPI was promoted as a global model for fast, secure payments.
- Bridging the Global South: India positioned itself as a voice for developing countries, highlighting climate finance and inclusive growth needs.
These achievements boosted India’s global profile and reinforced its position as a leading player in shaping the future of the world economy.
Short exam ready facts & example questions
For exams, memorizing India’s Presidency theme, economic indicators, and achievements helps answer both MCQs and essay-style questions. Below are key facts followed by possible exam questions.
Key facts to remember
- G20 Theme 2023: “One Earth · One Family · One Future”
- GDP (2024): USD 3.91 trillion
- Trade (FY 2024-25): Exports USD 437.42B, Imports USD 720.24B, Deficit USD 282.83B
- FDI Ranking (2024): 15th globally
- UPI Users (2025): 491 million
Example Questions
Q1. Assess the impact of India’s 2023 G20 Presidency on its global economic diplomacy.
Answer: India’s Presidency emphasized renewable energy, digital public infrastructure, and development finance, positioning it as a bridge between developed and developing nations. UPI was showcased as a global model, while focus on renewable targets enhanced India’s leadership. However, trade imbalances remain an area of concern.
Q2. Assess the role of India’s G20 Presidency in shaping global economic governance. Discuss with reference to renewable energy and digital public infrastructure.
Answer:
- India’s G20 theme: “One Earth · One Family · One Future” highlighted sustainability & inclusivity.
- Key achievement: launch of Global Biofuels Alliance (with Brazil & US) → promotes green energy transition.
- Push for tripling renewable energy capacity by 2030 supported at G20.
- India showcased Digital Public Infrastructure (DPI) — UPI, Aadhaar, CoWIN — as models for financial inclusion.
Outcome: India positioned itself as a voice of the Global South, balancing growth with climate and digital innovation.
Q3. India’s GDP in 2024 is approximately:
a) USD 2.91 trillion
b) USD 3.50 trillion
c) USD 3.91 trillion
d) USD 4.25 trillion
Answer: (c)
Q4. “India’s demographic advantage is both an opportunity and a challenge.” Explain in the context of India’s global economic role.
Answer:
- Opportunity:
- 1.45 billion population → strong consumption-driven growth.
- Young workforce → demographic dividend, potential boost to productivity.
- Challenge:
- Need to generate enough jobs → unemployment remains a concern.
- Skills gap in workforce vs. industry needs.
- Pressure on infrastructure, resources, and social services.
- Conclusion: Harnessing youth potential with education, skilling & jobs will determine India’s long-term global role.
Q5. India’s merchandise trade deficit in FY 2024-25 was:
a) USD 150 billion
b) USD 282.83 billion
c) USD 437.42 billion
d) USD 720.24 billion
Answer: (b)
Q6. “Digital public infrastructure has become India’s soft power tool.” Discuss with examples.
Answer:
- India’s DPI showcased globally → UPI, Aadhaar, CoWIN.
- UPI adoption: 491 million users (2025) → promoted as model for financial inclusion.
- During G20, India shared DPI framework with developing nations.
- Soft Power Impact: Enhances India’s credibility as a tech leader, strengthens partnerships with Global South, reduces dependence on Western payment systems.
- Conclusion: DPI is emerging as a strategic asset in India’s global economic diplomacy.
FAQs
Answer: “One Earth · One Family · One Future,” emphasizing inclusivity, sustainability, and global cooperation.
Answer: India showcased renewable energy targets, digital public infrastructure (UPI, Aadhaar, CoWIN), and positioned itself as a voice for developing countries, strengthening its diplomatic and economic influence.
Answer:
GDP (2024): USD 3.91 trillion
Real GDP growth (2024/25 est.): 6.5%
Merchandise exports (FY 2024-25): USD 437.42B
Merchandise imports (FY 2024-25): USD 720.24B
Trade deficit (FY 2024-25): USD 282.83B
FDI ranking (2024): 15th globally
UPI users (2025): 491 million
Answer:
Climate & Energy: Tripling global renewable energy capacity by 2030
Finance & Development: Strengthening multilateral development banks and investment pipelines
Digital Public Infrastructure: Promoting UPI & Aadhaar as global models
Start-up20: Platform for entrepreneurship & innovation
Global South Focus: Inclusive growth and amplifying developing economies’ voices
Answer: DPI, including UPI and Aadhaar, is shared globally as a model for secure, inclusive financial systems. UPI has 491 million users (2025) and during G20, India showcased DPI frameworks, enhancing its tech leadership and influence with the Global South.
- NABARD Grade A 2026 Interview Preparation Tips, Check Details

- PFRDA Grade A Admit Card 2026, Download Hall Ticket PDF

- PFRDA Grade A Apply Online 2026, Online Application Form Link

- NABARD Grade A Vacancy 2026, Post Wise Vacancy Trend

- NABARD Grade A Selection Process 2026, Phase 1,2 & Interview

- SEBI Grade A Phase 2 Information Handout 2026, Download PDF


Priti Palit, is an accomplished edtech writer with 4+ years of experience in Regulatory Exams and other multiple government exams. With a passion for education and a keen eye for detail, she has contributed significantly to the field of online learning. Priti’s expertise and dedication continue to empower aspiring individuals in their pursuit of success in government examinations.
