Risk and Basic Risk Management Framework JAIIB. Businesses now confront a variety of hazards in their day-to-day operations. A company’s network, for example, may be hacked, exposing employee and customer information. Natural catastrophes like hurricanes, tornadoes, and wildfires may all have an influence on a company’s capacity to function. It takes more than being able to react promptly to a danger to ensure the safety of a firm and its personnel. Effective risk management entails anticipating a threat before it occurs.
How To Download The Risk and Basic Risk Management Framework for JAIIB?
Step 1: Click on the download link. You will be taken to Oliveboard’s FREE E-Books Page.
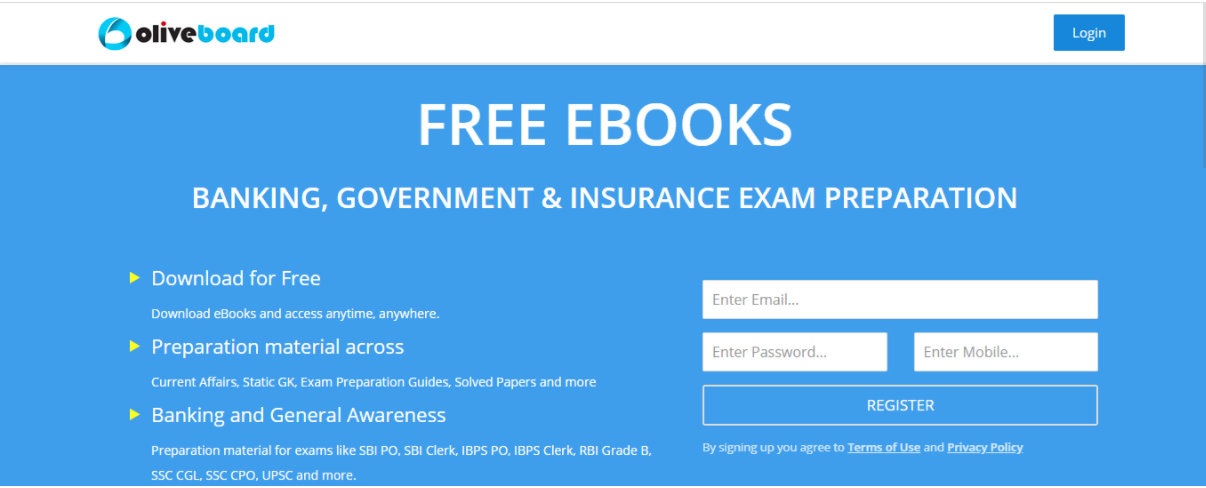
Step 2: Register/Login to the Free E-Books Page of Oliveboard (It is 100% free, You just enter your valid email ID and a password to be able to download the JAIIB Practice questions pdf.
Step 3: After Logging in, you will be able to download the free e-book by clicking on “click here” as shown in the snap below.
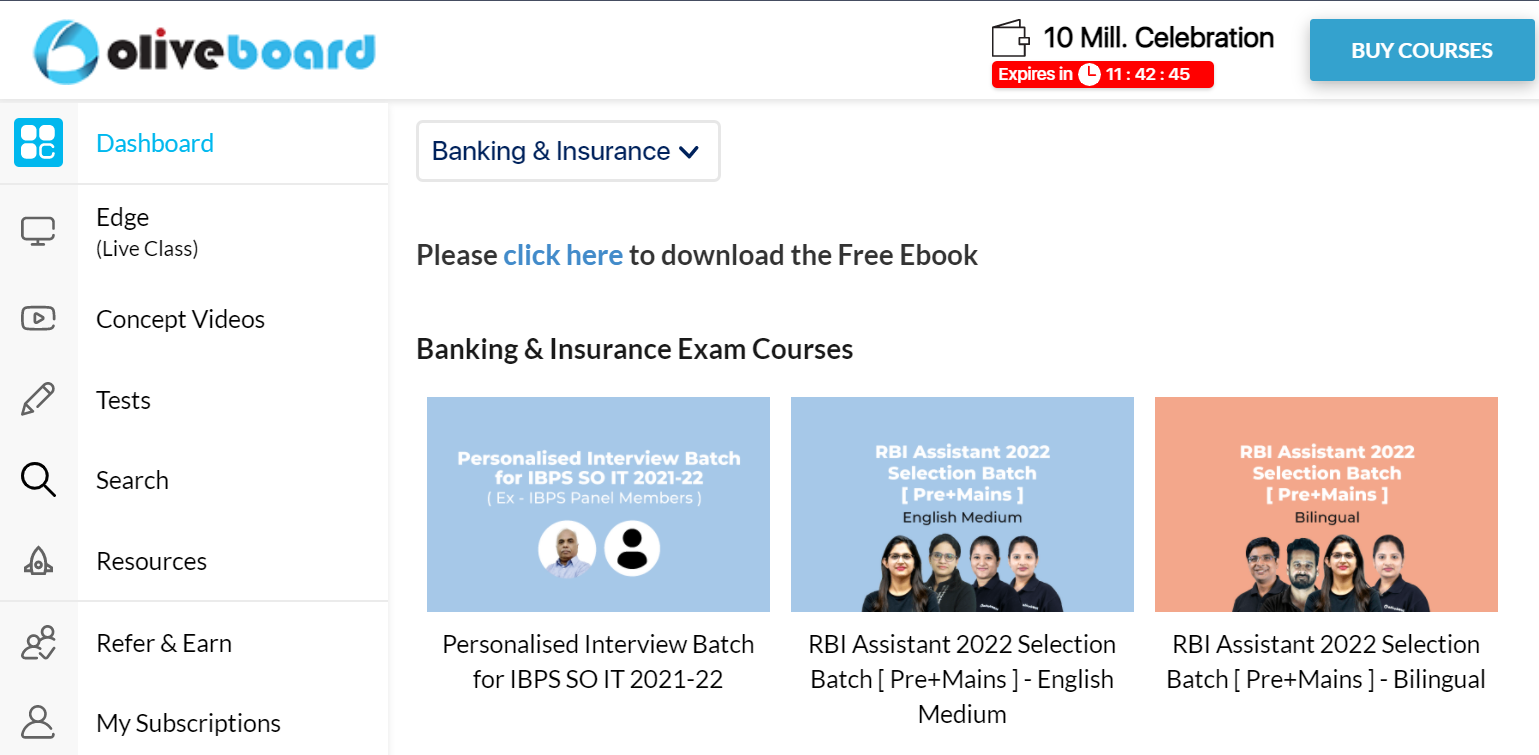
Sneakpeak into the free JAIIB eBook


Types of Risks – Risk and Basic Risk Management Framework JAIIB
The following is a list of the most essential forms of risk to consider while analysing investment possibilities for a financial analyst:
- Systematic Risk – The market’s total influence.
- Unsystematic Risk — Uncertainty about a single asset or firm.
- Political/Regulatory Risk – The consequences of political actions and regulatory changes.
- Financial Risk – A company’s capital structure (degree of financial leverage or debt burden)
- Changes in interest rates have an influence on interest rate risk.
- Uncertainties that are peculiar to a nation are referred to as country risk.
- Changes in social norms, movements, and discontent have an influence on social risk.
- Uncertainty regarding environmental obligations or the impact of environmental changes is one example of environmental risk.
- Uncertainty regarding a company’s operations, such as its supply chain and the delivery of its products or services, is known as operational risk.
- Management Risk – The influence of a management team’s choices on a corporation.
- Legal Risk – Uncertainty about litigation or operating freedom.
- Competition – The level of competition in a certain sector and the influence that rivals’ decisions will have on a business.
What is Risk Identification? – Risk and Basic Risk Management Framework JAIIB
The process of detecting and analysing hazards to an organization’s operations and employees is known as risk identification. For example, identifying IT security risks such as malware and ransomware, accidents, natural catastrophes, and other potentially detrimental occurrences that might interrupt corporate operations are all examples of risk identification. Companies that have strong risk management plans are more likely to be able to mitigate the effect of risks when and if they materialise.
What are risk measures?
Risk measurements are statistical predictors of investment risk and volatility in the past, and they are also important components of current portfolio theory (MPT). MPT is a typical financial and academic tool for evaluating a company’s or a stock fund’s performance in relation to its benchmark index.
Risk measurement can be based on
- Sensitivity
- Volatility
- Downside
Sensitivity – The deviation in the target variable is measured on the basis of variation on one variable component. It has a drawback as it considers variation in only one variable and not all variables at a time.
Volatility – It reflects instability or stability of any random variable. It is possible to combine sensitivity targets with variation in underlying parameters. It captures upside and downside deviations.
Downside potential – It is an adverse deviation target. It captures the possible loss & ignores the possible profit. The Value at Risk (VAR) is the downside risk measure.
Risk Mitigation Strategies
The following are the types of risk mitigation strategies.
Risk Avoidance – When the repercussions of an issue are regarded too severe to warrant the expense of resolving it, risk avoidance is applied. An organisation, for example, might choose not to engage in particular economic operations or practises in order to avoid being exposed to the harm they may offer. Risk avoidance is a common business strategy that can range from limiting investments to not constructing offices in potential war zones.
Risk Acceptance – Accepting a risk for a set amount of time allows you to focus your mitigation efforts on other hazards.
Risk Transfer – Risk transfer divides risk among various parties based on their ability to guard against or minimise the risk. A faulty product constructed utilising some third-party material is one example of this.
Risk monitoring – It is the process of keeping an eye on projects and their related risks for changes in their impact.
What is risk-based pricing?
Risk-based pricing happens when lenders charge varying interest rates or loan conditions to different customers depending on the likelihood that they would default on their loans.
This implies that lenders may charge you a higher interest rate if they consider you a higher-risk borrower, such as if you’ve recently filed bankruptcy, lost a job, or are several mortgage payments late. Lenders will normally provide a cheaper interest rate for the same exact loan if they see you as a lower risk, such as because you have a strong credit score and are employed.
Pricing includes the following:
1. Cost of Deploying funds
2. Operating Expenses
3. Loss Probabilities
4. Capital Charge
Risk Monitoring & Control
The process of maintaining track of recognised riks, monitoring residual risks, detecting new riks, assuring the execution of risk plans, and assessing their efficacy in decreasing risk is known as risk monitoring control. Risk monitoring and control keeps track of the risk indicators that come with putting contingency plans in place. Risk management and control is a continuous procedure that lasts the duration of the project. As the project progresses, new risks emerge, and previously predicted hazards vanish.
Successful risk monitoring and control systems give information that aids in making effective decisions prior to the occurrence of the risk. To assess the acceptability of the project’s risk level on a regular basis, communication with all project stakeholders is required.
Risk monitoring is used to assess whether:
- Risk mitigation has gone off without a hitch.
- Are risk response activities as successful as they should be, or should additional responses be developed?
- The assumptions made during the project are still valid.
- With the analysis of trends, risk exposure has altered from its previous condition.
- There has been a risk trigger.
- Policies and procedures are followed correctly.
- Risks that were not previously identified have happened or emerged.
Risk control may involve choosing alternative strategies, implementing a contigency plan, taking corrective action, or replanning the project. The risk response owner should report periodically to the project manager and the risk team leader on the effectiveness of the plan, any unanticipated effects, and any mid-course correction needed to mitigate the risk.
JAIIB Study Material Compilation
Also Read:
- 5-Important Tips To Crack JAIIB Exams| Check Here (oliveboard.in)
- JAIIB Frequently Asked Questions- 2022| Check Here (oliveboard.in)
- JAIIB Genius | JAIIB Weekly Quiz PDF – JAIIB Questions PDF (oliveboard.in)
- JAIIB Full Form – Junior Associate of the Indian Institute of Bankers (oliveboard.in)
- JAIIB and CAIIB Books- Exams Syllabus, Books, and more (oliveboard.in)
Also Check:
- JAIIB 2022 Exam -Notification Released (oliveboard.in)
- JAIIB Notification 2022 – Notification PDF, Eligibility, (oliveboard.in)
- JAIIB Apply Online – Application Form 2022, Fees, Instru (oliveboard.in)
- JAIIB Eligibility – Age, Degree, Nationality, Members (oliveboard.in)
- JAIIB Syllabus – Complete List of Papers, Modules (oliveboard.in)
- JAIIB Exam Pattern 2022 – Details of Pattern, Marking (oliveboard.in)
- JAIIB Admit Card November 2022 – Steps and Direct Download (oliveboard.in)
- JAIIB 2022 Cut Offs – Check JAIIB Minimum Cut Off (oliveboard.in)

The most comprehensive online preparation portal for MBA, Banking and Government exams. Explore a range of mock tests and study material at www.oliveboard.in
